![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
169 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the tx for acute mesenteric ischemia?
|
- Hemodynamic monitoring
- Pressors - Broad spectrum antibiotics - NG tube decompression - Heparin or Enoxaparin - Papaverine - Resection of Necrotic Bowel |
|
|
When is Rifampin prophlaxis indicated in cases of bacterial meningitis?
|
pg 169
close contacts or pt is diagnosed with neisseria meningitidis or H. influenza type B |
|
|
What is the treatment for acromegaly?
|
(1) transphenoidal resection of pituitary adenoma
(2) beam radiation (3) somatostatin (4) cabergoline |
|
|
What are the most common causes of acute pancreatitis?
|
gallstones & alcohol
|
|
|
A COPD pt comes to the ER with tachycardia & hypotension. During the evaluation he begins to have seizures. What is the most likely etiology?
|
Theophylline overdose
|
|
|
What is teh ACLS tx for asystole?
|
pg 155
transcutaneous pacing CPR epinephrine |
|
|
What is the treatment for febrile seizures?
|
pg 189
↓ temperature reassurance (DONT need anti-epileptics) |
|
|
What is the empiric treatment for pneumonia in a 2 month old? in a 2 yr old?
|
2 mo old = macrolide +/- cefotaxime
2 yr old = amoxicillin or ampicillin |
|
|
What are the causes of osmotic diarrhea?
|
Malabsorptive disorders (Pancreatic insufficiency, Celiac Sprue, Whipple Disease, Tropical Sprue)
- Lactose Intolerance - Excess sorbitol (chewing 3pks gum/day) - Lactulose - Magnesium |
|
|
What are the causes of Secretory Diarrhea?
|
Hormone-related tumors (VIPomas, Gastrinomas, Medullary Thyroid Cancer, Carcinoid Tumors)
- Enterotoxigenic bacterial infections - Ileal resection |
|
|
Where in the GI tract is alcohol absorbed?
|
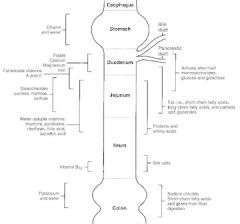
stomach
|
|
|
Where in the GI tract is Vit B12 absorbed?
|
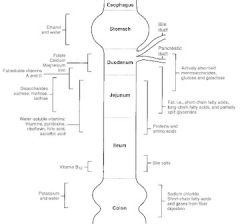
terminal ileum
|
|
|
Where in the GI tract are bile salts reabsorbed?
|
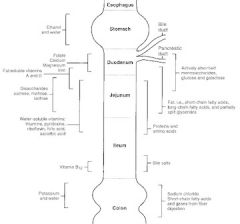
terminal ileum
|
|
|
Where in the GI tract is potassium absorbed?
|
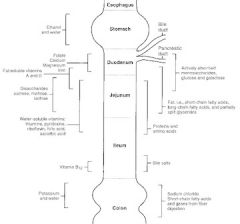
colon
|
|
|
What 2 serum markers aid in the diagnosis of Celiac sprue?
|
pg 67
anti-endomysial antibodies anti-gliadin antibodies |
|
|
What does the intestinal biopsy show in a pt with celiac sprue?
|
blunting of villi in duodenum & jejunum
|
|
|
What hematological finding commonly coincides with tropical sprue, and how do we treat this?
|
Megaloblastic anemia
tx: Folic acid supplementation |
|
|
What differentiates an intestinal biopsy of celiac sprue from one of Whipple disease?
|
celiac sprue = blunting of villi
Whipple disease = foamy macrophages (PAS stain) |
|
|
A pt is undergoing testing to identify the cause of her anemia. She was unable to absorb oral Vit B12, but when she was given B12 along with intrinsic factor, she was able to absorb the B12. What is her diagnosis?
|
(note that this was describing the Schilling test)
Dx: Pernicious Anemia |
|
|
What labs should be ordered to identify the pathogen in a pt with an acute diarrheal illness?
