![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
168 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
50yo M with 25 pack/yr history presents with his second bout of pneumonia in the last 6mos. CXR reveals a lobar consolidation in the same location as the previous pneumonia. What is the next step?
|
CT scan of the chest (to investigate cancer)
|
|
|
What imaging study is used to diagnose a DVT?
|
compressive venous ultrasound
|
|
|
What radiographic study is used to diagnose injury to the urethra?
|
retrograde cystourethrogram
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a basilar skull fracture?
|
- Raccoon eyes (periorbital bruising)
-Battle sign (bruising over mastoid process) - Bleeding behind the TM - CSF from the nose or ears |
|
|
What is the DOC for trigeminal neuralgia?
|
Carbamazepine (SU pg 174)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for normal pressure hydrocephalus? What is the treatment for peudotumor cerebri?
|
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (SU pg 179): CSF shunt
Pseudotumor Cerebri (neuro handout): - weight loss, acetozolamide - serial lumbar punctures - shunting of CSF |
|
|
What is the treatment for Guillain-Barre syndrome?
|
either plasmapheresis or IVIG (SU pg 185)
|
|
|
How do you distinguish the Somogyi effect from the Dawn phenomenon?
|
Somogyi effect: 2-3am glucose will be LOW
Dawn phenomenon: 3am glucose with be HIGH |
|
|
What type of immunodeficiency increases the risk of anaphylactic transfusion reaction?
|
IgA deficiency (SU pg 162)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with no comorbidities?
|
thiazide diuretics (HCTZ, chlorthalidone)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with diabetes?
|
ACE-I/ ARB
|
|
|
Which antihypertensives are needed in pts with heart failure?
|
ACE-I/ARB + Beta-blocker + Aldosterone Antagonist (Spironolactone)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with BPH?
|
alpha blocker
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with left ventricular hypertrophy?
|
ACE-I/ ARB
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with hyperthyroidism?
|
beta-blocker (Propanolol)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with Osteoporosis?
|
Thiazides (retain calcium)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with benign essential tremor?
|
Beta-blocker
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in post-menopausal females?
|
Thiazide diuretics (reduce risk of osteoporosis by retaining calcium)
|
|
|
Which antihypertensive class is first line in pts with migraines?
|
beta-blocker
|
|
|
What are the HACEK bacteria?
|
consider these bugs with culture negative endocarditis (SU pg 22):
Haemophilus Actinobacillus Cardiobacterium Eikenella Kingella |
|
|
At what pt do pts with chronic COPD qualify for home O2?
|
(1) Pulse ox <88%
(2) Pulmonary Hypertension (3) Peripheral Edema (4) Polycythemia |
|
|
What is the initial treatment of a localized non-small cell lung cancer?
|
Surgical resection (SU pg 45)
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
food poisoning as a result of mayonnaise sitting out too long |
staph aureus - self limiting (just hydrate!)
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
rice-water stools |
vibrio cholera (hydrate, tetracycline or doxycycline)
or ETEC (self-limiting) |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
diarrhea transmitted from pet feces |
Yersinia enterocolitis (self-limiting, just hydrate!)
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
food poisoning resulting from reheated rice (Chinese food) |
Bacillus cereus (self-limiting, hydrate!)
|
|
|
most common cause of traveler's diarrhea?
|
Enterotoxigenic E. Coli (ETEC) -self-limiting (just hydrate!)
|
|
|
What bug causes: diarrhea after a course of antibiotics? tx?
