![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
[27.a] Creating a National Security State (1945-1949). The advent of nuclear weapons and the growth of Soviet power converted Asia, Europe, the Third World, and even the US into a battleground of rival ideologies. Fear of an “_____________ _________ __________” induced most Americans to accept increased government power. The close unification of the Federal Government and weapon makers gave rise to the ________-__________ Complex. But everyone thought it was worth it to contain the USSR.
|
[27.a] Creating a National Security State (1945-1949). The advent of nuclear weapons and the growth of Soviet power converted Asia, Europe, the Third World, and even the US into a battleground of rival ideologies. Fear of an “(INTERNATIONAL COMMUNIST CONSPIRACY)” induced most Americans to accept increased government power. The close unification of the Federal Government and weapon makers gave rise to the (MILITARY-INDUSTRIAL) Complex. But everyone thought it was worth it to contain the USSR.
|
|
|
1. [27.a.1] The overarching US foreign policy goal after WWI was ___________ of the Soviet Union. [839-840]
|
[27.a.1] The overarching US foreign policy goal after WWI was (CONTAINMENT) of the Soviet Union. [839-840]
|
|
|
2. [27.a.2] Understand the difference between symmetrical and asymmetrical containment. Between 1917 and 1990, when the ____ axioms prevailed, relations between the US and USSR were bad; when the _____ axioms prevailed relations were relatively good.
|
[27.a.2] Understand the difference between symmetrical and asymmetrical containment. Between 1917 and 1990, when the (RIGA) axioms prevailed, relations between the US and USSR were bad; when the (YALTA) axioms prevailed relations were relatively good.
|
|
|
3. [27.a.3] Failure of the US to share ______ technology with the USSR may have been the first step toward cold war. The US put forward the ______ plan that would deny USSR a veto in the UN ________ Council, which violated the charter, and which the USSR ________. [838, L]
|
[27.a.3] Failure of the US to share (ATOMIC) technology with the USSR may have been the first step toward cold war. The US put forward the (BARUCH) plan that would deny USSR a veto in the UN (SECURITY) Council, which violated the charter, and which the USSR (REJECTED). [838, L]
|
|
|
4. [27.a.4] Another cause of the Cold War centered on whether the country of _______ should be unified or rearmed. [841-842, L]
|
[27.a.4] Another cause of the Cold War centered on whether the country of (GERMANY) should be unified or rearmed. [841-842, L]
|
|
|
5. [27.a.5] American public opinion soured toward the Soviet Union and Truman grew suspicious when Stalin denied free elections in ______. [839]
|
[27.a.5] American public opinion soured toward the Soviet Union and Truman grew suspicious when Stalin denied free elections in (POLAND). [839]
|
|
|
6. [27.a.6] The ______ Doctrine of March 1947 promised aid to peoples resisting aggression. At the time, this meant perceived Soviet threats in ______ and ______. [839]
|
[27.a.6] The (TRUMAN) Doctrine of March 1947 promised aid to peoples resisting aggression. At the time, this meant perceived Soviet threats in (GREECE) and (TURKEY). [839]
|
|
|
7. [27.a.7] ______ _____ ______ first used the word “containment.” What did he mean? [840]
a. 4 regions of the world are critical to security: (1) _______ __________, (2) ______ ____, (3) _____, and (4) _______ ______. b. Non-Military, ____________ containment of ______ Influence. c. _-________ (February 1946) – encouraged the US to make firm stand against the Soviets. d. Suggested _________ and ________ containment, believing USSR is too weak to expand militarily (denies that he meant a military containment of USSR). |
[27.a.7] (GEORGE FROST KEENAN) first used the word “containment.” What did he mean? [840]
a. 4 regions of the world are critical to security: (1) (WESTERN HEMISPHERE), (2) (MIDDLE EAST), (3) (JAPAN), and (4) (WESTERN EUROPE). b. Non-Military, (ASYMMETRICAL) containment of (SOVIET) Influence. c. (X-TELEGRAM) (February 1946) – encouraged the US to make firm stand against the Soviets. d. Suggested (POLITICAL) and (ECONOMIC) containment, believing USSR is too weak to expand militarily (denies that he meant a military containment of USSR). |
|
|
8. [27.a.8] The 1947 ________ ________ Act created (1) an independent ___ _____ (2), established the ___ Agency, (3) established a Department of _______, and (4) formed the National ________ Council. [840-841]
|
[27.a.8] The 1947 (NATIONAL SECURITY) Act created (1) an independent (AIR FORCE), (2) established the (CIA) Agency, (3) established a Department of (DEFENCE), and (4) formed the National (SECURITY) Council. [840-841]
|
|
|
9. [27.a.9] What 1947 economic plan was designed to promote European recovery along lines very similar to the “New Deal”? [841]
|
[27.a.9] What 1947 economic plan was designed to promote European recovery along lines very similar to the “New Deal”? [841]
Marshall Plan |
|
|
10. [27.a.10] What did the Soviets do when they feared that the Marshall Plan would rebuild Germany a little too good? [841-842]
a. Soviets walked out of _-_____ _____, charging that the West had violated _______ agreement by halting reparations. b. ______ seals off Berlin. c. ___,___ airdrops made over Berlin. |
[27.a.10] What did the Soviets do when they feared that the Marshall Plan would rebuild Germany a little too good? [841-842]
a. Soviets walked out of (4-POWER TALKS), charging that the West had violated (POTSDAM) agreement by halting reparations. b. (STALIN) seals off Berlin. c. (272,264) airdrops made over Berlin. |
|
|
11. [27.a.11] How did Truman, a democrat, win the 1948 election? [842-843]
a. b. c. |
[27.a.11] How did Truman, a democrat, win the 1948 election? [842-843]
a. Memory of FDR's "New Deal" (Truman's “Fair Deal”) b. Tougher on communism. c. New Deal Coalition held strong (big business, labor movement). |
|
|
12. [27.a.12] In the 1948 presidential elections, Strom ________ stood as candidate for the _________ (_______ ______) Party, which marks the beginning of the shift of the southern states from strongly Democratic to __________ by 1980? [842-843]
|
[27.a.12] In the 1948 presidential elections, Strom (THURMOND) stood as candidate for the (DIXIECRATS [STATES RIGHTS]) Party, which marks the beginning of the shift of the southern states from strongly Democratic to (REPUBLICAN) by 1980? [842-843]
|
|
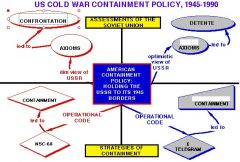
13. Fill in the Blanks (Axioms & Containment):
|
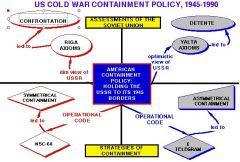
13. Fill in the Blank (Axioms & Containment):
|
|
|
[27.b] The Korean War Era (1949-1952). Some historians argue that the Korean War (1950-1953) transformed containment of the USSR into a global policy aimed at stopping ______ and _______ communist expansion everywhere. American entrenched themselves for the long Cold War, and the Military-Industrial Complex turned it _______.
