![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Clinical Turner Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Gonadal dysgenesis
XO syndrome Ullrich Turner |
|
|
Inheritance
|
Not inherited
|
|
|
prenatal
|
Amniocentesis/CVS chromosome analysis reveals XO karyotype
Ultrasound: (second trimester) constellation of findings suggest diagnosis: cystic hy¬groma, hydrops fetalis, chylothorax, ascites |
|
|
Incidence
|
1:2,500 to 5,000 female births; over 95% spontaneously abort in first trimester
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
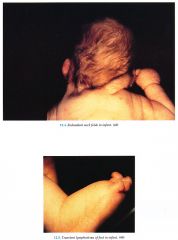
Newborn: small for gestational age (SGA) baby with redundant neck skin, peripheral edema Childhood: short stature, left sided cardiac/aortic anomalies Teenager: short stature, delayed puberty with primary amenorrhea
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Partial or total loss of one X chromosome (XO monosomy) secondary to nonclisjunction during gametogenesis in mother or father or a postfertilization mitotic error; 10% to 20% secondary to mosaicism
|
|
|
Clinical
|
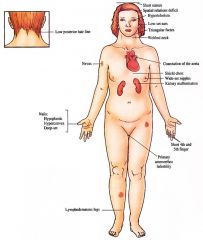
Skin
Redundant neck folds/webbed neck (remnant of fetal cystic hygroma), multiple pig¬mented nevi, increased keloid formation Hair Low set nuchal hairline Nails Hypopl'astic, hyperconvex,.deep set Craniofacial Triangular facies with micrognathia, low set ears, high arched palate, ptosis Musculoskeletal Short stature, shield chest with wide set nipples, cubitus valgus, shortened fourth and fifth metacarpals |
|
|
Clinical
|
Lymphatic Vessels
Congenital hypoplasia of lymphatic channels with resultant transient peripheral lymphedema of hands and feet Endocrine Primary amenorrhea, gonadal clysgenesis/streak gonads, infertility Cardiovascular Multiple anomalies (coarctation of the aorta with secondary hypertension most ommon) Kidney Multiple anomalies (horseshoe kidneys most common) Central Nervous System Spatial relations deficit, hearing impairment |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Noonan
Other short stature syndromes Milroy disease |
|
|
Lab
|
Chromosome analysis
Echocardiogram Abdominal ultrasound |
|
|
Management
|
Thorough physical examination by primary care physician
Referral to endocrinologist cyclic estrogen replacement in second decade, growth hormone therapy Referral to surgeon repair of coarctation, webbed neck, renal anomalies |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Normal life span with treatment of congenital anomalies; may have severe psychosocial. impact given short stature, infertility, body habitus
|