|
(assuming no fever or bloody diarrhea, -- which probably viral and don't need to do anything)
If there is a fever or bloody diarrhea for more than 5 days: - stool culture (for bacteria), stool acid fast stain, check stool for fecal leukocytes - stool ova & parasites, stool guaiac |
|
|
What is the most common cause of adult chronic diarrhea?
|
Lactose intolerance
|
|
|
What are the ROME II Diagnostic Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
|
(1) At least 12wks of abd discomfort or pain in the preceding year assoc with one of the following:
- relief with defecation - change in FREQ of stool - change in FORM of stool (2) characteristic of IBS: change in stool form or freq (>3 daily or <3 weekly), straining, ugency, or feeling of incomplete passage, bloating/ distention, mucus (3) NOT characteristic of IBS: anorexia, weight loss, malnutrition, progressively worsening pain, pain that prevents sleep |
|
|
What is the necessary workup before making the diagnosis of diarrhea predominant form of IBS? Tx?
|
- Labs: serum tissue transglutaminase antibody to r/o celiac sprue, CBC, Chem 7, TSH (hyperthyroidism can cause diarrhea), ESR, stool leukocytes
Treatment: - Tricyclic antidepressants (desipramine) or SSRIs (if TCAs not well tolerated) - if woman has severe disease -- alosetron (Lotronex) - Loperamide (Imodium) PRN |
|
|
What is the tx for the constipation predominant form of IBS?
|
Fiber bulking agents
|
|
|
What treatments are available for managing Crohn's Disease?
|
(1) 5-ASA agents (ie mesalamine, sulfasalazine) - usual initial therapy for mild disease
(2) Azathioprine or mercaptopurine > methotrexate (3) Anti-TNF-α agents (Infliximab, adalimumab) (4) Steroids +/- antibiotics for acute exacerbations |
|
|
What are the most common causes of small bowel obstruction (SBO)?
|
mneumonic: "ABC"
(1) Adhesions from previous surgeries (~75% of cases) (2) Bulge (hernia) (3) Cancer (most commonly metastatic colorectal cancer) (4) Other less common causes: volvulus, intussusception, Crohn's Disease, Gallstone Ileus, Bezoar (organic matter that balls up), bowel wall hematoma from trauma, inflammatory stricture, congenital malformation, radiation enteritis |
|
|
What are the classic s/s of SBO? What radiographic findings help you confirm the diagnosis?
|
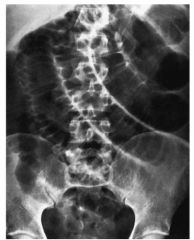
S/S: abd pain/ tenderness, N/V, +/- recent flatus/small BM; high-pitched hyperactive BS (also common is h/o prev abd surgery - think adhesions)
Dx: Distended loops of small bowel prox to the obstruction seen on plain film abd series or CT scan of the abdomen |
|
|
What is the tx for a SBO?
|
- NPO, IVF (usually LR) monitor electrolytes, Foley cath to monitor UOP
- NG tube to low intermittent wall suction (LIWS) - Hospital observation with freq reassessments +/- repeat CT scans - Avoid pain medication if possible which may interfere with identification of disease worsening - Surgery (laparotomy & lysis of adhesions) if: ... no improvement in 12-24hrs ... complete SBO ... suspected, impending, or ongoing strangulation |
|
|
What are the seronegative arthropathies?
|
"PAIR" - assoc with HLA-B27
Psoriatic arthritis Ankylosing Spondylitis Inflammatory Bowel Disease Reiter's Syndrome |
|
|
According to the ROME II Diagnostic Guidelines for IBS, what s/s are NOT characteristic of IBS?
|
Anorexia, weight loss, malnutrition, progressively worsening pain, pain that prevents sleep
|
|
|
Which form of IBD is often positive for ASCA and negative for pANCA?
|
ASCA = anti-yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies
pANCA = perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic Abs = Crohn's Disease |
|
|
Which form of IBD causes perianal fissuring & fistulas?