|
[27.b] The Korean War Era (1949-1952). Some historians argue that the Korean War (1950-1953) transformed containment of the USSR into a global policy aimed at stopping (SOVIET) and (CHINESE) communist expansion everywhere. American entrenched themselves for the long Cold War, and the Military-Industrial Complex turned it (PROFITS).
|
|
|
1. [27.b.1] The _____ ________ Treaty Organization (NATO) was a military alliance formed in 1949 to block Soviet expansion into Europe [843-844, map 844]
|
[27.b.1] The (NORTH ATLANTIC) Treaty Organization (NATO) was a military alliance formed in 1949 to block Soviet expansion into Europe [843-844, map 844]
|
|
|
2. [27.b.2] Who authored NSC-68? What did it propose? What event made it the official US containment policy? [845]
____ _____ (chair of the Policy Planning Staff of the US State Department) – Truman orders restudy of Soviet intentions (1949); the result was NSC-68 which provided a _________ for both the rhetoric and the substance of future Cold War foreign policy; this policy was passed due to the start of the ______ ___. These 3 events are what caused Truman to order the restudy: a. China revolution has change of leadership to ___ ______ (turn communist). b. The _______ detonate their own atomic bomb for the 1st time (much earlier than anticipated). c. The _____ ____ Case – accused of passing secrets to the Soviets, acquitted 1st trial, pumpkin papers found on his property so he was convicted and sent to Sing Sing for 5 years (spent 2); Vernona Project (look up). |
[27.b.2] Who authored NSC-68? What did it propose? What event made it the official US containment policy? [845]
(PAUL NITZE) (chair of the Policy Planning Staff of the US State Department) – Truman orders restudy of Soviet intentions (1949); the result was NSC-68 which provided a (BLUEPRINT) for both the rhetoric and the substance of future Cold War foreign policy; this policy was passed due to the start of the (KOREAN WAR). These 3 events are what caused Truman to order the restudy: a. China revolution has change of leadership to (MAO ZEDONG) (turn communist). b. The (SOVIETS) detonate their own atomic bomb for the 1st time (much earlier than anticipated). c. The (ALGER HISS) Case – accused of passing secrets to the Soviets, acquitted 1st trial, pumpkin papers found on his property so he was convicted and sent to Sing Sing for 5 years (spent 2); Vernona Project (look up). |
|
|
What did the NSC-68 Containment Policy propose?
NSC-68 called for ___________ Containment (Military Oriented) of USSR and remilitarized US foreign policy as it concluded the Soviets would try to take over the ____ _____ by military force, if necessary; and that the Soviets were dedicated to the overthrow of __________. NSC-68 called for: a. ________________ of US foreign policy. b. Raising of _____. c. More money spent on defense (from $11 billion in 1949 to over $__ billion in ____). d. US defense of every part of the free world, as it would be in remote regions that the communists might test US _______. e. NSC-68 planners believed increased defense spending would raise the American ________ __ ______ (considered a nice “by-product” of Cold War thinking). |
What did the NSC-68 Containment Policy propose?
NSC-68 called for (SYMMETRICAL) Containment (Military Oriented) of USSR and remilitarized US foreign policy as it concluded the Soviets would try to take over the (FREE WORLD) by military force, if necessary; and that the Soviets were dedicated to the overthrow of (CAPITALISM). NSC-68 called for: a. (REMILITARIZATION) of US foreign policy. b. Raising of (TAXES). c. More money spent on defense (from $11 billion in 1949 to over $(50) billion in (1950)). d. US defense of every part of the free world, as it would be in remote regions that the communists might test US (RESOLVE). e. NSC-68 planners believed increased defense spending would raise the American (STANDARD OF LIVING) (considered a nice “by-product” of Cold War thinking). |
|
|
3. [27.b.3] List the origins of the Korean War. [L]
There are 3 main dynamics of the cause of the Korean War, name them: a. b. c. |
[27.b.3] List the origins of the Korean War. [L]
There are 3 main dynamics of the cause of the Korean War, name them: a. North Korea v. South Korea b. US v. USSR c. US v. China |
|
|
What were the issues between North and South Korea?
a. Korea _______ since WWII. b. _______ ____ – president of ROK (Republic of Korea). Religious, anti-communist, Princeton educated, would have made a better prison warden than national leader. c. ___ __ ___ – Cult-style leader of North Korea. Fought Japanese in WWII; intensely nationalistic. d. _____________ – both leaders wanted it, under their own government; therefore, it was a Civil War. |
What were the issues between North and South Korea?
a. Korea (DIVIDED) since WWII. b. (SYNGMAN RHEE) – president of ROK (Republic of Korea). Religious, anti-communist, Princeton educated, would have made a better prison warden than national leader. c. (KIM IL SUN) – Cult-style leader of North Korea. Fought Japanese in WWII; intensely nationalistic. d. (REUNIFICATION) – both leaders wanted it, under their own government; therefore, it was a Civil War. |
|
|
What were the 2 solutions for solving the Korean dilemma?