|
C diff - tx with Metronidazole or oral vancomycin
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
diarrhea after recent ingestion of water from a stream? |
Giardia lamblia - tx with Metronidazole
Entamoeba Histolytica - tx with metronidazole or paromomycin in both cases will see cysts & trophozoites in stool sample |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
mild intestinal infection that can become neurocysticercosis? |
Taenia solium
tx: Praziquantel, corticosteroids if >5cysts |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
food poisoning from undercooked hamburger |
Enterohemorrhagic E Coli (EHEC) (0157:H7)
This is self-limiting - just hydrate - DO NOT GIVE ANTIBIOTICS - they can worsen symptoms by leading to greater toxin release |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
diarrhea from seafood |
Vibrio cholera (will have copious watery diarrhea - tx with hydration, tetracycline or doxy)
Vibrio parahemolytica (will have abd pain + watery diarrhea w/in 24hrs of eating seafood - self-limiting, just hydrate) |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
bloody diarrhea from poultry |
Salmonella (self-limiting, unless immunosuppressed give fluoroquinolone)
Campylobacter (generally self-limiting, can give erythromycin) |
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?
Diarrhea + pink eye |
Adenovirus - just hydrate
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
Bloody diarrhea then liver abscess |
Entamoeba histolytica - Metronidazole or paromomycin
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
Diarrhea in AIDS pt |
Cryptosporidium (tx with nitazoxanide) or Isospora
|
|
|
What's the likely bug & best tx?:
dehydrated child with greenish diarrhea in winter months |
rotavirus
|
|
|
What virus is assoc with gastroenteritis in cruise boat passengers?
|
Norwalk virus
|
|
|
What virus is assoc with gastroenteritis in the winter time?
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
What is the tx for clostridium difficile infection?
|
oral or IV metronidazole
oral vancomycin |
|
|
After examining a pt with C diff, how should you wash your hands?
|
clean with soap & water
|
|
|
A pt has bloody diarrhea following ingestion of ground beef. What sequela is he at risk for developing?
|
EHEC (0157:H7) can cause Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) characterized by:
(1) Hemolytic anemia (2) thrombocytopenia (3) acute renal failure |
|
|
What pathogen is likely responsible for a pt that ate some egg salad made with mayonnaise that had been sitting out at a party for hrs and subsequently began vomiting several hrs later?
|
Staph Aureus - self-limiting
|
|
|
A family went camping and developed greasy, foul-smelling diarrhea. What is the likely pathogen?
|
Giardia Lamblia - tx with Metronidazole
|
|
|
Trophozoites and cysts are seen in the stool sample of a pt with bloody diarrhea. What is the likely pathogen, and what is the likely source?
|
Entamoeba histolytica (note that this bug can invade the intestinal wall and lead to bloody diarrhea)
Transmitted via contaminated water Tx: Metronidazole or paromomycin |
|
|
how does the treatment for cure of Hep B differ than that for Hep C?
|
Hep B tx: Interferon-α (standard or pegylated) or antiviral (Lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir, or telbivudine)
Hep C tx: pegylated interferon + ribavirin |
|
|
Clinically, what differentiates HBV surface antibody from HBV core antibody?
|
HBV surface Ab: indicates resolved HBV or former vaccine
HBV core Ab: indicates resolved HBV |
|
|
What test results would you expect for someone with resolved HBV infection? if they had the former HBV vaccine?
|
resolved infection will have BOTH (+) HbS Ab and (+) HbC Ab
Former vaccine: (+) HbS Ab only |
|
|
What does it mean if a pt has HBV core antibodies, but no HBV surface antibodies or HBV surface antigen?
|
Has Hep B infection, during "window" period
|
|
|
How can you differentiate chronic HBV infection with a good prognosis (because of less viral replication) from that with a worse prognosis?
|
HBV e antigen indicates infectivity & will be present in the patient with worse prognosis
|
|
|
What is a common vector for Hep A virus?
|
shellfish
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus confers an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
HBV (3-5% risk of hepatocellular carcinoma)
|
|
|
Which hepatitis virus confers a high risk of chronic hepatitis?
|
- Hep C - 80% become chronic
- Hep B - 5% of adults become chronic note: Hep A & E do NOT cause chronic hepatitis |
|
|
What anatomical structures does a Barium swallow highlight?