|
Crohn's Disease
|
|
|
In which form of IBD would you see a "lead pipe" appearance on barium enema?
|
Ulcerative Colitis
|
|
|
What are the first-line treatments for IBD?
|
5-ASA medications (Mesalamine, Sulfasalazine)
|
|
|
What are the 3 most common causes of SBO in descending order (in the US)?
|
"ABC"
Adhesions Bulge (hernia) Cancer |
|
|
What is the most common cause of large bowel obstruction?
|
cancer
|
|
|
What is the most common BENIGN small bowel tumor?
|
leiomyoma
|
|
|
what is the most common MALIGNANT small bowel tumor?
|
adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What radiological studies can be used to diagnose appendicitis?
|
- CT scan with oral contrast (2 hrs required, but allows visualization of pathology in the entire abdomen)
- CT scan with rectal contrast (+/- IV contrast) - fastest & most accurate CT scan - CT scan without contrast - higher rate of false negatives, still better than no CT scan - Plain xray - may aid in the diagnosis but does not allow you to make the dx - Ultrasound - good first study in children, not as accurate as CT scan, can identify any pelvic pathology present in women |
|
|
What is the specific treatment for appendicitis?
|
- NPO & IVF
- Pain control: morphine or meperidine PCA - Antibiotics ASAP (Unasyn, ZOsyn, Levofloxacin+metro, Cipro + metro, Ampicillin + levofloxacin + Metro, Imipenem/cilastatin, Meropenem - Surgical removal - if abscess seen on CT scan do percutaneous drainage via IR |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of gallstone ileus?
|
- gallstone ileus is impaction of a gallstone in the ileum after passage thru a biliary-enteric fistula
classically presents as an episodic subacute obstruction in an elderly female = vague, recurrent abdominal pain & vomiting that recurs as the stone repeatedly lodges & dislodges - avg time from symptom onset to hospitalization = 5 days |
|
|
What is the treatment for sigmoid volvulus?
|
(1) sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy for decompression
- volvulus usually 25cm from the anal verge - contraindicated if signs of gangrene due to perforation risk (2) if gangrenous or scope unsuccessful = lap resection of the affected colon and colostomy (3) once corrected, the recurrence rate in 40-60% of pts can be prevented with one of the following: - mesosigmoidopexy - resection with primary anastomosis - Hartman's procedure (proximal colostomy + stapling but not removal of the distal segment) |
|
|
What might you see on CT scan of the abdomen in a pt suspected of having ischemic colitis?
|
(1) Bowel wall thickening
(2) air w/in bowel wall (pneumatosis coli) |
|
|
What is the classic presenting history of appendicitis?
|
- dull periumbilical pain, N/V, anorexia
- pain migrates to RLQ & becomes more severe |
|
|
In a woman with history and labs suggestive of acute appendicitis, what additional lab should be done first before surgery?
|
Pregnancy test (check B-hCG)
|
|
|
Describe the different signs that might be seen in pts with appendicitis
|
(1) Psoas sign = RLQ pain on passive extension of hip
(2) Rovsing's sign = RLQ pain with LLQ palpation (3) Obturator sign = pain on passive internal rotation of flexed hip |
|
|
HYQ: What is the classic time-frame for which post-op ileus resolves in the different parts of the gut?
|
pg 72
small bowel = <24hrs stomach = 48-72hrs Colon = 3-5 days |
|
|
What patient populations are most susceptible to volvulus
|
- infants & elderly
|
|
|
What should you look for on an abdominal xray in a pt suspected of volvulus?
|
- bowel distended with air proximal to volvulus
- volvulus itself distended with air ("double bubble") |
|
|
HYQ: What is the next step in the management of a pt that comes to the ER with severe abdominal pain and abd xray shows free air in the abdomen?
|
think perforation (b/c of free air)
tx: exploratory laparotomy |
|
|
HYQ: A recent Cuban immigrant with symptoms of malabsorption is found to also have megaloblastic anemia. What is the disease and treatment?
