![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
245 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What complication may arise from performing an LP in a pt with ↑ ICP?
|
Uncal herniation
|
|
|
A child presents to the ER with mental status changes, hypoglycemia, and lesions suggestive of chickenpox. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
reye's syndrome
|
|
|
What is the most effective way to prevent bacterial meningitis in newborns?
|
Prevent Group B Strep (GBS) exposure – give Penicillin or ampicillin to mom during labor
|
|
|
How do the symptoms of encephalitis differ from that of meningitis?
|
Encephalitis = altered mental status & focal neurologic defects
Meningitis = neither of these |
|
|
What is the initial radiologic study in a pt with TIA/stroke symptoms? What radiologic studies need to be performed later to evaluate the underlying cause of the TIA/stroke?
|
Initial study: CT head without contrast
Then: Carotid duplex, echocardiogram, MRA, CTA |
|
|
What are the symptoms of a basilar artery stroke?
|
Cranial nerve defects
AMS/ coma Contralateral full body weakness and ↓ sensation Vertigo, loss of coordination Difficulty speaking, visual changes |
|
|
What is the treatment for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by lithium toxicity?
|
Hydrochlorothizide + amiloride
|
|
|
How do the features of acute dystonia differ from tardive dyskinesia?
|
Acute dystonia: neck spasm (torticollis)
Tardive dyskinesia: repetitive facial movements |
|
|
How does the treatment of acute dystonia differ from that of tardive dyskinesia?
|
Acute dystonia: diphenhydramine, benztropine
Tardive dyskinesia: d/c neuroleptic or change to one with lower potency |
|
|
What EEG pattern is seen in cases of absence seizures?
|
3 cycles/sec spike & wave pattern
|
|
|
What medications are used in the management of Parkinson’s symptoms?
|
Levodopa + carbidopa
Selegiline (MAO-B inhibitor) used in early disease and has neuroprotective effects Dopamine agonists: Bromocriptine (ergot compound) Non-ergot D3 stimulators – Pramipexole, Ropinirole, Rotigotine (transdermal) Apomorphine (subQ) – rescue therapy for sudden akinetic episodes COMT inhibitors: to potentiate levodopa – Entacapone, Tolcapone Anticholinergics: for tremor – Trihexyphenidyl, Benztropine Amantidine: to ↑ dopamine release, used as short-term monotherapy in mild disease |
|
|
What are the characteristic features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig’s disease)?
|
Weakness, but NORMAL sensation
Initial presenting symptoms: Asymmetric limb weakness (80%) in hands/fingers, shoulder girdle, foot drop, or pelvic girdle Dysarthria, dysphagia Upper motor neuron s/s: movement stiffness, slowness, and incoordination; spasticity and hyperreflexia (spastic paralysis); slowed rapid alternating movements; gait disorder Bulbar UMN s/s: dysarthria, dysphagia, pseudobulbar affect (PBA) with inappropriate laughing, crying, or yawning Lower motor neuron s/s: weakness, gait disorder, reduced reflexes (flaccid paralysis), muscle atrophy and fasciculations Cognitive defects: frontotemporal executive dysfunction Neuromuscular respiratory failure after months-yrs (avg survival from time of diagnosis is 3-5 yrs) |
|
|
What are the “C’s” of Huntington’s Chorea?
|
CAG repeat disorder on chromosome Cuatro (4)
Caudate and putamen atrophy on MRI ↓ ACh ↓ GABA Crazy (dementia) Choreoform movements Cuarenta (40) = age of onset |
|
|
What are the classic symptoms of Parkinson’s?
|
Resting tremor
Cogwheel rigidity Shuffling gait Mask-like facies Postural instability |
|
|
What medication is mot commonly used to treat Parkinson’s?
|
Levodopa + carbidopa (↑ dosage with progression of disease)
|
|
|
Overall, what are the key symptoms in the initial presentation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)?
|
Asymmetric limb weakness (hands, shoulder girdle, foot drop)
Dysarthria, dysphagia |
|
|
What will an electromyogram reveal in ALS?
|
Widespread muscular degeneration & motor block
|
|
|
What medication is used to treat ALS?
|
Riluzole (may slow progression)
|
|
|
What is the life expectancy once a pt is diagnosed with ALS?
|
3-5 yrs from diagnosis
|
|
|
What are the major symptoms of Huntington’s disease?
|
Chorea & cognitive dysfunction/ decline beginning in midlife
|
|
|
What drugs may be used to treat Huntington’s disease?
|
Neuroleptics, Dopamine antagonists
Tetrabenazine |
|
|
What are the unique features of dementia caused by Pick’s disease (aka Fronto-temporal dementia)
|
Dementia +
behavior changes personality changes progressive aphasia |
|
|
What are the unique features of Lewy Body dementia?
|
Dementia +
Parkinsonian features visual hallucinations repeated unexpected falls |
|
|
What are the usual components of a “dementia work-up”?
|
- Note: Alzheimer’s = diagnosis of exclusion
- mini mental status exam (MMSE) - CBC - UA - CMP - Ca2+ - RPR - HIV - TSH - B12 - CT/MRI of head |
|
|
What drugs are helpful in treating Alzheimer’s Disease?
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors – Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine
Vit E may help Memantine – may improve symptoms |
|
|
How does one differentiate btw vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease?
|
brain MRI
|
|
|
What are the differing presentations of Alzheimer’s dementia, Pick’s disease, and Lewy body dementia?
|
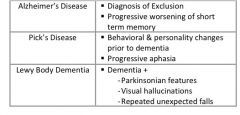
see above
|
|
|
What are 2 symptoms that should clue you in to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS)?
|
(1) Unilateral optic neuritis presents as diminished visual acuity in the central field of vision. These symptoms can be mild or may progress to severe visual loss. Periorbital pain (aggravated by eye movement) often precedes or accompanies the visual loss.