|
Esophagus, LES, and stomach
|
|
|
What anatomical structures does a gastric emptying study highlight?
|
stomach, pyloric sphincter, and duodenuma
|
|
|
What anatomical structures does a small bowel follow through (SBFT) highlight?
|
stomach to the terminal ileum
|
|
|
What anatomical structures does a barium enema highlight?
|
colon & appendix
|
|
|
What is the difference btw mallory-weiss and Boarhaave's syndrome?
|
MW: longitudinal mucosal laceration of distal esophagus & prox stomach (minor injury)
Boerhaave's: esophageal perforation or rupture of distal esophagus (life-threatening injury) |
|
|
How does the treatment for diffuse esophageal spasm differ from that of achalasia?
|
(SU pg 60)
DES: medical therapy (Nifedipine, Nitrates, TCAs) Achalasia: intervention such as dilation, botox, myotomy or meds (Nifedipine, Nitrates) |
|
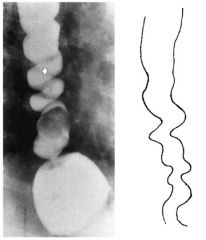
Pt c/o chest pain + dysphagia
manometry shows uncoordinated esophageal contractions barium swallow shows "corkscrew" pattern |
Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) - a neuromuscular disorder in which nonperilstaltic contractions of the esophagus occur
|
|
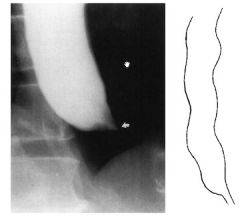
Pt c/o dysphagia of solids & liquids, regurgitation, cough
manometry shows incomplete LES relaxation Barium swallow shows "bird's beak" sign Diagnosis? next step? |
Dx: Achalasia
Next step: EGD to r/o malignancy |
|
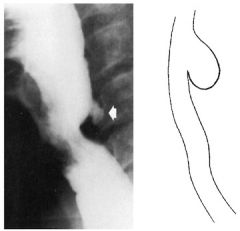
Pt has bad breath & regurgitation of food eaten days ago
barium swallow shows outpouching |
Zenker diverticulum - an outpouching in the upper esophagus caused by smooth muscle weakness
Tx: cricopharyngeal myotomy or diverticulectomy |
|
|
What are the initial steps in treatment of GERD?
|
weight loss
elevate the head of the bed dietary changes |
|
|
Besides the sensation of "heart burn" what is a common symptom of GERD?
|
persistent cough
|
|
|
What is Barrett's esophagus? Why is it important?
|
Definition: normal squamous epithelium has undergone columnar transformation
Can lead to adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Which type of esophageal cancer is most prevalent in the US?
|
adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Which medicines are the most effective in combating GERD?
|
PPIs
|
|
|
What are the different types of esophageal diverticula and their locations?
|
(1) Zenker - immediately above the upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
(2) Traction - near the midpt of the esophagus (3) Epiphrenic - just above the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) |
|
|
What is the tx for entamoeba histolytica?
|
Metronidazole
|
|
|
What is the tx for Giardia Lamblia?
|
Metronidazole
|
|
|
What is the tx for salmonella?
|
Fluoroquinolones
|
|
|
What is the tx for shigella?
|
Fluoroquinolones or TMP-SMX (Bactrim)
|
|
|
What is the tx for campylobacter?
|
Erythromycin
|
|
|
What type of current or past Hep B exposure in pt with:
(-) Heb BsAg (-) Hep BsAb (+) Hep BcAb |
acute infection
|
|
|
What type of current or past Hep B exposure in pt with:
(+) Heb BsAg (-) Hep BsAb (+) Hep BcAb |
chronic infection
|
|
|
What type of current or past Hep B exposure in pt with:
(-) Heb BsAg (+) Hep BsAb (-) Hep BcAb |
vaccinated
|
|
|
What type of current or past Hep B exposure in pt with:
(-) Heb BsAg (+) Hep BsAb (+) Hep BcAb |
Recovered
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hep C virus infection?
