![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell |
Fundamental building block of all organisms |
|
|
What are most cells? |
Most cells are single cell |
|
|
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells |
* simple * no membrane bound nucleus * small size * single cellular |
|
|
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells |
* complex * nucleus is membrane bound * membrane bound organelles * larger sized * multi-cellular |
|
|
What can smaller cells do faster than larger cells? |
Reginerate |
|
|
3 Domains of Classification? |
* Archaea * Bacteria * Eukaryotic |
|
|
4 Kingdoms of Eukaryotic? |
*Animalia * Plantae * Fungi * Protista (protest) |
|
|
Binomitails are what? |
Scientific nomenclature; 2 Latin names |
|
|
Scientific Nomenclature for humans |
Homo sapiens; H. sapiens |
|
|
Scientific Nomenclature of Cardinals |
Cardinalis cardinalis; C. cardinalis |
|
|
Scientific Nomenclature of stomach bacteria |
Escherichia coli; E. Coli |
|
|
Atoms and elements are what? |
The same |
|
|
What is the atomic mass? |
# of protons & neutons |
|
|
What is the atomic number? |
# of protons |
|
|
Carbon atomic mass and atomic number? |
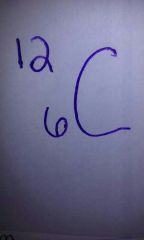
|
|
|
Atomic mass and atomic number of Hydrogen? |

|
|
|
Atomic mass and atomic number of Nitrogen? |
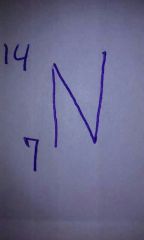
|
|
|
Atomic mass and atomic number of Oxygen? |

|
|
|
What's a double bond? |

|
|
|
What's a single bond? |
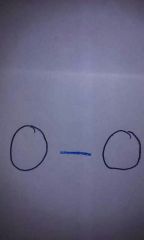
|
|
|
What is an atomic nucleus |
Atomic mass |
|
|
What is a valence shell |
Outer most shell of an atom |
|
|
What makes up the 1st shell of valence shell |
1st sphere orbital (2 elections per shell) |
|
|
What makes up the 2nd valence shell? |
1= 2s orbital 3= 2b oribitals _______________ 8 total |
|
|
List the bonds from strongest to weakest |
* covalent bonds * ionic bonds * hydrogen bond * van der Waals interactions |
|
|
Covalent bond characteristics |
Strong, share electrons |
|
|
Ionic bond characteristics |
Slightly positive, two oppositely charged ions |
|
|
Hydrogen bond characteristics |
Weak water bond between two h2o molecules |
|
|
Polar molecule characteristics |
Shape water molecule with one one negative end and one positive end |
|
|
Van der Waal interactions characteristics |
Weakest bond, induced electrical interactions between two or more molecules |
|
|
Is h2o organic or not? |
They are not organic |
|
|
What is CH4 |
Methane |
|
|
Is carbon an organic molecule? |
Yes, to be organic it must contain carbon. |
|
|
What is C6 H12 O6? |
Glucose |
|
|
How many atoms in a molecule? |
6.022 |
|
|
How many atoms are in hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon? |
Hydrogen has two atoms, oxygen has one atom, and carbon has 12.01 atoms. |
|
|
What are hydrocarbons? |
Hydrocarbons or a compound of hydrogen and carbon atoms; makes up the gases |
|
|
List of hydrocarbons from weakest potential of energy to strongest potential of energy |
Methane, Ethane, Propane, brutane, Pentland, became and octane |
|
|
Kinetic energy is |
The energy of motion |
|
|
Potential energy is |
Stored energy that has the potential to be change to kinetic energy |
|
|
What happens when you create a bond? |
Energy is used but when broken the energy is returned |
|
|
Independent Variable |
Stands alone (ex. Someone's age) |
|
|
Control |
Constant and unchanged |
|
|
Qualitative data |
Info about qualities, can't be measured |
|
|
Control group |
Baseline measure |
|
|
Treatment |
Experimental manipulation |
|
|
Theory |
Opinion not fact |
|
|
Scientific law |
Statement repeatedly proven |
|
|
Scientific method |
1. Observation 2. Ask ? 3. Hypothesis 4. Experiment 5. Results 6. Conclusion |
|
|
Bar graphs |
Show numeric data |
|
|
Line graph |
Data over time |
|
|
Dependent variable |
Depends on Independent, is what you measure |
|
|
Ion |
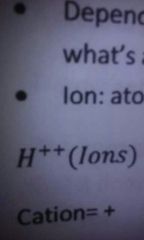
|
|
|
Cation |
+ charge |
|
|
Anion |
- charge |
|
|
Isotopes |
Change of neutrons in an atom |
|
|
Boiling point of water |
100° C |
|
|
Melting and freezing point of water |
0°C |
|
|
Solvent |
Receiving somethin in a solution |
|
|
Solute |
Being dissolved into solution |
|
|
Solution is made of |
Solvent and solute |
|
|
Aqueous solution |
Water is the solvent |
|
|
Water found in what 3 states |
1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas |
|
|
Sublimation |
Water from solid --> gas |
|
|
Deposition |
Water from gas --> solid |
|
|
Melting |
Water from solid --> liquid |
|
|
Freezing |
Liquid --> solid |
|
|
Vaporization |
Water from liquid --> gas |
|
|
Condensation |
Water from gas --> liquid |
|
|
Types of Isomers |
1. Structural: formulate how the are put together 2. Geometric: CIS (adjacent); TRANS (across) 3. Enantiomers: mirror image; R&S and L&D |
|
|
Macromolecules |
1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Lipids 4. Nucleic Acid |
|
|
Ph Scale |
0- 6.9 = ACID 7.0 = PURE WATER 7.1 - 14 = BASE |
|
|
ACID formulation |
H2O + H+ |
|
|
Base formulation |
H2O + O+H- |
|
|
Quanitive data |
Can be measured |