(2) Internuclear opthalmoplegia (affected eye cannot adduct due to lesion in ipsilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus) pt presents with diplopia - Prominent nystagmus is often observed in the abducting eye = Marcus Gunn Pupil |
|
|
What LP finding is diagnostic of MS?
|
CSF shows ↑ protein, mildly ↑ WBCs, oligoclonal bands, ↑IgG
|
|
|
WTQ that you missed:
36yo F is brought to the ED due to paraplegia and bladder incontinence. She immediately tells you that she has "multiple sclerosis in remission". She has a h/o optic neuritis and internuclear ophthalmoplegia, and both resolved with treatment. At that time, MRI showed plaques in the periventricular region. She is currently not taking any medications. What is the most appropriate treatment at this time? |
Corticosteroids (NOT interferon!)
Notes: Acute exacerbations of MS are treated with corticosteroids. Beta-interferon or glatiramer acetate are used to decrease the frequency of exacerbations in pts with relapsing-remitting or secondary progressive form of MS |
|
|
What will the brain MRI in an MS pt show?
|
Multiple asymmetric white matter lesions
|
|
|
What important neuronal tract is the first to be compressed and compromised in the case of syringomyelia?
|
Spinothalamic tract (pain & temp)
|
|
|
What is the cause of and treatment for Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
|
Cause: antibodies to presynaptic Ca2+ channels secondary to paraneoplastic syndrome
Tx: immunosuppressive agents & plasmapheresis |
|
|
What is required to make the diagnosis of Bell’s palsy?
|
It’s a clinical diagnosis
Diffuse involvement of the entire facial nerve → facial muscle paralysis (upper and lower) R/O Lyme disease by history: tick bite, heart block, arthritis, vertigo, hearing loss R/O otitis media by inspecting the TM R/O stroke by neurological defects Acute onset (1-2 dys) → progressively worsening weakness for 3 weeks → recovery w/in 6 months Anything other than the above presentation requires imaging (CT and/or MRI) and screening blood tests to r/o other pathology |
|
|
What is the treatment for Bell’s palsy?
|
Eye care to prevent corneal trauma
Artifical tears hourly while awake Lubricating ointment qHS Patch covering the eye at night Glucocorticoids (ie Prednisone 60mg daily x 1 week) +/- Valacyclovir 100mg tid x 1 week (acyclovir provides no additional benefit over glucocorticoids) |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
|
Symmetric muscle weakness that progresses over days to 4 weeks (usually 2 weeks)
Usually beginning in the distal legs but may begin in the arms or facial muscles in 10% of cases Respiratory muscle paralysis requiring mechanical ventilation in 30% of cases Facial muscle paralysis and/or oropharyngeal weakness in 50% which may include bilateral facial muscle paralysis Autonomic dysfunction in 70% - usually tachycardia Absent or depressed deep tendon reflexes Little if any change in sensation No fever at onset of symptoms GBS may be preceded by Campylobacter jejuni diarrheal illness (about 20% of cases), HIV infection, CMV or EBV infection, Mycoplasma infection, orther viral illness, or immunization (extremely rare) |
|
|
What’s the prognosis of a pt with Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)?
|
Spontaneous regression & complete recovery by 1 yr in 80-90%
Relapse in 10% Prolonged disease (delayed/incomplete recovery) in 5-10% Death despite ICU care in 5% |
|
|
What is the treatment of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)?
|
Hospitalization for respiratory monitoring including vital capacity, BP monitoring, cardiac monitoring (telemetry), and daily abdominal auscultation for ileus
Mechanical ventilation required in 30% of pts ICU monitoring for auronomic dysfunction required in 20% of pts Plasmapheresis or IVIG Equally effective at shortening time to independent walking by 50% Combining the two offers no additional benefit (Steroids are NOT recommended in the treatment of GBS. Previously the mainstay of therapy – but new studies show absolutely no benefit) if neuropathic pain (40-50% → gabapentin or carbamazepine if ileus → erythromycin or neostigmine if hypotensive episodes → fluids +/- phenylephrine (avoid drugs with hypotensive SE) physical therapy for rehabilitation |
|
|
HYQ: What causes slowing of nerve conduction velocity?
|
Demyelination
|
|
|
HYQ: What causes fasciculations and fibrillations at rest on EMG?
|
LMN lesion
|
|
|
HYQ: What causes a silent EMG at rest (no muscle activity) and a decrease in the amplitude of muscle contraction on stimulation?
|
Intrinsic muscle disease
|
|
|
What are the different etiologies of Bell's Palsy?
|
Bell’s Palsy: “my Lovely BELL Had An STD”
- Lyme disease - Herpes Zoster - AIDs - Sarcoidosis - Tumors - Diabetes |
|
|
How does Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LES) differ from Myasthenia Gravis (MG) on history & physical exam?
|
Lambert-Eaton: weakness ↓ with use
Myasthenia Gravis: weakness worse with use |
|
|
What are common symptoms of Myastenia Gravis (MG)?
|
Ptosis
Diplopia Dysphagia (worse at end of day) |
|
|
What test can help diagnose Myasthenia Gravis (MG)?
|
Tensilon Test (Edrophonium administered)
|
|
|
How does Edrophonium, neostigmine, pyridostigmine work in the treatment of Myasthenia Gravis (MG)?
|
Edrophonium: short acting, used in diagnosis
Neostigmine: used in treatment PrRIDostigmine: used to treat (longer acting) Gets “RID” of MG |
|
|
How can Bell’s palsy be easily differentiated from a motor cortex stroke?
|
Bell’s: complete unilateral facial paralysis
Stroke: unilateral lower facial paralysis |
|
|
What is a classic presentation of GBS?
|
Ascending paralysis presenting after a recent viral illness
|
|
|
How do you treat GBS?
|
Supportive care
Plasmapheresis IVIG |
|
|
Compare changes in sleep patterns of the elderly to changes in sleep patterns seen in depressed pts:
|
Depressed: ↓ slow wave sleep (↓ stage 3& 4), ↑ REM sleep, less time to get into REM sleep
Elderly: ↓ REM sleep, ↑ time to get to REM, ↓ slow wave sleep (↓ stage 3&4) |
|
|
What are the differences btw nightmares vs night terrors?
|
Nightmares: during REM sleep, pts that appear to wake-up are actually awake
Night Terrors: during non-REM sleep, pts that appear awake (and are frightened/ screaming, tachycardic, and diaphoretic) are actually not fully awake, difficult to arose, and usually fall right back to sleep after the episode |
|
|
What is Pickwickian syndrome?
