![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cytoplasm |
Material inside of a cell |
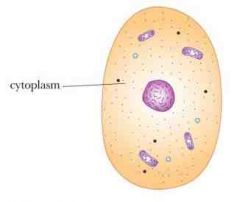
Where the transport proteins bring substances. |
|
|
Phospholipids |
A phosphate and lipid combined which help to form the bilayer of a cell. |
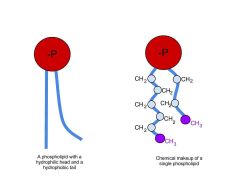
Phosphate is polar. Lipid is nonpolar |
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer |
2 layers of phospholipids making the outer shell of the cell. Polar phosphate face outward and no polar lipids face inward. |
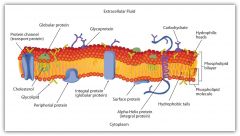
Certain substance can only pass through if they have a transport protein. |
|
|
Polar |
When a molecule has a magnetic of electrical pull and one side is more positive while the other is more negative. |
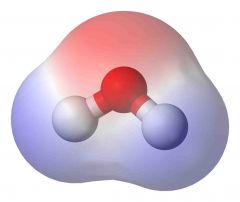
Water |
|
|
Nonpolar |
No slight charge or polarity on a molecule. |
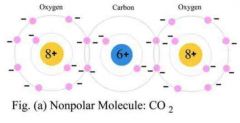
Gasoline |
|
|
Transport proteins |
Attach to substances to allow them across the phospholipid bilayer |
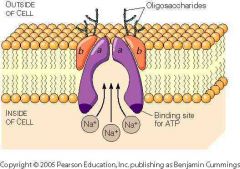
Sodium-potassium pumps |
|
|
Selective permeability |
Only allows certain this through |
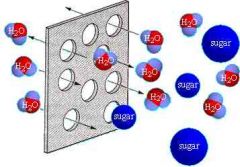
The cell membrane |
|
|
Glycoproteins |
A receptor protein made of sugar and protein |
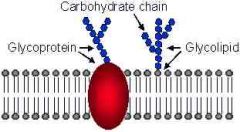
Make up part of the cell membrane and look like satellites |
|
|
Glycolipids |
A receptor lipid made of a sugar and a lipid |
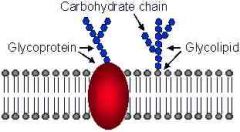
Make up part of the cell membrane and go along with glycoproteins |
|
|
Fluid mosaic model |
Shows the makeup of the cell membrane |
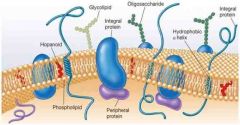
A flexible structure with bilayer, transport proteins, and receptor proteins and lipids |
|
|
Diffusion |
Substances which are drawn together from their particles' movement |
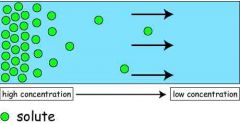
Try to achieve equalibrium |
|
|
Concentration gradient |
A difference in the amount of a single substance in an area |

A lot of potential energy |
|
|
Osmosis |
Molecules travel through something selectively permeable |
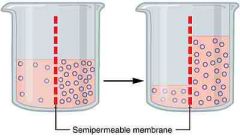
"Some things can pass! Other things cannot!" |
|
|
Turgor |
Cells become rigid |
When the plasma membrane is pushed against the cell wall. |
|
|
Isotonic |
Having equal pressure |
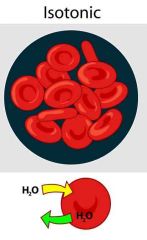
Separated by a semipermeable membrane |
|
|
Hypotonic |
Osmotic pressure is less than another substance |
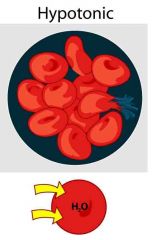
Potential energy |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Osmotic pressure is greater than another substance |
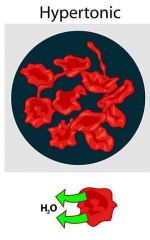
Cannot reach equalibrium without transport proteins |
|
|
Passive transport |
Does not require energy to move substance through cell membrane |
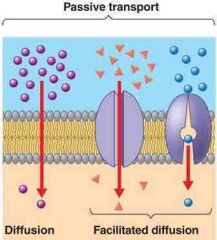
Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Active transport |
Transporting a substance that requires energy |
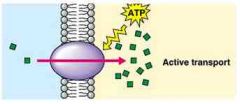
Moving to a place of higher concentration |
|
|
Endoctyosis |
Folding section of cell membrane so larger substances can pass through |
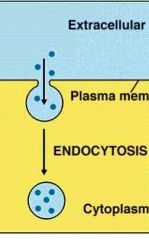
A vacuole is formed |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Allow large substance out of the cell by releasing the contents of the vacuole |
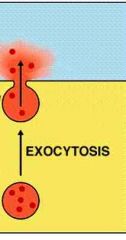
The unfolding of the cell membrane |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Molecules are moved to an area of low concentration by transport proteins |
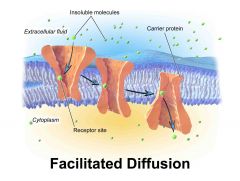
No energy is required |