a. Solution #1 – Allow the USSR to occupy Korea ____________ (done by 1 side only). It lay outside US ________ interests and the Koreans were unlikely to go along with Soviet rule for long. b. Solution #2 – US-USSR sponsors a _________ government (which was done in Czechoslovakia, Hungary, France, and Italy). |
What were the 2 solutions for solving the Korean dilemma?
a. Solution #1 – Allow the USSR to occupy Korea (UNILATERALLY) (done by 1 side only). It lay outside US (SECURITY) interests and the Koreans were unlikely to go along with Soviet rule for long. b. Solution #2 – US-USSR sponsors a (COALITION) government (which was done in Czechoslovakia, Hungary, France, and Italy). |
|
|
What were the issues between the US and the USSR?
a. Korea ranked low in _______ __________ of both countries. b. US knew Rhee was highly _________. c. US was already pulling out troops and merely giving ______ and ___. d. USSR – too weak for ________ _____________ with US. e. Stalin did arm the North Koreans and ultimately supported their attack __ ____ 1950. |
What were the issues between the US and the USSR?
a. Korea ranked low in (DEFENSE PRIORITIES) of both countries. b. US knew Rhee was highly (UNPOPULAR). c. US was already pulling out troops and merely giving (ADVICE) and (AID). d. USSR – too weak for (MILITARY CONFRONTATION) with US. e. Stalin did arm the North Koreans and ultimately supported their attack (26 JUNE) 1950. |
|
|
What were the issues between the US and China?
a. Continued US support of ______ ___-_____ angered Mao Zedong. Perceived US as still intervening in China’s internal affairs. b. After Inchon, New York Times reported hawkish attitude of US ___________. c. General MacArthur ignored ___'_ warning not to approach Yalu River. d. “Prudence required _____ to intervene in Korea.” |
What were the issues between the US and China?
a. Continued US support of (CHIANG KAI-CHECK) angered Mao Zedong. Perceived US as still intervening in China’s internal affairs. b. After Inchon, New York Times reported hawkish attitude of US (CONGRESSMEN). c. General MacArthur ignored (MAO'S) warning not to approach Yalu River. d. “Prudence required (CHINA) to intervene in Korea.” |
|
|
Ultimately, what were the origins of the Korean War?
The Korean War was a _____ ___ – Kim Il Sun (north) and Syngman Rhee (south) were both fighting to unify the country under one government and were ready to go to war to do so. Neither the US nor the USSR viewed Korea as a vital security area, although the _______ did. The North Koreans attacked on ______’s approval and the US intervened complying with NSC-68, believing Korea to be the 1st major test of US resolve to contain _________. |
Ultimately, what were the origins of the Korean War?
The Korean War was a (CIVIL WAR) – Kim Il Sun (north) and Syngman Rhee (south) were both fighting to unify the country under one government and were ready to go to war to do so. Neither the US nor the USSR viewed Korea as a vital security area, although the (CHINESE) did. The North Koreans attacked on (STALIN’S) approval and the US intervened complying with NSC-68, believing Korea to be the 1st major test of US resolve to contain (COMMUNISM). |
|
|
4. [27.b.4] General Douglas _________ underestimated Chinese warnings and caused a Chinese intervention in the Korean War when UN troops came too close to the ____ River in November 1950? [846-847]
|
[27.b.4] General Douglas (MacARTHUR) underestimated Chinese warnings and caused a Chinese intervention in the Korean War when UN troops came too close to the (YALU) River in November 1950? [846-847]
|
|
|
5. [27.b.5] Why did Truman fire MacArthur? [847]
|
[27.b.5] Why did Truman fire MacArthur? [847]
MacArthur pushed too far – he continued to advance toward the Yalu River which made China respond by entering the war. President Truman ordered a truce at the 38th parallel, but MacArthur challenged him arguing for an all-out victory over North Korea and China too (speaking out against Truman inappropriately to the press); Truman fired him for disobeying the direct orders of the Commander-in-Chief with the full approval of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. (more online on Livingston’s website) |
|
|
6. [27.b.6] Under what terms did the Korean War end (1953)? [848, 869-870, L]
The war lasted _ years, long enough for NCS-68 to take effect as the US containment policy. _____ had given up demanding a seat in the UN, the annexation of Taiwan, and the unification of Korea. In 1953, ______ died, which further weakened Chinese desire to continue the war, yet the issue of ____________ (return of POW’s) was still an issue. a. China wants ________ ____________ (all POW’s automatically returned “home,” regardless where they wanted to go). b. The UN stood for _________ ____________ (POW’s are sent to the destination of their choice). c. About 25,000 (1/4) of the 100,000 _____ ______ and _______ POW’s didn’t want to return home. d. 359 out of the 13,444 __ POW’s didn’t want to return (this raised issue of potential brainwashing by _____). e. China eventually agreed to voluntary repatriation once the war was over (____ ____). f. A special UN commission headed by _____ supervised the transfer of prisoners and determined what their wishes were. g. Once operation ______ ______ and ___ ______ were completed, the war ended. |
[27.b.6] Under what terms did the Korean War end (1953)? [848, 869-870, L]
The war lasted (3) years, long enough for NCS-68 to take effect as the US containment policy. (CHINA) had given up demanding a seat in the UN, the annexation of Taiwan, and the unification of Korea. In 1953, (STALIN) died, which further weakened Chinese desire to continue the war, yet the issue of (REPATRIATION) (return of POW’s) was still an issue. a. China wants (FORCIBLE REPATRIATION) (all POW’s automatically returned “home,” regardless where they wanted to go). b. The UN stood for (VOLUNTARY REPATRIATION) (POW’s are sent to the destination of their choice). c. About 25,000 (1/4) of the 100,000 (NORTH KOREAN) and (CHINESE) POW’s didn’t want to return home. d. 359 out of the 13,444 (UN) POW’s didn’t want to return (this raised issue of potential brainwashing by (CHINA)). e. China eventually agreed to voluntary repatriation once the war was over (JUNE 1953). f. A special UN commission headed by (INDIA) supervised the transfer of prisoners and determined what their wishes were. g. Once operation (LITTLE SWITCH) and (BIG SWITCH) were completed, the war ended. |
|
|
7. [27.b.7] How did the Korean War impact on American foreign policy and Civil Rights? [848, 850]
What were the International Effects of the Korean War? a. Stalin _____________ US response; East-West _______ postponed for 20 years. b. Containment turns ______. c. Arms race ___________. d. ____ strengthened (German Army reappears). e. Peace treaty signed with _____; integrated in US-led world system. f. Only 5% of Americans believed that _____ had intervened on its own volition. |
[27.b.7] How did the Korean War impact on American foreign policy and Civil Rights? [848, 850]
What were the International Effects of the Korean War? a. Stalin (MISCALCULATED) US response; East-West (DETENTE) postponed for 20 years. b. Containment turns (GLOBAL). c. Arms race (INTENSIFIES). d. (NATO) strengthened (German Army reappears). e. Peace treaty signed with (JAPAN); integrated in US-led world system. f. Only 5% of Americans believed that (CHINA) had intervened on its own volition. |
|
|
How did the US suffer directly from the Korean War?