|
obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) – characterized by
Hypersomnolence dyspnea hypoxemia → resulting in cyanosis, polycythemia, and plethora pulmonary hypertension → leading to right-sided heart failure → peripheral edema |
|
|
What is required to make the diagnosis of narcolepsy?
|
Cataplexy (sudden loss of muscle tone) only occurs in narcolepsy and is virtually diagnostic when present
other causes of excessive daytime sleepiness are ruled-out overnight polysomnogram (to r/o OSA and periodic limb movement disorder) R/O sedating medications as a cause Multiple sleep latency test – when given 4-5 opportunities to nap every 2 hrs, narcolepsy pts fall asleep in less than 8min |
|
|
What is the treatment for narcolepsy?
|
Avoidance of drugs that cause sleepiness
Scheduled naps (once or twice a day for 10-20min) Stimulants – Modafinil is 1st line Support group attendance If cataplexy → venlafaxine, fluoxetine, atomoxetine |
|
|
What medications are common in the treatment of insomnia? What makes each one unique?
|
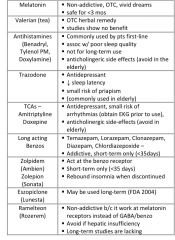
see above
|
|
|
Explain restless leg syndrome
what's the treatment? |
The sensation of unpleasant paresthesias that compels the pt to have voluntary, spontaneous, continuous leg movements that temporarily relieves the sensations. The discomfort worsens at rest, in the evening, and/or during sleep. Sensation of “spiders or ants” on/in feet/calf muscles
Usually a primary, idiopathic disorder Secondary RLS can result from iron deficiency, end-stage renal disease, diabetic neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, pregnancy, rheumatic diseases (RA), varicose veins, caffeine intake … Treatment: Pramipexole or Ropinirole qHS (or levodopa/carbidopa), iron replacement, avoid caffeine, clonazepam qHS, gabapentin, opioids |
|
|
What kind of tumor is the most common brain tumor?
|
Metastatic cancer (#1 Lung – #2 Breast- #3 Melanoma)
|
|
|
Are Adult brain tumors most often supra- or infra- tentorial?
|
Adults = supratentorial, kids = infratentorial
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common primary brain tumors in adults?
|
“MGM Studios”
Meningioma Glioblastoma multiforme (most common) |
|
|
What are the 3 most common primary brain tumors in kids?
|
(1) Astrocytoma – mc tumor, curable if completely reseted
(2) Medulloblastoma – mc malignant tumor in kids (3) Ependymomas |
|
|
What are imp characteristics of Neurofibromatosis type 1?
|
Café-au-lait spots
Freckling of axilla & inguinal areas Lisch nodules Neurofibromas |
|
|
Benzodiazepines increase which stage of sleep at the expense of what other stages of sleep?
|
↑ stage 2
↓ stage 3 & 4 |
|
|
What is the symptom that, when present, cinches the diagnosis of narcolepsy?
|
Cataplexy
|
|
|
A pt comes to your office c/o feeling like “bugs are crawling on or in her legs”. This sensation is relieved by movement of her legs but doing so interferes with her sleep. What are some treatment options for this pt?
|
Dx: Restless leg syndrome
Treatment options: Dopamine agonists: Pramipexole, Ropinirole Levodopa/ carbidopa Iron replacement Caffiene avoidance Clonazepam Gabapentin Opioids |
|
|
What are the different causes of syncope?
|
Causes (↓ cerebral perfusion)
Reflex syncope Vasovagal: a/w emotional stress, trauma, pain, sight of blood, prolonged standing Situational: a/w micturition, defecation, coughing, GI Stimulation Carotid-sinus hypersensitivity: a/w head-turning, shaving, tight collar Cardiogenic: a/w exertion, palpitations, CP, SOB Orthostatic Cerebrovascular: a/w prolonged LOC, seizures, neuro deficits No cause will be found in at least 20% of pts. If hospitalized previously for syncope and no cause was found, then less than 15% chance of identifying cause on subsequent hospitalizations |
|
|
What is the basic work-up for syncope?
|
Work-up basics:
r/o orthostatic hypotension via Tilt test on multiple occasions (ie 30 min after meals, 0200, before and after BP meds given) r/o seizure by H&P more likely seizure: h/o seizure, prodrome of déjà vu, postictal confusion, tongue lacerations more likely syncope: prodrome of lightheadedness or sweating, h/o prolonged standing nonspecific: brief limb jerking (15% of syncope pts), urine incontinence CBC, electrolytes, BUN/Cr. Glucose, assess volume status, pulse ox, EKG, evaluation of medications In pts over 40 (without h/o carotid disease or carotid bruits) r/o carotid sinus hypersensitivity with carotid sinus massage while on tele monitor. Massage one carotid at the angle of the jaw with circular motion for about 5 seconds. Perform supine then with head of bed elevated. Positive test is symptoms reproduced, SBP falls >49mmHg, or asystole > 3 seconds Also consider: Serial CEs and EKGs x3 (esp if >45 yrs old, DM, smoker, prior MI, or >2-3 risk factors) Echo (esp if murmur, exertional syncope, or h/o heart dz) Cardiac stress test Bilateral carotid duplex (esp if >65 yrs old, CAD, PVD, bruit) 24 hour Holter monitor (esp if abnormal EKG, palpitations, heart disease, or FHx of sudden death) CT head without contrast, EEG (esp if neurologic symptoms, new seizure, HA) |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for a pt presenting to the ER for loss of consciousness?
|
“AEIOU TIPS”
Alcohol Epilepsy/ Environment Insulin Overdose/ Opioids Uremia (electrolyte disturbances) Trauma Infection Psychogenic Stroke |
|
|
What should you think about for initial empiric therapy in a pt coming into the ER with loss of consciousness?
|
Glucose, Thiamine, Naloxone
|
|
|
Why is thiamine given in a glucose infusion to alcoholics with hypoglycemia?
|
Glucose administration in the absence of thiamine can theoretically exacerbate damage to the mammillary bodies and worsen Wernicke’s encephalopathy
|
|
|
What measurements make for a (+) Tilt test?