|
Dx: Tropical Sprue
Tx: Folate + tetracycline or sulfa drug |
|
|
Elderly pt presents to the ER with vomiting, abd pain + distention. Abd Xray reveals two distinct but sequential portions of bowel in the sigmoid colon that are distended with air. What is the treatment?
|
Dx: Volvulus ("double bubble")
Tx: Colonscopy (try to untwist portion of affected colon) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Crohn's Disease
|
5-ASA
Azathioprine or mercaptopurine Anti-TNFa agents Steroids Antibiotics |
|
|
What is the classic characteristic of acute mesenteric ischemia?
|
Pain out of proportion to physical exam findings
|
|
|
Which characteristics are associated with IBS?
|
Bloating, mucus
abd pain relieved with defecation change in freq/form of stool straining, urgency, feeling of incomplete passage |
|
|
Which characteristics are NOT assoc with IBS?
|
anorexia, weight loss, malnutrition, progressively worse pain, or pain that interferes with sleep
|
|
|
What tumors can cause a secretory diarrhea?
|
Carinoid tumor
VIPoma Gastrinoma Medullary Thyroid Cancer |
|
|
What is the most likely cause of malabsorption in a pt with (+) Sudan stain in the stool sample and a normal D-xylose test?
|
Pancreatic insufficiency
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Whipple disease?
|
TMP-SMX (Bactrim) or Ceftriaxome for 12 months
|
|
|
What serum lab findings might help you distinguish Crohn's from UC?
|
Crohn's = (+) ASCA
Ulcerative Colitis = (+) pANCA |
|
|
When is inpatient admission for diverticulitis treatment indicated? What are the steps in the inpatient management of diverticulitis?
|
● the following pts need to be hospitalized for tx of acute diverticulitis: elderly, immunocompromised, significant comorbidities, high fever, and significant leukocytosis, unable to tolerate PO intake... otherwise it can be treated on an outpatient basis
● IV Fluids ● Broad Spectrum Antibiotics (same as appendicitis): - fluroquinolone + metronidazole - TMP-SMX + metronidazole - amoxicillin - clavulanate (Augmentin) ● if signs of peritonitis ➙ emergency exploration thru midline incision |
|
|
A 65yo F that presented to the ER with severe abdominal pain is found to have leukocytosis and an abscess in the region of the sigmoid colon. What is the most likely predisposing lesion, and what is the next step in management?
|
● diverticulosis ➜ diverticulitis ➜ abscess
● Next step: CT-guided or U/S guided percutaneous drainage ● IV antibiotics |
|
|
What are the classic features of carcinoid syndrome?
|
"B FDR"
● Bronchospasm (10-20%) ● Flushing (85%) ● Diarrhea (80%) ● Right-sided valvular disease/ murmurs |
|
|
What is the treatment for carcinoid syndrome?
|
● somatostatin analog such as octreotide
● other drugs that can be used for symptom relief: - Cyproheptadine (5-HT1 antagonist) for diarrhea and/or anorexia - Albuterol and/or theophylline for asthma symptoms - Codeine and/or cholestyramine for diarrhea ● if symptoms are refractory to octreotide ➜ INFα combined with hepatic artery embolization ● surgical resection in certain circumstance of isolated tumors ● valvular surgery for symptomatic carcinoid heart disease |
|
|
What are the risk factors for diverticulosis?
|
age >60yrs
low fiber high fat diet |
|
|
What is the treatment for mild diverticulitis?
|
● can be treated as an outpatient
● Broad spectrum ABX that cover gram negs & anaerobes: - Fluoroquinolones + MEtronidazole - TMP-SMX (Bactrim) + Metronidazole - Amoxicillin + Clavulonate (Augmentin) ● Bowel rest for 3 days |
|
|
What is the treatment for diverticulitis with abscess formation?
|
- CT guided or U/S guided percutaneous drainage
- IVF, bowel rest, antibiotics |
|
|
Which type of hemorrhoids are painful, and where are they located?