Attention diverted from ______ ______ to ___ _______ (the Korean War disrupted American Life). a. ______ politicians assert themselves (since attention was diverted from ______): Eugene Talmadge, George Wallace, and George Rankin. b. Attention was diverted from the problems posed by ___________ and _______; these much-needed reforms had to wait for the 1960’s. c. Anti-communist hysteria kicked in with the ________ accusations, hunting down suspected communists were right-wing’s full focus. d. Anti-_____: George Solkolsky, journalist; National Association of Manufactures; R.J. Reynolds. e. (Political) Opportunists: Joseph McCarthy, Richard Nixon, Herbert Hoover, Ronald Reagan. People like Joseph McCarthy gained popularity by accusing anyone he didn’t like as being a communist; ______ _________, a journalist, was a one-man clearing house on whether you were a communist or not; and the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) began to crack down on labor again. |
How did the US suffer directly from the Korean War?
Attention diverted from (SOCIAL REFORM) to (RED BAITING) (the Korean War disrupted American Life). The fear of international communism and the vision of millions of Chinese killing American boys in Korea had the following effects: a. (RACIST) politicians assert themselves (since attention was diverted from (RACISM)): Eugene Talmadge, George Wallace, and George Rankin. b. Attention was diverted from the problems posed by (SEGREGATION) and (POVERTY); these much-needed reforms had to wait for the 1960’s. c. Anti-communist hysteria kicked in with the (McCARTHY) accusations, hunting down suspected communists were right-wing’s full focus. d. Anti-(LABOR): George Solkolsky, journalist; National Association of Manufactures; R.J. Reynolds. e. (Political) Opportunists: Joseph McCarthy, Richard Nixon, Herbert Hoover, Ronald Reagan. People like Joseph McCarthy gained popularity by accusing anyone he didn’t like as being a communist; (GEORGE SOLKOLSKY), a journalist, was a one-man clearing house on whether you were a communist or not; and the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) began to crack down on labor again. |
|
|
[27.c] Containment at Home. Fear of communist advances triggered a nasty side-effect in America: ____-_____ sentiment and political ____________.
|
[27.c] Containment at Home. Fear of communist advances triggered a nasty side-effect in America: (ANTI-UNION) sentiment and political (McCARTHYISM).
|
|
|
1. [27.c.1] The ____-_______ Act of 1947 rolled back some of the gains made in the 1953 Wagner Act. [850]
|
[27.c.1] The (TAFT-HARTLEY) Act of 1947 rolled back some of the gains made in the 1953 Wagner Act. [850]
|
|
|
2. [27.c.2] In what industry did HUAC open its first investigation of communist conspirators? [851]
|
[27.c.2] In what industry did HUAC open its first investigation of communist conspirators? [851]
The Entertainment Industry in Hollywood, California. |
|
|
3. [27.c.3] Two future presidents, ______ ______ and _______ _____ launched their careers hunting down “Red Subversives.” [851]
|
[27.c.3] Two future presidents, (RONALD REAGAN) and (RICHARD NIXON) launched their careers hunting down “Red Subversives.” [851]
|
|
|
4. [27.c.4] Put on trial again in 1950, _____ ____, a reputable diplomat who was at Yalta, was convicted of espionage. Released after 5 years in prison, he was guilty of passing information to the Soviets. [851]
|
[27.c.4] Put on trial again in 1950, (ALGER HISS), a reputable diplomat who was at Yalta, was convicted of espionage. Released after 5 years in prison, he was guilty of passing information to the Soviets. [851]
|
|
|
5. [27.c.5] FBI chief _. _____ ______ and US Attorney General ______ _______ used Federal power to hunt communist subversives. [851-852]
|
[27.c.5] FBI chief (J. EDGAR HOOVER) and US Attorney General (HOWARD McGRATH) used Federal power to hunt communist subversives. [851-852]
|
|
|
6. [27.c.6] Many people mistakenly believed the ______ Report identified homosexuals as a security risk because communist agents could blackmail them. [853]
|
[27.c.6] Many people mistakenly believed the (KINSEY) Report identified homosexuals as a security risk because communist agents could blackmail them. [853]
|
|
|
7. [27.c.7] Were Ethel and Julius Rosenberg given a fair trial in an unprejudiced atmosphere? [854]
No, it provoked intense controversy: a. The trial, the verdicts of guilty, the sentences of death at Sing Sing prison, the numerous _____ appeals, the worldwide ________, and the executions in 1953 all provoked intense controversy. b. The Rosenbergs continuously maintained their innocence (they had fallen victim to _____________ hysteria). c. Many believed the government seemed less interested in conducting a fair trial than in finding __________. d. In 1997, the government ________ to prosecute “a fair number of Americans who almost certainly were atomic spies.” e. Of those prosecuted for dealing with the Soviets, only Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were charged with a crime that carried the _____ _______. |
[27.c.7] Were Ethel and Julius Rosenberg given a fair trial in an unprejudiced atmosphere? [854]
No, it provoked intense controversy: a. The trial, the verdicts of guilty, the sentences of death at Sing Sing prison, the numerous (LEGAL) appeals, the worldwide (PROTESTS), and the executions in 1953. b. The Rosenbergs continuously maintained their innocence (they had fallen victim to (ANTICOMMUNIST) hysteria). c. Many believed the government seemed less interested in conducting a fair trial than in finding (SCAPEGOATS). d. In 1997, the government (DECLINED) to prosecute “a fair number of Americans who almost certainly were atomic spies.” e. Of those prosecuted for dealing with the Soviets, only Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were charged with a crime that carried the (DEATH PENALTY). |
|
|
8. [27.c.8] The 1950 ________ ________ ________ Act empowered the government to detain _________ suspects in special camps and forced members of “subversive” groups to ________ with the government. [855]
|
[27.c.8] The 1950 (McCARRAN INTERNAL SECURITY) Act empowered the government to detain (COMMUNIST) suspects in special camps and forced members of “subversive” groups to (REGISTER) with the government. [855]
|
|
|
9. [27.c.9] In early 1950 Senator ______ ________ started a new red scare in Wheeling, West Virginia, charging, “I have in my hand 57 cases of individuals who would appear to be either card carrying members…of the Communist Party, [and] who…are still helping to shape our foreign policy.” [I, 855]
|
[27.c.9] In early 1950 Senator (JOSEPH McCARTHY) started a new red scare in Wheeling, West Virginia, charging, “I have in my hand 57 cases of individuals who would appear to be either card carrying members…of the Communist Party, [and] who…are still helping to shape our foreign policy.” [I, 855]
|
|
|
[27.d] Truman’s Fair Deal. In 1948 Truman promised a “Fair Deal” to all Americans. Essentially, his administration was committed to advancing the New Deal programs. _____________ and the ______ ___ blocked many advances, but Truman did commit the Federal Government to “____ __________” for all Americans, and encouraged Congress to raise the minimum wage from 40₵ to 75₵.
