![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
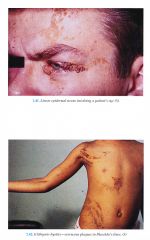
Epidermal Nevus Syndrome/ Ichthyosis Hystrix/ Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus/ Linear Sebaceous nevus syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Ichthyosis Hystrix
Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus Linear sebaceous nevus syndrome |
|
|
Inheritance
|
Sporadic
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
None
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Over 400 cases reported; M= F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth to first few months of life
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Thought to include many distinct genetic diseases all sharing a phenotype reflecting genetic mosaicism
|
|
|
Clinical
|
Skin
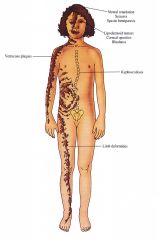
Epidermal nevi (usually more than 2 to 3 cm in length, more than 0.5-2 cm in width); Nevus unius laterus: ILVEN (most common): long, linear, verrucous plaques on limbs; with/without scale, erythema; Ichthyosis hystrix: extensive verrucous plaques in whorl like pattern on trunk Linear nevus sebaceous: linear, orange tan, waxy plaques on scalp extending onto the face Localized row of pigmented papillomas Other Skin Findings Hemangiomas, capillary malformations, hypopigmentation, cafe au lait macules Central Nervous System (associated with head and neck or extensive nevi) Mental retardation, seizures, spastic hemiparesis/paralysis, sensorineural deafness. cerebral hemangiomas, vascular malformations Skeletal (associated with location of nevi) Hemihypertrophy, kyphoscoliosis, ankle/foot deformities, vitamin D resistant Rickets Eyes Extension of nevus to lid and bulbar conjunctiva, lipodermoids, colobomas, corneal opacity, nystagmus, cortical blindness Neoplasms (rare) Variety of tumors reported; syringocystaclenorna papilliferum, Wilms tumor, astrocytoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, salivary gland adenocarcinoma |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Epidermal nevi
Proteus Klippel-Trenauny |
|
|
Lab
|
Skin biopsy rule out features of (EHK)
Eletroencephalogram Brain CT/MRI Skeletal survey Serum calcium/phosphorus |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to dermatologist/dermatologic surgeon surgical removal, dermabrasion, C02 laser, topical lactic acid in propylene glycol, oral retinoids Referral to neurologist, ophthalmologist, orthopedist Genetic counseling if at risk for EHK offspring
|
|
|
Prognosis
|
Malignancy, cerebral vascular lesion with hemorrhage, or intractable seizures may shorten life span
|

