![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Clinical Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome/ Nevoid Basal Cell carcinoma syndrome/ Gorlin Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
Gorlin Syndrome |
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal dominant; PTCH I (PATCHED/) gene on 9q22 31
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
DNA mutation analysis
|
|
|
Incidence
|
DNA mutation analysis
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Birth (bossing, skeletal anomalies); childhood (jaw cysts, basal cell carcinoma)
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Mutations in PTCH I, a tumor suppressor gene encoding the sonic hedgehog transmembrane receptor protein; receptor interacts with signaling proteins important for controlling cell fate, patterning, and growth
|
|
|
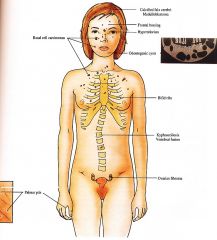
Clinical
|
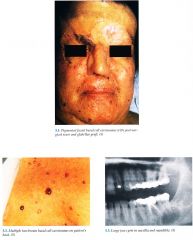
Skin
Basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) multiple, skin colored to tan, dome shaped papules on face, neck, trunk Palmoplantar pits 2 to 3 mm erythematous pits, rarely develop into BCCs; milium, epidermoid cysts Musculoskeletal Jaw cysts (oclontogenic keratocysts) secondary pain, swelling, drainage, increased in molar and premolar areas in maxilla, usually multiple, lining with malignant potential Frontal bossing, bifid ribs, vertebral fusion, kyphoscoliosis Central Nervous System Calcification of falx cerebri, agenesis of corpus callosum, medulloblastoma, mental retardation (less common) Eyes Hypertelorism, congenital blindness, cataracts, colobomas, strabismus Genitourinary Ovarian fibromas, fibrosarcoma |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Bazex syndrome
Unilateral linear nevoid basal cell carcinomas Melanocytic nevi Rombo syndrome Xeroderma pigmentosa (XP) |
|
|
Lab
|
Skin biopsy
Skeletal surveys of skull, maxilla, mandible, ribs, vertebrae |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to dentist/oral surgeon
Referral to dermatologist/Moh's surgeon surgical excision, electrodesiccation and curettage with/without general anesthesia, topical 5 fluorouracil, imiquimod; frequent cutaneous examinations Oral retinoids suppression of new BCCs Avoid radiotherapy/x rays induces new BCCs Sun avoidance, broad spectrum sunscreen, protective clothing Referral to orthopedist, neurologist, ophthalmologist |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Normal life span if BCCs treated early on and no other malignancies develop; close surveillance with physician throughout life; disfiguring scars may create psychosocial problems
|