|
[27.d] Truman’s Fair Deal. In 1948 Truman promised a “Fair Deal” to all Americans. Essentially, his administration was committed to advancing the New Deal programs. (CONSERVATIVES) and the (KOREAN WAR) blocked many advances, but Truman did commit the Federal Government to “(FULL EMPLOYMENT)” for all Americans, and encouraged Congress to raise the minimum wage from 40₵ to 75₵.
|
|
|
1. [27.d.1] The National Association of _____________ (NAM) believed government sponsored aid and welfare programs would destroy the ____ enterprise system. [857]
|
[27.d.1] The National Association of (MANUFACTURERS) (NAM) (anti-labor) believed government sponsored aid and welfare programs would destroy the (FREE) enterprise system. [857]
|
|
|
2. [27.d.2] How was the Full Employment Bill altered in its final form when incorporated in the Employment Act of 1946? [858]
1. Truman, Council of ________ Advisors formed. Business, “Full” Employment changed to “_______ __________.” 2. Truman, Government encourages growth by own ________. Business, Government ______ instead of planning. 3. Business, Economic growth ensures ______ stability. 4. Business, _______ enterprise makes economic decisions. |
2. [27.d.2] How was the Full Employment Bill altered in its final form when incorporated in the Employment Act of 1946? [858]
1. Truman, Council of (ECONOMIC) Advisors formed. Business, “Full” Employment changed to “(MAXIMUM EMPLOYMENT).” 2. Truman, Government encourages growth by own (SPENDING). Business, Government (ADVICE) instead of planning. 3. Business, Economic growth ensures (SOCIAL) stability. 4. Business, (PRIVATE) enterprise makes economic decisions. |
|
|
3. [27.d.3] By 1947, __% of students in college received government aid under the _._. Bill. [859]
|
[27.d.3] By 1947, (50)% of students in college received government aid under the (G.I.) Bill. [859]
|
|
|
4. [27.d.4] The ____-Burton Act built _________ instead of establishing a national health coverage plan. [859]
|
[27.d.4] The (HILL)-Burton Act built (HOSPITALS) instead of establishing a national health coverage plan. [859]
|
|
|
5. [27.d.5] Did Social Security benefits expand or contract between 1947-1954? [859]
|
[27.d.5] Did Social Security benefits expand or contract between 1947-1954? [859]
Expand |
|
|
6. [27.d.6] How did the white South respond to Truman’s civil rights initiatives? [860]
|
[27.d.6] How did the white South respond to Truman’s civil rights initiatives? [860]
They didn't like it, they migrated to the Republicans from the Democrats. |
|
|
1. [27.e.1] The communities of _________ in PA and NY represented a trend in America toward the _______ but discriminated against _______ _________. [862-863]
|
[27.e.1] The communities of (LEVITTOWN) in PA and NY represented a trend in America toward the (SUBURBS) but discriminated against (AFRICAN AMERICANS). [862-863]
|
|
|
2. [27.e.2] What caused the “Baby Boom,” and between what years did this phenomenon occur? [863]
|
[27.e.2] What caused the “Baby Boom,” and between what years did this phenomenon occur? [863]
Servicemen returning home wanting a family and start a “normal life.” |
|
|
3. [27.e.3] What was the difference between the “public sphere” and the “private sphere”? [884]
|
[27.e.3] What was the difference between the “public sphere” and the “private sphere”? [884]
Public – Men (CEO’s, Lawyers, etc.). Private – Women (Home). |
|
|
4. [27.e.4] Working married women rose from 25% in 1948 to __% in 1959. [885]
|
[27.e.4] Working married women rose from 25% in 1948 to (40)% in 1959. [885]
|
|
|
5. [27.e.5] Media in the form of _________ recognized the challenge of raising a family and doing housework and sometimes featured positive articles about work outside the home. At the same time, articles gave pointed advice that all happiness a woman should expect would come in the _______ sphere. [885-886]
|
[27.e.5] Media in the form of (MAGAZINES) recognized the challenge of raising a family and doing housework and sometimes featured positive articles about work outside the home. At the same time, articles gave pointed advice that all happiness a woman should expect would come in the (PRIVATE) sphere. [885-886]
|
|
|
1. [27.f.1] Republican candidate for president ______ _. __________ won in 1952 on a “KC2” platform, promising to end the ___ in Korea, be even tougher on communism, and end perceived Truman era corruption. [965 and see paragraph starting, “honored his campaign pledge to go to… 870]
|
[27.f.1] Republican candidate for president (DWIGHT D. EISENHOWER) won in 1952 on a “KC2” platform, promising to end the (WAR) in Korea, be even tougher on communism, and end perceived Truman era corruption. [965 and see paragraph starting, “honored his campaign pledge to go to… 870]
|
|
|
2. [27.f.2] In 1954 McCarthy’s smear campaign ended after accusing former Defense Secretary George Marshall, Army Secretary Robert Stevens, and Voice of America radio of being communist dupes. The Senate ________ him, and McCarthy’s influence declined until his death in 1957. [870]