|
pegylated interferon (INFα) + ribavirin
|
|
|
What is the next step after H&P in the work-up of a pt c/o dysphagia?
|
Barium swallow
|
|
|
How can active H. pylori be diagnosed?
|
- urea breath test
- H. pylori stool antigen - EGD with biopsy - serum antibodies |
|
|
What is the treatment regimen for eradication for H. Pylori infection?
|
PPI + clarithromycin + metronidazole or amoxicillin
|
|
|
What are the key differences in symptoms of a gastric ulcer vs duodenal ulcer?
|
Gastric ulcer = pain soon after eating, worsens with eating
Duodenal ulcer (more common) = pain 2-4hrs postprandial, initial improvement with eating |
|
|
Name 2 big risk factors for peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
|
(1) H. pylori
(2) Chronic NSAID use |
|
|
What are 2 major complications that can occur with PUD?
|
(1) Bleeding (melena, hematochezia, etc)
(2) Perforation |
|
|
What quick & easy study may reveal a perforation? What specifically are you looking for?
|
Upright Abdominal xray - you will be able to see air in cavity
|
|
|
What are some physical signs of a bleeding ulcer?
|
- coffee ground emesis
- hematomesis - hematochezia - melena |
|
|
What is the tumor marker to look for in gastric cancer?
|
CEA
|
|
|
Where is Virchow's node?
|
left supraclavicular node
|
|
|
Where is sister mary Joseph's node?
|
Periumbilical node
|
|
|
What are the most common causes of acute pancreatitis in the US?
|
"BAD HITS"
Biliary (Gallstones) - #1 cause Alcohol #2 cause Drugs Hypertriglyceridemia & calcemia Idiopathic Trauma Scorpion sting |
|
|
Pancreatitis can cause bluish skin discoloration in what two locations? What are the names of these signs?
|
Periumbilical eccymosis - Cullen's sign
Flank ecchymosis - Grey Turner's sign |
|
|
If pancreatitis is due to gallstone obstruction of the pancreatic duct, what should be done after the pancreatitis has passed?
|
cholecystectomy
|
|
|
What is a likely cause for pancreatic pseudocyst?
|
previous pancreatitis
|
|
|
What is the tumor marker most useful in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer?
|
CA 19-9
|
|
|
What procedure is performed to treat an isolated cancerous tumor in the head of the pancreas?
|
SU pg 79
Whipple procedure - Pancreaticoduodenectomy (remove head of pancreas, distal stomach, gall bladder, common bile duct, duodenum, prox jejunum) |
|
|
What test would confirm the diagnosis in a pt with >3L/day of watery diarrhea?
|
Serum VIP level
Dx: VIPoma (VIP-producing tumor) of the non-β-islet cells |
|
|
What are the possible complications that can arise after partial gastrectomy for recurrent gastric ulcers?
|
(1) Dumping (20%) - postprandial GI discomfort including N/V, diarrhea, cramps, diaphoresis, palpitations, flushing
(2) alkaline reflux gastritis (2%) - burning epigastric pain & nausea exacerbated by meals (3) early satiety (4) deficiencies of B12, iron and/or calcium (5) Afferent & efferent loop syndromes (after Billroth II) - epigastric pain & bilious vomiting due to obstruction of the duodenal limb |
|
|
Who are candidates for obesity surgery?
|
BMI >40 or BMI >35 with high risk comorbid conditions (DM, OSA, obesity-related cardiomyopathy, severe joint disease)
|
|
|
What benefits can be expected from surgical therapies for obesity?
|
sustained weight loss (usually 30-50%)
reduction or cure of DM improvement in dyslipidemia reduction or cure of HTN reduced mortality (40-60% at 5-7 yrs) |
|
|
What needs to be done with pt prior to bariatric surgery?
