![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the function and innervation of serratus posterior superior?
|
---Elevates ribs (2-5) as respiratory aid
---Innervated by ventral rami of T1-T4 |
|
|
What is the function and innervation of serratus posterior inferior?
|
---Draws back ribs of 9-12 as respiratory aid
---Innervated by ventral rami of T9-T12 |
|
|
What is the function, innervation and blood supply of splenius capitis?
|
---Bilaterally: extends head and neck
---Unilaterally: rotate and bend laterally head and neck ---Innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves ---Muscular branch of aorta |
|
|
What is the function, innervation and blood supply of splenius cervicis?
|
---Bilaterally: extends head and neck
---Unilaterally: rotate and bend laterally head and neck ---Innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves ---Muscular branch of aorta |
|
|
What is the function, innervation and blood supply of erector spinae muscles?
|
Spinalis:
---extends vertebral column ---innervated by dorsal rami of cervical/thoracic spinal nerves ---muscular branch of aorta Longissimus: ---extends and laterally flexes vertebral column ---dorsal rami of cervical/thoracic/lumbar spinal nerves ---muscular branch of aorta Iliocostalis: ---extends, laterally flexes and assists in rotation of vertebrae ---dorsal rami of cervical/thoracic/lumbar spinal nerves ---muscular branch of aorta |
|
|
What is the function, innervation and blood supply of semispinalis capitus?
|
---Extends head/vertebral column and rotates head of opposite side
---Innervated dorsal rami of cervical/greater occipital ---Muscular branch of aorta |
|
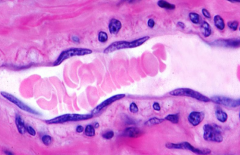
What type of epithelium is shown here?
|
Simple squamous epithelium
|
|
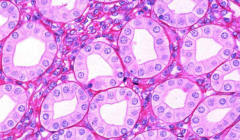
What type of epithelium is shown and where is it found?
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium
---kidney tubules, glands, covering of ovary |
|
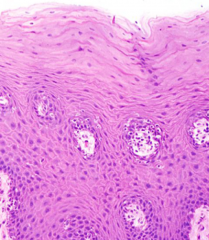
What type of epithelium is this and where is it found?
|
Stratified squamous epithelium
---oral cavity, epidermis, vagina |
|
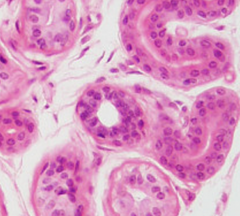
What type of epithelium is this and where is it found?
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
---ducts of sweat glands |
|
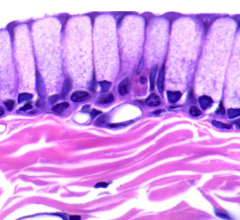
What type of epithelium is this and where is it found?
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
---ducts of glands, conjunctiva of eye |
|
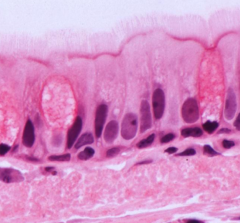
What type of epithelium is this and where is it found?
|
Pseudostratified (columnar) epithelium
---lining of nasal cavity, sinuses, trachea and bronchi ---lining of auditory tube and part of tympanic cavity ---lining of epididymis and ductus deferens |
|
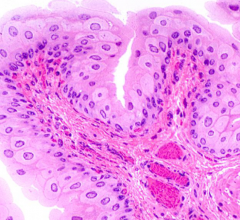
What type of epithelium is this and where is it found?
|
Transitional epithelium
---lining of urinary tract from kidney to urethra |
|
|
What are the steps of cutaneous wound healing?
|
---Hemostasis (seconds to hours):
------platelet adhesion, activation and aggregation ------fibrin formation ------release of signaling molecules/growth factor ---Inflammation (hours to days): ------recruitment of neutrophils/monocytes/macrophages ------kill invading bacteria/remove dead debris ---Reparation (days to weeks): ------fibroblast recruitment ------angiogenesis ------granulation tissue (blood vessels, fibroblast, macrophases in loose provisional matrix) ------re-epithelialization ---Remodeling (weeks to years): ------ECM production/maturation ------apoptosis of inflammatory cells ---Healed! |
|
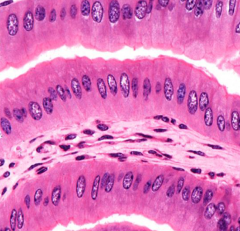
What type of epithelium is shown here and where is it found?
|
Simple columnar
---lining of GI tract and reproductive tract |