|
[27.f.2] In 1954 McCarthy’s smear campaign ended after accusing former Defense Secretary George Marshall, Army Secretary Robert Stevens, and Voice of America radio of being communist dupes. The Senate (CENSURED) him, and McCarthy’s influence declined until his death in 1957. [870]
|
|
|
3. [27.f.3] Have historians upheld the view that Eisenhower was a “befuddled, grandfatherly” president who let others control his administration? [871]
No, they contend that Eisenhower firmly controlled the hostile John Foster Dulles, his _________ __ _____; he also made contact with Nikita Khruschev, the Soviet _______, thus reducing some cold war tension. He did, however, allow the US nuclear stockpile to grow immensely (in 1955, the US had 5,000 warheads, by 1960, we had __,___). He also authorized the 1954 CIA overthrow of Jacobo Arbenz, the president of Guatemala, in favor of a right-wing ________. |
[27.f.3] Have historians upheld the view that Eisenhower was a “befuddled, grandfatherly” president who let others control his administration? [871]
No, they contend that Eisenhower firmly controlled the hostile John Foster Dulles, his (SECRETARY OF STATE); he also made contact with Nikita Khruschev, the Soviet (PREMIER), thus reducing some cold war tension. He did, however, allow the US nuclear stockpile to grow immensely (in 1955, the US had 5,000 warheads, by 1960, we had [20,000]). He also authorized the 1954 CIA overthrow of Jacobo Arbenz, the president of Guatemala, in favor of a right-wing (DICTATOR). |
|
|
1. 1A – WWII general who came out of retirement in 1950 and took command of UN forces in Korea. Famous for his statement that, “There is no substitute for victory.” Truman fired him for making public statements that advocated the bombing of China. [b.5]
|
1A – WWII general who came out of retirement in 1950 and took command of UN forces in Korea. Famous for his statement that, “There is no substitute for victory.” Truman fired him for making public statements that advocated the bombing of China. [b.5]
General Douglas MacArthur |
|
|
2. 5A – Headed the Policy planning staff of the State Department that produced NSC-68 in 1950. This controversial 70-page document called for continued military spending to raise the American standard of living. [b.2]
|
5A – Headed the Policy planning staff of the State Department that produced NSC-68 in 1950. This controversial 70-page document called for continued military spending to raise the American standard of living. [b.2]
Paul H. Nitze |
|
|
3. 7A – Workers in this industry struck for 59 days. Truman threatened to take over these mines unless owners and union reconciled. Laborers everywhere were demanding a share of postwar prosperity. [hinted at pg. 850]
|
7A – Workers in this industry struck for 59 days. Truman threatened to take over these mines unless owners and union reconciled. Laborers everywhere were demanding a share of postwar prosperity. [hinted at pg. 850]
Coal |
|
|
4. 8A – Historian Bruce Cumings reminds readers that the Korean War (1950-1953) was really a _____ war between North and South Korea. [b.3]
|
8A – Historian Bruce Cumings reminds readers that the Korean War (1950-1953) was really a (CIVIL) war between North and South Korea. [b.3]
|
|
|
5. 10A – Anti-communists in the ____ industry targeted the “Hollywood Ten,” accusing them of membership in or sympathies with the American Communist Party. [c.2]
|
10A – Anti-communists in the (FILM) industry targeted the “Hollywood Ten,” accusing them of membership in or sympathies with the American Communist Party. [c.2]
|
|
|
6. 12A – The Office of Economic Stabilization was supposed to ease the transition from wartime economy to peace economy, but an “unprecedented wave of labor _______” showed this was not an easy process. [pg. 850]
|
12A – The Office of Economic Stabilization was supposed to ease the transition from wartime economy to peace economy, but an “unprecedented wave of labor (STRIKES)” showed this was not an easy process. [pg. 850]
|
|
|
7. 13A – Membership in this party during the 1950’s would likely cost you your job (abbreviation). [c.8]
|
13A – Membership in this party during the 1950’s would likely cost you your job (abbreviation). [c.8]
CP (Communist Party) |
|
|
8. 14A – Senator McCarthy was ultimately discredited when he accused this American institution of harboring communists. [f.2]
|
14A – Senator McCarthy was ultimately discredited when he accused this American institution of harboring communists. [f.2]
Army |
|
|
9. 17A – The US led a UN force in this country to prevent communist forces from overrunning the entire peninsula. [b.3]
|
17A – The US led a UN force in this country to prevent communist forces from overrunning the entire peninsula. [b.3]
Korea |
|
|
10. 18A – Counts for 6 points (acronym).
|
18A – Counts for 6 points (acronym).