|
Type ➜ external hemorrhoids
Location ➜ distal to dentate/pectinate line |
|
|
What is the treatment for hemorrhoids?
|
Sitz baths
High fiber diet, adequate hydration avoid excessive straining ligation with rubber bands sclerotherapy surgery/excision I&D |
|
|
What do you call an abnormal tract btw a hollow viscus (such as the bowel) and the perianal skin?
|
Fistula-in-ano
|
|
|
How can a carcinoid tumor be localized?
|
CT Scan or octreotide scan
|
|
|
Fever + LLQ pain
|
think Diverticulitis
|
|
|
What are the current colon cancer screening recommendations for normal risk patients?
|
For the average risk pt, the following screening should start at AGE 50:
● fecal occult blood test (FOBT) ANNUALLY with stool guaiac (samples from 3 consecutive stools is ideal) ● Colonoscopy every 10 years (or flex sig and double-contrast barium enema every 5 yrs) ● (CT colonography is NOT currently used for screening b/c it does not have adequate sensitivity & specificity) Screening should stop when a pt's life expectancy is <5yrs (or at age 75, whichever comes first) |
|
|
A 20yo pt with a strong FHx of colon cancer is found to have an Aut Dom mutation in the APC gene. What prophylactic measures should this pt take to prevent future morbidity & mortality?
|
Patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) have a 95-100% chance of developing colorectal cancer. Prophylaxis includes:
● Flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonscopy every 1yr starting at age 10 ➜ when multiple adenomas are identified, then colectomy is indicated (if no adenomas are identified, then continue annual flex sig thru age 40 then q3-5years) ● Colectomy when adeonmas identified (abdominal colectomy, mucosal proctectomy, and ileoanal anastomosis) ● Upper GI endoscopy at the time of colectomy (or early 30s) then q3-5 yrs if no lesions are seen |
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of 1-2 tubular adenomas <1cm?
|
repeat colonoscopy in 5 yrs
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of 2 or more tubular adenomas?
|
repeat colonoscopy in 3 years
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of tubular adenomas >1cm
|
repeat C-scope in 3 yrs
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of Villous adenoma or high-grade dysplasia ?
|
repeat C-scope in 3 yrs
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with family history of colon cancer?
|
repeat C-scope in 3 years
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of >2cm sessile polyp
|
repeat C-scope in 3-6 months
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts that had a poor prep, so the cecum was not able to be seen during the first colonoscopy?
|
repeat C-scope <3yrs
|
|
|
Whats the recommendation for f/u colonoscopy for pts with history of more than 10 adenomas?
|
repeat C-scope <3yrs
|
|
|
Which type of colonic polyps are precancerous?
|
Tubular adenomas
Tubulovillous adenomas Villous adenomas NOTE: hyperplastic polyps are NOT precancerous |
|
|
During a routine exam, a 70yo M is found to have a new-onset iron-deficiency anemia. What should you suspect and investigate further?
|
Suspect colon cancer
next steps: stool guaiac & colonoscopy |
|
|
A patient with colon cancer has local lymph node involvement without distal mets. What stage of cancer is this?
|
Stage 3 (will need chemotherapy)
|
|
|
What tumor marker is used in colon cancer patients?
|
CEA
|
|
|
At what intervals will a post-colon cancer resection pt need colonscopy?
|
at 1 yr then 3 yrs then every 5 yrs
|
|
|
What gene is responsible for familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)?
|
mutation in APC gene
|
|
|
In what condition does the pt have intestinal polyps that are hamartomas, and pigmentation of the lips, oral mucosa, hands and genitals?