|
must be referred to psychiatry for evaluation of freq overeating to cope with stress/emotional distress, a current eating disorder, or uncontrolled psychiatric disorders
note: depression & suicide may increase in the first year after surgery - need to monitor closely |
|
|
What is the preferred bariatric surgery?
|
Laparoscopic gastric banding ("lap band"): silicone band is placed around the upper part of the stomach to induce feeling of satiety
usually OR time 1 hr, can return to work in 1wk |
|
|
What are complications of lap gastric banding?
|
nutritional defiencies (iron, Vit D)
GERD reoperation required in 13% for band reposition, removal, or revision |
|
|
What is the most common bariatric surgery in the US?
|
Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y)
|
|
|
What are the possible complications of gastric bypass?
|
operative mortality (0-1.5%)
anastomotic leakage (2%) wound infection (8%) incisional hernia (15-30%) |
|
|
HYQ: An EGD with biopsy in a 65yo M reveals gastric cancer. What is the next step in management?
|
CT scan of abdomen and pelvis
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the next step in the management of a pt with recurrent duodenal ulcers seen on at least two EGDs?
|
serum gastrin level
think Zollinger Ellison Syndrome |
|
|
HYQ: What is the most effective tx of a duodenal ulcer not due to ZE syndrome?
|
triple therapy for H. pylori
PPI + Clarithromycin + Metronidazole or amoxicillin |
|
|
HYQ: What Chem 7 lab abnormality is often elevated in pts with an upper GI bleed?
|
increased BUN
|
|
|
What are Ranson's criteria in determining prognosis of pts with acute pancreatitis?
|
On admission: "GA LAW"
Glucose >200 AST >250 LDH >350 Age >55 WBC >16,000 <48hrs "Calvin & HOBBES" Calcium <8 Hematocrit ↓ >10% O2 arterial (PaO2) <60 ↑ BUN >5 Base deficit >4 Sequestration of fluid >6L |
|
|
What is the treatment for gastric cancer?
|
Distal 1/3 = subtotal gastrectomy + chemo/radiation
Middle/upper stomach = total gastrectomy + chemo/radiation |
|
|
What is the most sensitive and specific lab test for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis?
|
low fecal elastase level
|
|
|
What is the treatment for chronic pancreatitis?
|
stop alcohol consumption
replace pancreatic enzymes control pain |
|
|
You suspect your patient has gastric cancer. During the exam you palpate in two places for enlarged lymph nodes associated with this disease. Where will you palpate and what are the names of these enlarged nodes?
|
Left supraclavicular node - Virchows node
Periumbilical - Sister Mary Joseph's node |
|
|
A female pt has a known duodenal ulcer that has been refractory to high-dose PPI therapy. What two tests may diagnose her disease
|
think ZE syndrome
(1) fasting serum gastrin level (2) positive secretin-stimulation test |
|
|
WTQ: 45yo policeman presents to your office c/o tiredness & sleepiness. He says that his job seems tiring to him recently. It is difficult for him to get up in the morning and go to work. He goes to bed early b/c he feels tired & sleepy. 2mos ago, he was investigating a case of mass murder. He slipped on the blood on the floor, fell and hit his head. He also describes recent abdominal pain that is constant and gnawing, interfering with his sleep. His appetite is poor, he lost 15lbs over the last month. Exam is significant only for tenderness and fullness in the epigastrium. What's the likely dx?