TD (Touchdown) |
|
|
11. 21A – Starred in Rebel Without a Cause, a movie depicting the generation gap but ends on a happy note. [961]
|
21A – Starred in Rebel Without a Cause, a movie depicting the generation gap but ends on a happy note. [961]
James (Dean) |
|
|
12. 23A – The ____-Burton Act (1946) built hospitals but fell short of est. national health coverage. [d.4]
|
23A – The (HILL)-Burton Act (1946) built hospitals but fell short of est. national health coverage. [d.4]
|
|
|
13. 24A – Senator McCarthy took advantage of American fears by using the anticommunist brush to “___” his political enemies (slang). [c.9]
|
24A – Senator McCarthy took advantage of American fears by using the anticommunist brush to “(TAR)” his political enemies (slang). [c.9]
|
|
|
14. 25A – The fall of this country to communism (1949) and its intervention in the Korean War (1950) provoked an anti-Communist backlash in the US. [b.2]
|
25A – The fall of this country to communism (1949) and its intervention in the Korean War (1950) provoked an anti-Communist backlash in the US. [b.2]
China |
|
|
15. 27A – General MacArthur’s continued advance toward this river despite Peking’s warning to back off resulted in a massive Chinese counter-attack in November 1950. [b.4]
|
27A – General MacArthur’s continued advance toward this river despite Peking’s warning to back off resulted in a massive Chinese counter-attack in November 1950. [b.4]
Yalu |
|
|
16. 28A – The ______ Doctrine of March 1947 promised US aid to freedom seeking nations everywhere. First applied to Greece and Turkey. [a.6]
|
28A – The (TRUMAN) Doctrine of March 1947 promised US aid to freedom seeking nations everywhere. First applied to Greece and Turkey. [a.6]
|
|
|
17. 34 – Form of the ugly, non-descriptive verb “to be.”
|
34 – Form of the ugly, non-descriptive verb “to be.”
Is |
|
|
18. 36A – Women were supreme in the _______ sphere. [e.3]
|
36A – Women were supreme in the (PRIVATE) sphere. [e.3]
|
|
|
19. 37A – Established by the National Security Act (1947) and charged with gathering intelligence. Also contained “covert operations” division. [a.8]
|
37A – Established by the National Security Act (1947) and charged with gathering intelligence. Also contained “covert operations” division. [a.8]
CIA |
|
|
20. 39A – Soviet refusal to grant free elections in this easy European country made many Americans think that Stalin was reneging on the 1945 Yalta agreement. [a.5]
|
39A – Soviet refusal to grant free elections in this easy European country made many Americans think that Stalin was reneging on the 1945 Yalta agreement. [a.5]
Poland |
|
|
21. 40A – The ____-Hartley Act (1947) repealed some provisions of the Wagner Act. States were allowed to regulate unions, and the president could order a “cooling off” period to prevent a strike. [c.1]
|
40A – The (TAFT)-Hartley Act (1947) repealed some provisions of the Wagner Act. States were allowed to regulate unions, and the president could order a “cooling off” period to prevent a strike. [c.1]
|
|
|
22. 41A – Percentage of women working out of the house by 1959. [e.4]
|
41A – Percentage of women working out of the house by 1959. [e.4]
Forty |
|
|
23. 43A – Secretary of State whose plan for the economic reconstruction of Europe bears his name. [a.9]
|
43A – Secretary of State whose plan for the economic reconstruction of Europe bears his name. [a.9]
George (Marshall) |
|
|
24. 46A – The 1947 National ________ Act created the Defense Department, an independent air force, the NSC, and the CIA. [a.8]
|
46A – The 1947 National (SECURITY) Act created the Defense Department, an independent air force, the NSC, and the CIA. [a.8]
|
|
|
25. 48A – El ___ was a Spanish soldier of fortune who lived in the 11th century. Also acronym for army’s Criminal Investigation Department.
|
48A – El (CID) was a Spanish soldier of fortune who lived in the 11th century. Also acronym for army’s Criminal Investigation Department.
|
|
|
26. 49A – Acronym. An association that hated labor organizations and warned that many Fair Deal programs smacked too much of communism and should be abolished. [d.1; pg. 857]
|
49A – Acronym. An association that hated labor organizations and warned that many Fair Deal programs smacked too much of communism and should be abolished. [d.1; pg. 857]
NAM (National Association of Manufacturers) |
|
|
27. 51A – Like the GI Bill, this government program expanded during the late 1940’s and into the 1950’s (acronym). [d.5]
|
51A – Like the GI Bill, this government program expanded during the late 1940’s and into the 1950’s (acronym). [d.5]
SS (Social Security) |
|
|
28. 52A – Term given to the view implying that the US could tolerate living on the same planet with the USSR. Named after one of the last WWII conferences. [a.2]
|
52A – Term given to the view implying that the US could tolerate living on the same planet with the USSR. Named after one of the last WWII conferences. [a.2]
YALTA |
|
|
29. 53A – Getting one will likely result in melanoma.
|
53A – Getting one will likely result in melanoma.
Tan |
|
|
30. 54A – He and wife Ethel Rosenberg were executed in 1953 in New York’s Sing Sing prison for passing atomic secrets to the USSR. (Contemporaries and historians since have doubted this was necessary.) [c.7]
|
54A – He and wife Ethel Rosenberg were executed in 1953 in New York’s Sing Sing prison for passing atomic secrets to the USSR. (Contemporaries and historians since have doubted this was necessary.) [c.7]
(Julius) & Ethel Rosenberg |
|
|
31. 55A – A report that concluded homosexuality was more commonplace than previously believed. Gays and lesbians subsequently became targets of the anti-Communist crusade. [c.6]
|
55A – A report that concluded homosexuality was more commonplace than previously believed. Gays and lesbians subsequently became targets of the anti-Communist crusade. [c.6]
Kinsey Report |
|
|
32. 2D – A sharp instrument used to poke holes through leather.
|
2D – A sharp instrument used to poke holes through leather.