|
Measurements made while standing:
↑ HR >20 bpm ↓ SBP > 20 mmHg ↓ DBP > 10 mmHg |
|
|
What is the most common cause of syncope?
|
Vasovagal response
|
|
|
In an intact brainstem, the pt’s eye should move in which direction with ice water infusion into an ear canal?
|
Toward the ear receiving the ice water
|
|
|
What are the elbows doing in decorticate posturing?
|
Flexing
|
|
|
A pt is brought into the ER with loss of consciousness. What do you give before starting empiring glucose administration?
|
Thiamine
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope if it occurred while shaving?
|
carotid sinus hypersensitivity
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope if it occurred while singing in a choir concert?
|
vasovagal (prolonged standing)
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope if pt has a (+) tilt test after taking BP meds?
|
orthostatic hypotension
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope if pt has a prolonged loss of consciousness?
|
cerebrovascular
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope if it was preceded by palpitations?
|
cardiogenic
|
|
|
Whats the likely cause of syncope in a Type I diabetic pt
|
hypoglycemic
|
|
|
HYQ: Lung cancer accompanied by muscle weakness is indicative of what?
|
Lambert-Eaton Syndrome (most common 2° small cell cancer of lung)
|
|
|
HYQ: A 66yo F with forgetfulness and decreased bilateral parietal lobe activity on PET scan has what form of dementia?
|
Alzheimer’s Dementia
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the most sensitive test for multiple sclerosis?
|
MRI of head & orbits
|
|
|
HYQ: What medication decreases the frequency of relapses in pts with multiple sclerosis (MS)?
|
Interferon-β
Glatiramer |
|
|
HYQ: A 35yo F presents with ptosis and diplopia that worsens throughout the day. What is the underlying problem?
|
Dx: Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
Pathophysiology: antibodies to ACh receptor at the neuromuscular junction |
|
|
HYQ: What is the MOA of the preferred medication in the treatment of restless leg syndrome?
|
Dopamine agonists
|
|
|
What EEG waveforms correspond to the different stages of sleep?
|
Stage 1: theta
Stage 2: sleep spindles & K+ complexes Stage 3 & 4: Delta REM: beta |
|
|
What is the next step once a brain tumor has been identified on CT or MRI of the head?
|
Full body CT scan
Bone Scan |
|
|
What are the treatment options for benign essential tremor?
|
β-blockers
Benzos Primidone Thalamotomy Deep brain stimulation |
|
|
WTQ that you missed:
54yo M presents to the office with several months h/o hand tremors that are unresponsive to OTC medication. The tremors always become worse when he is in public places. Sometimes, the hand tremors are so bad that he is unable to grasp. He denies trauma, fever, loss of muscle function or any prior stroke. His PMHx is significant for vague abdominal pains, the cause of which was never found. He is given some medication. A month later, he comes back and says, "the tremor is gone, but now I have colicky abdominal pain, confusion, headaches, hallucinations, and dizziness". What is the medication that the pt was given that caused this pt's new symptoms? |
Primidone
Propanolol & Primidone are used to treat essential tremors. Primidone is an anticonvulsant that converts into phenylethylmalonamide & phenobarbital. The administration of primidone can precipitate acute intermittent porphyria, which manifests as abd pain, neurologic & psychiatric abnormalities (as seen in this pt). It can be diagnosed by checking for urine porphobilinogen |
|
|
What medications are used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease?
|
Cholinesterase inhibitors: Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine
NMDA receptor blocker: Memantine |
|
|
What test is used to confirm the most common cause of syncope?
|
Tilt table test
|
|
|
Describe what light reflexes will be seen in both eyes if the right optic nerve is damaged prior to the pretectal nucleus (aka afferent defect)
|
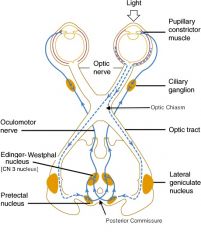
No constriction of either the left or right eye when light is shone in the right eye
Both pupils constrict if the light is shone in the left eye |
|
|
Describe what light reflexes will be seen in both eyes if the right oculomotor nerve is damaged (aka efferent defect)
|
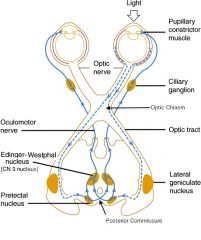
Right eye will not respond to light shone in either eye
Left eye will constrict when a light is shone in either eye |
|
|
What is amblyopia and what are the signs/symptoms?
|
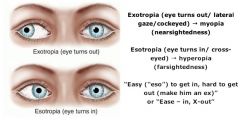
↓ vision due to a disruption in the normal development of vision usually from strabismus, cataracts, or refractive error prior to age 10
possible presentations: esotropia (inward deviation), exotropia (outward deviation), diplopia and/or refractive error not correctable with lenses |
|
|
What is the most common cause of blindness in the following populations of adults in the US?
|
Over age 55 → macular degeneration
Under age 55 → diabetes mellitus Blacks of any age → glaucoma |
|
|
What are the distinguishing features of bacterial, viral, and allergic conjunctivitis?
|
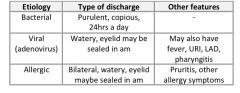
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
May indicate a collagen-vascular disorder |
Uveitis
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
Potential serious complication of corneal ulceration |
Herpes simplex keratitis
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
Colored halos |
Acute angle closure glaucoma
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
Itching eye |
Allergic conjunctivitis
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
Preauricular lymph node enlargement |
Viral
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
“dry eyes” |
Sjogren’s Syndrome
|
|
|
What cause of red eye most closely matches the statement:
Shallow anterior chamber |
Acute angle closure glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of conjunctivitis appearing in the first 24 hrs of life?
|
Chemical conjunctivitis
|
|
|
What are the classic features that distinguish orbital cellulitis from periorbital cellulitis?
|
Orbital: proptosis, opthalmoplegia, ↓ vision, double vision, pain with movement
(orbital involves the eye & more serious than periorbital) |
|
|
What is the treatment for orbital cellulitis?