|
Dx: Pancreatic Cancer
you missed this question, thinking he had a subdural hematoma from his fall - READ CAREFULLY, you ignored all the abd signs!! notes: Pancreatic cancer classically presents insidiously with a combination of constant visceral epigastric pain radiating to the back, jaundice due to extrahepatic biliary obstruction and anorexia with weight loss. |
|
|
which study design:
Identifies TWO groups: diseased group & healthy group. Retrospectively compares them. Weakened by recall & selection bias |
Case control study
|
|
|
which study design:
Seeks to estimate disease prevalence & exposure across a population |
Cross-sectional survey
|
|
|
which study design:
Examines a collection of studies on a given subject |
Meta-analysis
|
|
|
which study design:
Prospective blinded study involving placebos, existing therapies, and experimental interventions |
Randomized control trial
|
|
|
which study design:
Focuses on ONE group with shared exposure or disease & either prospectively or retrospectively compares them |
Cohort study
|
|
|
which study design:
Examines a collection of cases to seek insight into disease of interest. Useful in rare diseases |
Case series
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Memory errors produce incorrect data |
Recall bias
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Subject awareness of being studied alters their answers and behavior from normal |
Observational bias
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Certain medical studies attract subjects with particular medical histories rather than general population |
Self-selection bias
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Studies that show a difference are preferably published & then later included in meta-analysis rather than studies that support the null hypothesis |
Publication bias
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Screening tests designed to detect asymptomatic disease may miss rapidly progressive disease because the interval btw successive screenings only detects slowly progressive ones |
Length-time bias
|
|
|
Which type of bias:
Screening test may allow earlier diagnosis of disease but does not translate into actual length of survival |
Lead-time bias
|
|
|
What does an odds ratio estimate in the case of a disease with low prevalence?
|
Relative risk
|
|
|
Live births/ 1000 population
|
Birth rate
|
|
|
Live births/1000 population of women 15-45 yr
|
Fertility rate
|
|
|
Deaths / 1000 population
|
Death rate
|
|
|
Neonatal deaths (first 28 days of life)/ 1000 live births
|
Neonatal mortality rate
|
|
|
Neonatal deaths + still births/ 1000 total births
|
Perinatal mortality rate
|
|
|
Deaths (from 0-1 yo)/ 1000 live births
|
Infant mortality rate
|
|
|
Maternal pregnancy- related deaths (deaths while pregnant or in first 42 days after delivery)/ 1000 live births
|
Maternal mortality rate
|
|
|
what is Attributable risk (AR)?
|
AR= incidence of disease in the exposed group – incidence of disease in the unexposed group
Example: in a population of smokers, 5% have pneumonia. In a population of non-smokers, only 1% has pneumonia. The attributable risk of smoking to pneumonia is 4% |
|
|
what is Number Needed to Treat (NNT)?
|
NNT = 1/ absolute risk reduction (ARR)
Number of patients you would need to treat in order to save/ affect one life Important number to help determine if a drug should be used or is cost-effective Example: if out of 10,000 pts that took t-PA during a STEMI, 100 were saved by the t-PA then the NNT is 100. In other words, you would need to treat 100 pts in order to save/affect 1 life |
|
|
what is Confidence interval?
|
A range of values in which the examiner can be (90%, 95%, 99%) confident that the value obtained from the study truly reflects reality
The confidence interval rand = mean +/- (Z x SEM) If a 90% confidence interval is desired, then use Z = 1.645 95% → Z = 1.96 99% → Z = 2.57 |
|
|
What is the absolute risk reduction (ARR) in the following? Pt group A given β-blockers after MI had 66% survival, and pt group B not given β-blockers had 50% survival.
|
ARR = 15%
|
|
|
What is a null hypothesis?
|
Assumes that a particular exposure has no effect on the disease
|
|
|
What is type I error?
|
Null hypothesis is rejected even though it is true
|
|
|
What is type II error?
|
A false null hypothesis is accepted as truth
|
|
|
A study shows that taking 325mg of aspirin a day has no effect on ischemic cardiac events. What type of error is this?
|
Type II error
|
|
|
What is the formula for positive predictive value (PPV)?
|
A/ A + B
|
|
|
What is the formula for negative likelihood ratio (NLR)?
|
(1-sensitivity) / specificity
|
|
|
What is the number needed to treat (NNT) if an intervention offers an absolute risk reduction (ARR) of 15?