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
|
|
|
At what age should colon cancer screening begin?
|
- all pts at age 50yrs
- if pt has first degree relative with colon cancer, start 10 yrs before the relative age of diagnosis |
|
|
What is the recommendation for colon cancer screening by fecal occult blood testing (FOBT)?
|
annually
|
|
|
What is the recommendation for colon cancer screening by flexible sigmoidoscopy + double contrast barium/air enema?
|
every 5 yrs
|
|
|
What is the recommendation for colon cancer screening by colonoscopy?
|
every 10 years
|
|
|
what are the next steps in the management of a pt that presents to the ER with massive lower GI bleeding?
|
(1) Assess & Stabilize
- Hx & PE - Continuous monitor of vital signs - Obtain IV access with 2 large bore IV's (18-gauge in both arms) or central line - Blood volume resuscitation with NS or LR as needed - Type & cross 2units pRBCs - Labs: CBC, coags (guaiac stool if necessary to confirm blood) (2) treat & determine cause - NGT lavage to r/o massive GI bleed - Surgery consult for admission (colonoscopy, +/- surgical intervention) - if colonoscopy is nondiagnostic & not feasible (ie too much active bleeding may obscure visualization) and bleeding persists ➜ radionucleotide scan and/or angiogram |
|
|
How to assess volume status in bleeding pts?
|
Blood pressure
Urine output Heart rate |
|
|
What is a HIDA scan (aka cholescintigraphy)?
|
- technetium labeled hepatic iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) given IV ➜ taken up by hepatocytes ➜ excreted into bile ➜ visualization of gallbladder
- inability to visualize gallbladder with this test indicates cystic duct obstruction usually from acute cholecystitis or an obstructing stone |
|
|
What are the common etiologies of UPPER GI bleeds?
|
- Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
- Esophageal varices - AVM - Tumors - Esophageal erosions - Mallory Weiss Tears |
|
|
What are the most common causes of LOWER GI bleeds?
|
-Diverticulosis or Diverticulitis
- Bowel Ischemia - hemorrhoids or anal fissures - neoplasms - polypectomy |
|
|
A pt in the ER has just thrown up his second basin full of blood. He is drunk and tachycardic. What is the next step in managing this pt?
|
IV fluid resuscitation
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for cholelithiasis?
|
Fat, Female, Forty, Fertile, Family Hx
|
|
|
What are the key features of the history of a pt with cholelithiasis?
|
- Postprandial RUQ pain & discomfort
- nausea & maybe vomiting - worse after fatty or heavy meals |
|
|
How is the HIDA scan used?
|
to show failure of the gallbladder to fill ➜ obstruction of the cystic duct
ability to fill but not empty ➜ dyskinesia, due to chronic cholecystitis |
|
|
What lab value is reliably elevated in the case of bile duct obstruction?
|
alkaline phosphatase
|
|
|
What is the term for a stone caught in a bile duct?
|
choledololithiasis
|
|
|
A pt has an abdominal xray taken as part of an ER workup. The radiologist noted that the pt's gallbladder appears calcified. What is the next step?
|
calcified gallbladder aka "porcelain" gallabladder
think CANCER! - remove the gallbladder (its too hard to biopsy) |
|
|
HYQ: what is the next step in management of a pt younger than 50 with minimal bright red blood per rectum (ie only seen on the toilet paper after wiping)?
|
anoscopy (looking for hemorrhoids)
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the most likely cause of acute pain and swelling of the midline sacrococcygeal skin & subcutaneous tissues?
|
Pilonidal cyst
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of recurrent LLQ abdominal pain that improves after defecation?
|
Diverticulosis
|
|
|
What type of pt is at high risk of acalculous cholecystitis?
|
Pts on TPN or in the ICU
|
|
|
What is charcot's triad? Reynold's pentad?
|
Charcot's triad: Fever + RUQ pain + Jaundice
Reynolds Pentad: Fever/RUQ Pain/Jaundice + mental status changes + hypotension |
|
|
How does the interventional component of treatment of cholecystitis differ from that of cholangitis?
|
cholecystitis ➜ choleystectomy
cholangitis ➜ ERCP, then cholecystectomy |
|
|
A 60yo M undergoes colonoscopy and is found to have 3 small tubular adenomas that are completely removed. When should he undergo his next colonoscopy?