|
Immediate IV Vancomycin + IV cefotaxime (or ceftriaxone) until afebrile and clinically improved (3-5days) then oral antibiotics (based on sensitivity) for 2-3 weeks
Consult ophthalmology and ENT for recommendations and consideration for need of surgical debridement |
|
|
What are the diff btw a chalazion, hordeolum & anterior blepharitis? What is the treatment for each?
|
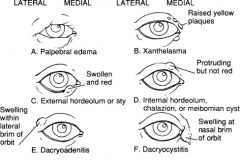
Chalazion: Inflammation of internal Meibomian sebaceous glands (eyelid swelling)
Tx: Usually self-limiting but can be tx with surgical excision and/or intralesional steroid injection Hordeolum: Infection of external sebaceous glands of Zeiss or Mol (tender, red swelling at the lid margin) Tx: how compress 3-4x/day for 10-15 min If unresolved in 48hrs, then I&D +/- antibiotic ointment q3hrs Anterior Blepharitis: infection of eyelids & lashes secondary to seborrhea (red, swollen lid margins + dandruff on lashes) Tx: wash lid margins daily with shampoo Removal scales daily with cotton ball Antibiotic ointment qd to lid margins |
|
|
How does damage to the right optic nerve (CN 2) present differently than damage to the right oculomotor nerve (CN 3)?
|
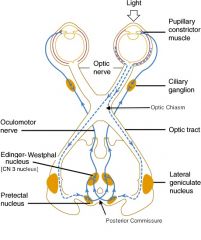
Damage to Right CN 3 (Oculomotor n)
Shine light into right pupil → constriction only of L pupil Shine light into left pupil → left pupil will constrict Damage to Right CN 2 (Optic n) Shine light into right pupil → no constriction of right or left pupil Shine light into left pupil → BOTH pupils will constrict |
|
|
Does strabismus cause amblyopia or does amblyopia cause strabismus?
|
Strabismus causes amblyopia
|
|
|
Does viral conjunctivitis form pus?
|
Yes, but not as much as bacteria
|
|
|
Compression or lesion of the sympathetic trunk will give a cluster of symptoms collectively known as Horner’s syndrome. What are those symptoms? What is the classic cause?
|
S/S: miosis, anhidrosis, ptosis of the eyelid
Cause: tumor in the apex of the lung (Pancoast’s tumor) |
|
|
A pt c/o watery, red, itchy eyes. On exam you notice evidence of mild pharyngitis. What might be the cause of her condition?
|
Adenovirus or allergies
|
|
|
What important diseases are assoc with uveitis?
|
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): Chrohn’s Disease & Ulcerative Colitis
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) Ankylosing spondylitis |
|
|
On morning OB/GYN rounds, a very concerned new mother asks you about her 12 hr newborn’s red eyes. What is the likely reason for the baby’s red eyes?
|
Chemical irritation from antibiotic drops
|
|
|
What is the classic presentation of a pt that has a cataract?
|
Painless, progressive ↓ in vision manifested with difficulty driving at night, reading road signs, or reading fine-print
Usually bilateral, but often unilateral Near-sightedness is often an early manifestation Possible disabling glare in bright sunlight or from oncoming headlights (more likely with steroid induced cataracts) |
|
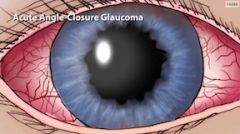
What is the treatment for acute angle-closure glaucoma?
|

|
|
|
What is the treatment for a corneal abrasion?
|

|
|
|
What disease would you suspect in a 35yr old F with new-onset rapid loss of vision and pain when moving the eye? Tx?
|
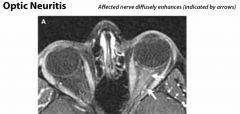
Dx: optic neuritis of multiple sclerosis
Tx: IV steroids |
|
|
What eye abnormalities might be seen in pt with Vit A def?
|
Night blindness or complete blindness
Xerothalmia Bitot’s spots (areas of abnormal squamous cell proliferation and keratinization of the conjunctiva) |
|
|
During a yearly physical, a middle aged man jokes that he needs to buy some reading glasses b/c he is having difficulty reading fine print. He also notes that he has trouble driving at night and reading road signs. Though the pt may have some presbyopia, for what else should you examine him?
|
Cataracts
|
|
|
What is the pattern of vision loss in open angle glaucoma?
|
From peripheral → central (tunnel vision)
|
|
|
What is the major exam finding in open angle glaucoma?
|
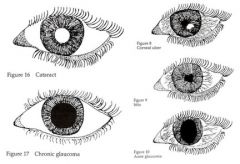
Cup to optic disc ratio > 50%
|
|
|
What are some major exam findings in open angle glaucoma?
|
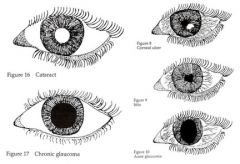
Severe eye pain, Red, inflamed eye
Hard orbit, Dilated pupil |
|
|
Central to peripheral vision loss is characteristic of which type of eye pathology?
|
Macular degeneration
|
|
|
Retinal detachment occurs acutely and is painless, what does the patient experience?
|
Window shade being pulled over eye
Might see numerous floaters |
|
|
What are some things that would be seen on funduscopic exam of a pt suspected of having retinal vessel occlusion?
|
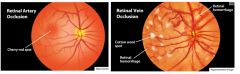
Retinal artery occlusion → cherry red spot
Retinal vein occlusion → cotton wool spot, retinal hemorrhages |
|
|
What are the causes of a cherry red spot seen on funduscopic exam?
|
Retinal artery occlusion
Niemann-Pick Disease, Tay-Sachs disease |
|
|
What medication can be given for both glaucoma & altitude sickness?
|
acetozolamide
|
|
|
When is observation without antibiotics appropriate for a child with acute otitis media?
|
According to the 2004 AAP/AAFP guidelines you may refrain from antibiotics & simply observe if:
Age 6mos – 2yrs + dx is questionable + illness is not severe + appropriate f/u available + ABX can be started promptly if symptoms worsen Age > 2 + illness is not severe + appropriate f/u available + ABX can be started promptly if symptoms worsen Antibiotics should be started if improvement is not noted in 48-72hrs |
|
|
What are the classic s/s of bullous myringitis?
|
What it is: a bullous/vesicular inflammation of the tympanic membrane that may occur in a/w acute otitis media
s/s: more painful than usual acute otitis media otoscopy: large, reddish vesicle on the TM |
|
|
What is the tx for bullous myringitis?