|
NNT = 1/15
|
|
|
What is most imp in a screening test? In a confirmatory test?
|
Screening → high sensitivity
Confirmatory → high specificity |
|
|
HYQ: The mother of an adolescent boy wants you to ask her son (your patient) if he is gay. How do you proceed?
|
Tell the mother you are happy to talk to her son but you will respect confidentiality if her son wants it to remain confidential
|
|
|
HYQ: A teenage boy wants to ask you some questions about masturbation. What should this discussion entail?
|
Tell them masturbation is common, dispel myths (won’t lead to pregnancy, STDs…)
|
|
|
HYQ: The family of a malnourished elderly woman with multiple chronic medical problems, who resides in a local nursing home, asks you for advice on options to feed her. What ethical factors need to be considered?
|
Is she competent? Are the options medically futile?
|
|
|
What are the 4 elements of a malpractice claim?
|
Duty of care: a legal obligation to conform to a reasonable standard of care
Breech of duty: failure to conform to the standard of care Harm: injury or harm to the plaintiff Causation: the breech of duty was the legal cause of the injury or harm |
|
|
HYQ: What are the 2 ways that the standard of care can be established in a malpractice case?
|
Expert testimony
Res Ipas Loquitur |
|
|
A surgical sponge is left behind in patient’s abdomen following a laparotomy. The hospital, surgeon, the scrub nurse, and the circulating nurses are all named in the subsequent malpractive suit. The surgeon claims that the scrub nurse is responsible for making sure that the sponge count was correct. Does this free him from legal liability?
|
NO – supervisors are held responsible for subordinates (viscarious liability)
|
|
|
What must be communicated to a pt in order for him to be considered informed to give consent?
|
What the procedure/ therapy offered is & why it is indicated
What is hoped to be gained by intervention Risks associated with intervention Other options & their benefits |
|
|
When is it OK to withhold information from a pt?
|
Never (almost)
|
|
|
Where is euthanasia legal?
|
No where in the US (Oregon)
|
|
|
Why can a heavily intoxicated pt refusing medical intervention be treated against his will temporarily?
|
Heavily intoxicated = not competent
|
|
|
A pt has a living will that states he does not want to be placed on a ventilator. His wife tells you to place him on the ventilator for one week and then remove it if he is not improving. What should you do in this scenario?
|
No ventilation – follow the living will
|
|
|
In what scenarios does an unemancipated minor not require parental consent for treatment?
|
Emergency situations
STD Pregnancy Wants contraception Illicit drug treatment or counseling |
|
|
HYQ: Assuming a normal bell shaped distribution, what percentage of the study population falls within 1 standard deviation, 2 standard deviations, and 3 standard deviations from the mean?
|
68%, 95%, 99.7%
|
|
|
What is the equation for odds ratio (OR)? What is the equation for relative risk (RR)?
|
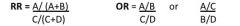
|
|
|
HYQ: When is the odds ratio a good approximation of relative risk (RR)?
|
If the disease is not common in the population
|
|
|
What does it mean when the relative risk is equal to one?
|
No association btw risk factors & disease
|
|
|
What should you do in the case of a child’s parents refusing a clearly life-saving treatment for their child in an emergency situation?
|
Can treat without parental consent, get court order later
|
|
|
Under what circumstances are you allowed to break confidentiality with a patient?
|
Patient permission, reportable disease, suicidal or homicidal
Penetrating assault wound with law |
|
|
A cancer patient is emergently intubated in the ER after a motor vehicle accident. The patient’s family brings you a DNR signed by the patient stating that she does not wish to be intubated. What do you do next?
|
Extubate
|
|
|
A patient tells you she does not want to know the result of her recent lung biopsy, but the family is begging you to tell them. Who do you tell the result to ?
|
No one
|
|

What equations represent sensitivity, specificity, positive & negative predictive value using antibodies to X to detect disease X?
|
see notes
|