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
A 40yr M tells you his father had colon cancer at age 55. When should this man's first colonoscopy be scheduled?
|
45 yrs
|
|
|
What antibiotic combinations are used in the treatment of diverticulitis as an outpatient?
|
(1) TMP-SMX (Bactrim) + metronidazole
(2) Fluoroquinolone + Metronidazole (3) Amoxicillin + clavulonate (Augmentin) |
|
|
How are anal fissures managed?
|
- stool softeners & topical nitroglycerine
- topical nifedipine, bethanecol, diltiazem - Botox - Partial sphincterectomy |
|
|
How is volume status assessed in a pt with a GI bleed?
|
HR, BP & urine output
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hepatic encephalopathy?
|
● identify & correct the underlying precipitating factors (hypovolemia, GI bleeding, hypoxia, infection)
● Lactulose titrated to 2 soft bowel mvmts a day (causes osmotic diarrhea) ● Neomycin or rifaximin antibiotics to reduce toxins formed by gut bacteria ● Protein restriction to decrease nitrogen/ammonia related toxins |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of Budd-Chiari syndrome?
|
Budd-Chiari is the thrombosis and occlusion of the hepatic vein or hepatic stretch of the inferior vena cava (IVC) and presents with:
● ascites (84%) ● hepatomegaly (76%) ● Jaundice ● acute presentation: acute RUQ pain + hepatomegaly, and rapid development of jaundice and ascites ● subacute or chronic presentation: gradual development of ascites, LE edema, cirrhosis, and portal hypertension over a few months ● eventual development of liver failure and hepatic encephalopathy |
|
|
What criteria compose the Child's classification of operative mortality in pts with liver disease?
|
"A BEAN"
Ascites Bilirubin Encephalopathy Albumin iNr |
|
|
What is the treatment for SBP (Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis)?
|
● Cefotaxime (2g IV q8hrs), ceftriaxone or other 3rd Gen Cephalosporin for at least 5 days to cover for gut bacteria (E. coli, Klebsiella, enterococcus), and Staph/ Strep
● Albumin dosed IV (1.5g/kg at diagnosis then 1g/kg on day 3) maintains plasma volume ➔ preserves renal function ➔ reduces renal impairment and mortality |
|
|
How can alcohol-induced fatty liver disease be reversed?
|
stop drinking alcohol
|
|
|
What is the name of the disease where there is thrombosis of the hepatic vein or hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava (IVC)?
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
|
|
|
How is the liver different in Budd Chiari vs Cirrhosis?
|
SIZE is the difference
Budd-Chiari = large liver Cirrhosis = small liver |
|
|
What antibiotics can be used to treat spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)?
|
Cefotaxime
3rd Gen Cephalosporins |
|
|
What lab values will help to make the diagnosis of SBP?
|
● PMNs >250
● glucose <50mg/dL ● total protein >1g/dL ● LDH > normal serum LDH |
|
|
What is the medical treatment for varices?
|
beta-blockers
vasopressin octreotide |
|
|
What 2 diuretics are used in conjunction for the treatment of ascites/ portal hypertension?
|
Furosemide
Spironolactone |
|
|
What is the surgical procedure used as a temporizing measure for severe portal hypertension?
|
TIPS - tranjugular intrahepatic portacaval shunt
|
|
|
What PE and lab findings would lead you to suspect Primary Biliary Cirrhosis as a diagnosis?
|
- Usually women (95% of pts) btw ages 30-65
- Fatigue & pruritis are the most common presenting sxs - Excessive daytime somnolence - Pruritis often starts during pregnancy but is not relieved postpartum - Pts are often initially referred to a dermatologist for pruritis and excoriations are common - Skin changes: hyperpigmentation due to melanin deposition (25-50%), xerosis (70%), dermatographism (57%) - Xanthelasma (cholesterol-filled plaques on the medial aspects of the eyelids bilaterally and/or xanthoma - Hepatomegal that progressively worsens +/- splenomegaly - Malabsorption and steatorrhea from less bile acid secretion - Cirrhosis, jaundice, ascites, edema, portal hypertension occur in late stage disease - Labs: ↑ alk PO43- & ↑ GGT, ↑ serum direct & indirect bili (but not in early disease) ↑ cholesterol - ↑ serum antimitochondrial Abs (>95% of pts) – THE HALLMARK FINDING OF PBC - ↑ ANA (70%) - assoc conditions: other autoimmune disorders (ie thyroiditis/hypothyroid, sicca syndrome, scleroderma, Sjogren’s, arthritis, Raynaud’s), osteoporosis, osteomalacia |
|
|
What is the treatment for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC)?