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia is a common organism → tx with oral macrolides
Topical analgesics |
|
|
What are the diagnostic features of mastoiditis?
|
Symptoms occur days- weeks after developing AOM
Erythema, edema, tenderness behind the ear External ear displaced Diagnosis made from CT scan of the mastoid process |
|
|
Cholesteatoma
|
Def: overgrowth of desquamated keratin debris w/in the middle ear space that may eventually erode the ossicular chain and external auditory canal
Causes: negative middle ear pressure (chronic retraction pocket) from Eustachian tube dysfunction or direct growth of epithelium thru a TM perforation Commonly a/w chronic middle ear infection PE: grayish-white “pearly” lesion behind or involving the TM, conductive hearing loss, vertigo Tx: surgical removal usually tympanomastoidectomy & reconstruction of the ossicular chain |
|
|
What are the distinguishing characteristics of acute labyrinthisitis?
|
Acute onset of vertigo, N/V, and nystagmus, auditory function preserved = vestibular neuritis
Hearing loss + above symptoms = labyrinthitis Single episode that last days-weeks (usually not >2wks) Preceded by a viral URI Nystagmus: horizontal, suppressed with visual fixation, and has a fast phase away from the affected side Abnormal head thrust test: when examiner rapidly turns the pt’s head to the affected side, the pt is unable to maintain visual fixation Gait instability but preserved ambulation Absence of focal neurologic defects |
|
|
What is the tx for acute labrinthitis (vestibular neuritis)?
|
Typically subsides spontaneously w/in weeks
Corticosteroid taper shown to improve recovery (ie methylprednisolone 22 day taper, start with 80mg and taper by 20mg q3days then by 50% q3 days after 20mg reached) Symptomatic treatment only in for the first 48hrs of illness Ie scopolamine patch, meclizine, metoclopramide, or promethazine Long-term recovery is theoretically delayed if used long-term Vestibular rehabilitation exercises MRI if >60yrs, headache, focal neuro signs, vascular risk factors, or sustained vertigo inconsistent with acute labyrinthitis (vestibular neuritis) |
|
|
What is the most common cause of conductive hearing loss in adults? What is the most common cause of sensorineural?
|
Conductive → otosclerosis (otic bones become fixed)
Sensorineural → presbycusis |
|
|
What is the treatment for Ramsay Hunt syndrome?
|
Ramsey hunt syndrome is herpes zoster oticus
Narcotic analgesia for pain reflied Oral steroids to ↓ inflammation Antiviral therapy with valacyclovir (highest efficacy) famciclovir, or acyclovir (lowest cost) |
|
|
What are the important characteristics seen on otoscopic exam of a pt with otitis media?
|
Red tympanic membrane
Bulging TM with decreases mobility |
|
|
What is the next step in the evaluation of a pt with hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus after a physical exam in the clinic?
|
MRI of temporal region to r/o acoustic neuroma
|
|
|
What are the potential complications of acute otitis media?
|
Ruptured TM
Meningitis Hearing loss Bullous myringitis Mastoiditis Brain abscess Sigmoid sinus thrombosis |
|
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is caused by?
|
Dislodged otolith in semicircular canal
|
|
|
How do you fix BPPV?
|
(self-limiting) Epley’s maneuver
|
|
|
In acute labyrinthitis, a pt will have symptoms of vertigo, nystagmus, and nausea & vomiting. What other imp symptom will they have?
|
Hearing loss (but NOT tinnitus)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms in Meniere’s Disesae?
|
Vertigo, ↓ hearing, tinnitus, N/V, feeling of ear fullness
|
|
|
What cranial nerve is associated in the deficit of an acoustic neruoma (schwannoma)?
|
CN 8
|
|
|
What would you see in a pt on exam of pt with cholesteatoma?
|
Grayish-white pearly lesion
|
|
|
HYQ: A 10yo boy develops worsening arm & leg weakness over a period of 3 days that has now worsened to include symmetric facial muscle weakness. Deep tendon reflexes are absent, and sensation is intact. What is the dx?
|
Guillain Barre Syndrome
|
|
|
What would be the visual field defect for a lesion of the optic tract?
|
Homonymous hemianopia
|
|
|
What is the pattern of vision less in glaucoma vs macular degeneration?
|
Glaucoma: peripherally → centrally
Macular Deg: central loss, peripheral vision maintained |
|
|
What is the easiest way to distinguish a hordoleum form a chalazion?
|
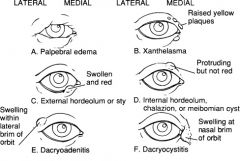
Hordeolum: swelling is at eyelid margin (acute infxn)
Chalazion: swelling is within eyelid (chronic) |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for dislocation of the lens?
|
Marfan syndrome, Homocystinuria, Alport Syndrome
|
|
|
What is the treatment for macular degeneration (MD) vs retinal detachment (RD)?
|
MD: supplementation with Vit C & E, copper, zinc
Intravitreal Ranibizumab Laser photocoagulation of lesions RD: Laser photocoagulation, cryotherapy |
|
|
Explain how the Weber test can help distinguish conductive hearing loss from sensorineural hearing loss:
|
Normally: sound heard midline
Conductive loss: sound will lateralize to affected side Sensorineural loss: sound will lateralize to unaffected side |
|
|
Which disorders are a/w cherry red spot on macula?
|
Tay-sachs, Niemann Pick, Retinal artery occlusion
|
|
|
What is the next step in the management of a pt that has sustained a chemical burn injury to the eye?
|
Wash out the eye with water!
|
|
|
What is the treatment for closed-angle glaucoma?