Awl |
|
|
33. 3D – Pete Rose’s nickname was “Charlie ______.”
|
3D – Pete Rose’s nickname was “Charlie (HUSTLE).”
|
|
|
34. 4D – Magazines began to depict the challenge ______ faced raising a family as well as portraying them favorably in the out-of-home work force. [e.5]
|
4D – Magazines began to depict the challenge (WOMEN) faced raising a family as well as portraying them favorably in the out-of-home work force. [e.5]
|
|
|
35. 5D – Initials of political party opposed to Ngo Diem, the US backed leader of South Vietnam. [pg. 876]
|
5D – Initials of political party opposed to Ngo Diem, the US backed leader of South Vietnam. [pg. 876]
NLF (National Liberation Front) |
|
|
36. 6D – Term given to years between 1950-1954 symbolizing the fanaticism and scare tactics of the anti-Communist crusade. [b.6; c.9]
|
6D – Term given to years between 1950-1954 symbolizing the fanaticism and scare tactics of the anti-Communist crusade. [b.6; c.9]
McCarthyism |
|
|
37. 9D – Name given to southerners who rallied behind Strom Thurmond in election of 1948. This political party consisting mostly of southern democrats, opposed Truman’s integration policies. Marked beginning of southern shift to Republican Party. [a.12]
|
9D – Name given to southerners who rallied behind Strom Thurmond in election of 1948. This political party consisting mostly of southern democrats, opposed Truman’s integration policies. Marked beginning of southern shift to Republican Party. [a.12]
Dixiecrat (States Rights) |
|
|
38. 11D – This 1950 act virtually outlawed the American Communist Party by forcing members to register with the government and by awarding the president the right to detain alleged communists in special camps. [c.8]
|
11D – This 1950 act virtually outlawed the American Communist Party by forcing members to register with the government and by awarding the president the right to detain alleged communists in special camps. [c.8]
McCarran (Internal Security Act) |
|
|
39. 15D – Whisper, don’t ______.
|
15D – Whisper, don’t (YELL).
|
|
|
40. 16D – The Korean War didn’t end until China agreed to UN sponsored “voluntary ___ repatriation.” (acronym) [b.6]
|
16D – The Korean War didn’t end until China agreed to UN sponsored “Voluntary (POW) Repatriation.” (acronym) [b.6]
|
|
|
41. 19D – Nickname of a British woman whose death was probably mourned by more people than any other person except Ghandi.
|
19D – Nickname of a British woman whose death was probably mourned by more people than any other person except Ghandi.
Di (Princess Diana) |
|
|
42. 20 – Levittown, PA was an example of the new ______ communities being built in the US during the 1950’s. [e.1]
|
20D – Levittown, PA was an example of the new (SUBURBAN) communities being built in the US during the 1950’s. [e.1]
|
|
|
43. 22D – Say __ to drugs.
|
22D – Say (NO) to drugs.
|
|
|
44. 26D – This Congressional committee was empowered to subpoena and interrogate suspected communists. [c.2]
|
26D – This Congressional committee was empowered to subpoena and interrogate suspected communists. [c.2]
HUAC (House Un-American Activities Committee) |
|
|
45. 29D – Term given to view that the US had to destroy Soviet communism or be destroyed by it. [a.2]
|
29D – Term given to view that the US had to destroy Soviet communism or be destroyed by it. [a.2]
RIGA |
|
|
46. 30D – Initials of country that broke Geneva Accords in 1956 by refusing to tolerate free elections in Vietnam and by trying to establish an independent southern “republic.” [28.b.2]
|
30D – Initials of country that broke Geneva Accords in 1956 by refusing to tolerate free elections in Vietnam and by trying to establish an independent southern “republic.” [28.b.2]
US |
|
|
47. 31D – Our European allies thought the US was _____ for waging war in Vietnam.
|
31D – Our European allies thought the US was (CRAZY) for waging war in Vietnam.
|
|
|
48. 32D – A bill that expanded college enrollment by granting tuition money to veterans. [d.3]
|
32D – A bill that expanded college enrollment by granting tuition money to veterans. [d.3]
GI (Bill) |
|
|
49. 33D – This party gained control of Congress in 1946 by implying that the Truman administration was being soft on the Soviets. [pg. 842]
|
33D – This party gained control of Congress in 1946 by implying that the Truman administration was being soft on the Soviets. [pg. 842]
Republican |
|
|
50. 35D – US attorney general who once declared that communists were the, “germs of death for society.” [c.5]
|
35D – US attorney general who once declared that communists were the, “germs of death for society.” [c.5]
J. Howard McGrath |
|
|
51. 38D – Although the Acheson-Lilienthal report suggested it, the US refused to internationalize ______ technology. Russia felt threatened, adding yet another factor that led to the Cold War. [a.3]
|
38D – Although the Acheson-Lilienthal report suggested it, the US refused to internationalize (ATOMIC) technology. Russia felt threatened, adding yet another factor that led to the Cold War. [a.3]
|
|
|
52. 42D – American Foreign Service officer in the Soviet embassy who authored the famous “X-Telegram” in 1946. He concluded that the US must contain the USSR, but that the Soviet threat was political and economic, not military. [a.7]
|
42D – American Foreign Service officer in the Soviet embassy who authored the famous “X-Telegram” in 1946. He concluded that the US must contain the USSR, but that the Soviet threat was political and economic, not military. [a.7]
George Frost (Keenan) |
|
|
53. 44D – A ___ scare gripped America during the early 1950’s. Politicos like McCarthy sought political advancement by portraying themselves as patriotic Americans fighting domestic communism. [c.10]
|
44D – A (RED) scare gripped America during the early 1950’s. Politicos like McCarthy sought political advancement by portraying themselves as patriotic Americans fighting domestic communism. [c.10]
|
|
|
54. 45D – He died in 1996, claiming to the end that he had not passed secret documents to the Soviets before and during WWII. He was released from jail in 1954 after serving nearly 4 years. Incarceration destroyed his marriage. [c.4]
|
45D – He died in 1996, claiming to the end that he had not passed secret documents to the Soviets before and during WWII. He was released from jail in 1954 after serving nearly 4 years. Incarceration destroyed his marriage. [c.4]
Alger (Hiss) |
|
|
55. 47D – His code name was “T-10.” [c.3]
|
47D – His code name was “T-10.” [c.3]
Ronald Reagan |
|
|
56. 50D – Earlier marriages and rising incomes accounted for the “____ Boom” between 1945-1960. [e.2]
|
50D – Earlier marriages and rising incomes accounted for the “(BABY) Boom” between 1945-1960. [e.2]
|
|
|
57. 51D – Acronym for the 1980’s defense program that called for space-based lasers to knock out incoming ICBM’s. Most scientists and analysts have discredited its feasibility.
|
51D – Acronym for the 1980’s defense program that called for space-based lasers to knock out incoming ICBM’s. Most scientists and analysts have discredited its feasibility.
SDI (Strategic Defense Initiative) |