|
Eye drop combination of β-blockers, α-agonists, cholinergic agonists, prostaglandin analogs
Acetazolamide orally IV mannitol Laser irridotomy |
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Excessive need to be taken care of, submissive & clinging behavior, low self-confidence, fears of separation & losing support |
dependent
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Grandiosity, feels he is entitled to things, lack of empathy |
narcissistic
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Suicide attempts (→ 15% mortality), unstable mood & behavior, sense of emptiness and loneliness, impulsiveness |
borderline
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Distrustful, suspicious, litigious |
paranoid
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Lifelong voluntary social withdrawal, no pscyhosis, emotional expression is limited (restricted range of affect) |
schizoid
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Feeling of inadequacy, hypersensitive to rejection or criticism, socially inhibited, shy |
avoidant
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Constant mood of unhappiness & pessimism |
depressive
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Odd appearance, thoughts & behavior; no psychosis; social awkwardness |
schizotypal
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Controlling, perfectionistic, orderly, stubborn, indecisive |
obsessive-compulsive
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Criminality, unable to conform to social norms, disregard for others’ rights |
antisocial
|
|
|
What personality disorder fits the following statement:
Excessively dramatic, emotional, and extroverted; sexually provocative behavior, unable to maintain intimate relationships |
histrionic
|
|
|
Paranoid PD - what defense mechanism is commonly used?
|
projection
|
|
|
Borderline PD - what defense mechanism is commonly used?
|
Splitting
|
|
|
Histrionic PD - what defense mechanism is commonly used?
|
Repression
|
|
|
Obsessive-Compulsive PD (OCPD) - what defense mechanism is commonly used?
|
isolation
|
|
|
What is the difference btw obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder?
|
Personality disorders do not recognize their behavior is disruptive
|
|
|
What are the distinguishing characteristics btw antisocial personality disorder & conduct disorder?
|
Conduct disorder = diagnosed < 18yrs
|
|
|
What is the diff btw alcohol abuse & alcohol dependence?
|
Alcohol abuse: repeated alcohol use despite recurrent adverse consequences
Alcohol dependence: at least 3 of the following: tolerance, withdrawal, alcohol abuse, inability to quit, cut-back, or regulate use, great amt of time spent obtaining, using or recovering |
|
|
What treatments are effective in helping prevent relapse in recovering alcoholics?
|
Alcoholics anonymous: is the best relapse prevention
Naltrexone (Revia, Vivitrol) Disulfran (Antabuse) Topiramate (Topamax) Acamprosate (Campral) tid |
|
|
What is the tx for an extremely agitated & possible violent pt under the influence of PCP?
|

|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Post-op constipation and/or respiratory depression |
Opioid OD
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Severe depression, HA, fatigue, insomnia/ hypersomnia, hunger |
Cocaine withdrawal or amphetamine withdraw
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Pinpoint pupils, N/V, seizures |
Opioid OD
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Belligerence, impulsiveness, nystagmus, homicidal ideations, psychosis |
PCP OD
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
HA, anxiety/depression, weight gain |
Caffeine, nicotine withdrawal
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Anxiety/depression, delusions, hallucinations, flashbacks |
LSD intoxication
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Euphoria, social withdrawal, impaired judgment, hallucinations |
Marijuana intoxication
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Rebound anxiety, tremors, seizures, life-threatening |
Withdraw from alcohol, benzos, barbiturates
|
|
|
What drug is causing the following symptoms:
Anxiety, piloerection, yawning, fever, rhinorrhea, nausea, diarrhea |
Opioid withdrawal
|
|
|
A pt comes to your office after becoming dissatisfied with her former doctor. She explains to you why she has changed physicians. According to her, the former doctor is the most evil creature with absolutely no redeeming qualities. She finishes her story and remarks that she “can tell you are so smart and will cure her of all things.” What personality d/o might she have?
|
Borderline (splitting)
|
|
|
An answer of “yes” to 2 or more questions on the CAGE questionnaire indicates that a pt may have a problem with a substance such as alcohol. What does it stand for?
|
Cut Down, Annoyance, Guilt, Eye opener
|
|
|
In which vitamins are alcoholics typically deficient?
|
Thiamine, B2, B6, Folate, B12, Vit A & C
|
|
|
What is the most successful treatment for alcoholism?
|
12-step programs
|
|
|
List the symptoms a/w the life threatening condition Delirium Tremens (DT):
|
Tachycardia, HTN, Diaphoresis, Delirium, Seizures, Agitation
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the DOC for alcohol withdrawal?
|
Long acting benzodiazepines
|
|
|
What drug should be avoided in the treatment of a pt in the ER with amphetamine intoxication?
|
β-blockers (will ↑BP even more b/c you leave α1 unopposed)
|
|
|
What drugs can be used in the case of HTN in a pt with cocaine or amphetamine intoxication?
|
Benzos, Phentolamine(Oraverse, Regitine)
|
|
|
What is the antidepressant used for help with nicotine addiction?
|
Buproprion (Wellbutrin) or Varenicline (Chantix)
|
|
|
Opioids do what to the pupils?
|
Miosis (pupillary constriction) = pinpoint pupils
|
|
|
What are the treatment options for a pt with PCP intoxication?
|
Benzos +/- Haldoperidol (or other antipsychotic)
Restraints, supportive care |
|
|
Which eating disorder can be treated with SSRIs?
|
Bulimia
Note: SSRIs are not helpful in treating anorexia, but can help depression a/w anorexia |
|
|
T/F: Anorexia & bulimia both involve vomiting/purging?
|
True
|
|
|
What serum lab abnormalities may be seen in a pt with prolonged excessive vomiting/ purging?
|
↑ amylase from salivary gland inflammation
hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis |
|
|
Refeeding syndrome can result in the following:
|
***Hypophosphatemia
cardiovascular collapse, rhabdomyolysis, confusion, seizures |
|
|
What are 2 key differences btw somatization disorder and conversion disorder?
|
Conversion: sensory or motor deficits linked to a preceding stressor
Somatization: physical symptoms that are hard to “pin down” (pain, nausea, vomiting) |
|
|
Are pain medications helpful in the tx of pain syndrome?
|
No (use SSRIs or TCAs)
|
|
|
What is a major difference btw factitious/Munchausen disorder and somatization/conversion disorder?
|
Factitious: pt performs actions to bring about symptoms
Somatization/conv: symptoms from no act on pt’s part |
|
|
What are key features of delirium that differ it from dementia?
|
Delirium: alterating levels of consciousness, develops & changes rapidly over course of day, changes are attributable to meds, disease, drug use/abuse, generally reversible
|
|
|
What is the difference btw “sundowning” and delirium?
|
Sundowning seen with dementia
|
|
|
What is a common cause of delirium in the elderly?
|
UTI or Meds (Anticholinergics, Benzos, mind-altering meds)
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common causes of dementia & how do you differentiate btw them when making a diagnosis?
|
Alzheimer’s Disease (70%)
Vascular Dementia (15%) CT/MRI can help you diagnose vascular dementia |
|
|
A nurse pages you, saying that one of your elderly pts has been sleeping most of the 2 days he’s been on the unit, but is very agitated and aggressive with the nurses while awake. She aske you to write for a benzodiazepine to sedate the pt- what do you propose instead & why?
|
Dx: Delirium, which can be worsened with benzos
Tx: antipsychotics (Haloperidol) |
|
|
What disease that causes dementia is also a/w visual hallucinations and frequent falls?
|
Lewy Body Dementia
|
|
|
What disease that causes dementia is also a/w unpleasant behavioral and personality changes?
|
Pick’s Disease
|
|
|
What lab work should be obtained in a pt with a new dx of dementia to r/o secondary causes?
|
Chem 7, CBC, TSH, Vit B12, RPR, HIV
|
|
|
What comorbidities are common with ADHD in children?
|
Up to 50% of kids with ADHD have at least one comorbidity:
Oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder, learning disabilities, depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorder |
|
|
What criteria must be met before a child can be started on pharmacotherapy for ADHD?
|
Completed diagnostic assessment
Age 6 or older Parents accept the medication as appropriate School will cooperate with administration & monitoring No previous sensitivity to the chosen medication Normal HR & BP (EKG before tx is not necessary) Seizure free Absence of Tourette’s syndrome or pervasive develop delay Household does not contain substance abusers |
|
|
What other medications can be used in the tx of ADHD in kids who fail to respond to stimulants or atomoxetine?
|
TCAs, Bupropion (Wellbutrin), α-2 agonists (Clonidine)
|
|
|
What are the common complications of ADHD stimulant medications, and how are these complications managed?
|

|
|
|
What therapeutic options are available for Tourette’s disorder?
|

|
|
|
What are some of the characteristic features of autism?
|
“living in his own world”
symptoms evident prior to age 3 lack of responsiveness to others, poor eye contact, absence of social smile impairments in communication, language delay, repetitive phrases peculiar repetitive, ritualistic habits (ie spinning around, hand flapping) Fascination with specific, seemingly mundane objects (vacuum cleaners, sprinklers) Usually below-normal intelligence |
|
|
What are the characteristic features of Asperger’s syndrome?
|
Social impairment
Repetitive activities Behavior & interest abnormalities No language problems No cognitive delays |
|
|
What are the characteristic features of childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD)?
|
Regression of development in multiple areas after a period of at least 2 yrs of normal development
Regression may be seen in the areas of expressive or receptive language, social skills or adaptive behavior, bowel or bladder control, play, or motor skills CDD is an “autism spectrum disorder” which looks just like autism except for the period of normal development CDD is often a/w an organic condition such as seizures or metabolic disorder |
|
|
How is ADHD diagnosed?
|
6 symptoms of ADHD, in 2 or more settings (ie home AND school); before age of 7, impairs ability to function
|
|
|
What’s the diff btw conduct disorder & oppositional defiant disorder?
|
Conduct: blatant disregard to the feelings & rights of others (& hurts animals)
ODD: doesn’t like rules, but not harmful to others |
|
|
When treating a child suspected of having a learning disorder, what first must be investigated?
|
Hearing or vision problems
|
|
|
How is Asperger’s syndrome different from autism?
|
Asperger’s doesn’t have cognitive or language problems
|
|
|
How is childhood disintegrative disorder different than autism?
|
CDD: regression of development, multiple areas, after a period of at least 2 yrs of normal development
Often a/w organic conditions – seizures, metabolic d/o |
|
|
HYQ: What features are unique to PCP intoxication that allows you to distinguish it from LSD intoxication?
|
PCP: visual hallucinations, aggression, agitation
LSD: visual hallucintations |
|
|
HYQ: A 19yo slender F presenting with recent weight loss is found to have erythema of her turbinates and nasal septum. What is the cause of her weight loss?
|
Cocaine abuse
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the downside of adding bupropion to nicotine replacement in a pt trying to quit smoking?
|
↑ risk of severe HTN
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Females only. Loss of previously acquired purposeful hand skills btw 6-30mos |
Rett Disorder
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Impairments in social interactions, communications, play. Repetitive behaviors |
Autism
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Impairment in social interaction, no language delay |
Asperger’s
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Stereotyped hand mvmts |
Rett Disorder
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Characterized by hostility, annoyance, vindictiveness, disobedience & resentfulness |
Oppositional Defiant d/o
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Multiple motor & vocal tics |
Tourette’s
|
|
|
Name the childhood psychiatric disorder:
Impulsive and inattentive |
ADHD
|
|
|
7yo that avoids going to school to stay home with parent
|
Separation anxiety
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
Unexplained pain |
Pain disorder
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
Pt with normal anatomy is convinced a part of their anatomy is abnormal |
Body dysmorphic disorder
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
Unexplained loss of sensory or motor function. Normal exam/tests |
Conversion disorder
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
Unwavering belief by the pt that she has a specific disease (despite medical assurances) |
Hypochondriasis
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
Unexplained complaints in multiple organ systems |
Somatization disorder
|
|
|
What somatoform disorder:
False belief of being pregnant |
Pseudocyesis
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of refeeding syndrome?
|
Metabolizing fat → carbs
Hypophosphatemia, cardiovascular collapse, rhabdomyolysis, confusion, seizures |
|
|
What are the components of the CAGE questionnaire?
|
Cut down
Annoyance Guilt Eye opener |
|
|
A pt is brought to the ER by police and is restrained and exhibiting violent behavior. What OD is likely? Tx?
|
Dx: PCP OD
Tx: benzos, antipsychotic (haloperidol), dark quiet room |