|
● Ursodeoxyxholic acid (UDCA) – delays disease progression and enhances survival → the ONLY approved therapy for PBC
● If UDCA not sufficient → may add colchicine +/- methotrexate ● If pruritis → cholestyramine ● Prevention of metabolic bone disease: - Calcium 1,500 mg/d + at least 800 IU of Vit D daily - Supplement vitamins A & D as needed based on annual serum levels of these vitamins - Evaluation with bone DXA scan at the L-spine and hup ● If low bone density → bisphosphonates ● If esophageal varices → β-blocker +/- band ligation +/- surgical intervention (splenorenal shunt or TIPS) ● If iron deficiency anemia → oral iron replacement ● If fatigue → modafinil (not well studied) ● Dietary changes: - If steatorrhea → reduce dietary fat - If weight loss → supplement medium-chain triglycerides which do not need bile for absorption - If pancreatic insufficiency → pancreatic enzyme replacement ● Treat hypOthyroidism as needed ● If painful or debilitating xanthomas on pals or soles, large volume plasmapheresis q 1-2wks to normalize serum cholesterol ● Definitive treatment is LIVER TRANSPLANT |
|
|
What are some of the possible etiologies of secondary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Intraductal biliary stones
Durgical trauma or blunt abdominal trauma to the biliary tree Drugs (IV Chemotherapy) Recurrent pancreatitis Autoimmune pancreatitis AIDS cholangiopathy |
|
|
What are the risk factors, signs/symptoms of and treatment for hepatic adenoma?
|
Most often in females 20-44 (OCP years)
Risk factors: OCP use, anabolic steroids, (glycogen storage disease types I and III) S/S: RUQ pain, but usually there are no symptoms b/c it is often an incidental finding on imaging Malignant transformation in 10% of pts Tx: d/c OCP, serial imaging & AFP +/- resection (esp if >5cm) |
|
|
What is the screening lab for hemochromatosis?
|
Serum ferritin
|
|
|
What are some key clues to the diagnosis of hemochromatosis?
|
Bronze skin
Symptoms of Diabetes Cardiac insufficiency Abdominal pain Hepatomegaly Arthalgias |
|
|
How is excess copper secreted from the body?
|
Thru the bile
|
|
|
Where does excess copper deposit and what symptoms does that cause?
|
CNS: psychiatric disturbance, loss of coordination, tremor
Cornea: Kayser Fleischer rings Liver: hepatomegaly |
|
|
What cooper-related lab value would you order in a pt suspected of having Wilson disease?
|
Serum ceruloplasmin level
|
|
|
What agents would be used to treat Wilson disease?
|
Penicillamine
Trientine Zinc Vit B6 |
|
|
What is the primary treatment for PBC?
|
Ursodeoxycholic acid, colchicine, methotrexate
Liver transplant |
|
|
What are the key differences btw PBC & PSC?
|
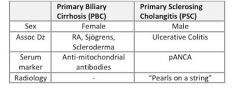
see above
|
|
|
What are the important characteristics of Gilbert’s disease?
|
Mild deficiency of glucuronosyltransferase
Mild jaundice Indirect bilirubin <5 No treatment |
|
|
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type I causes severe disease and often death b/c of the severe deficiency of what enzyme?
|
Glucouronosyltransferase (aka uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase (UGT))
|
|
|
What is the serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
|
α-fetoprotein (AFP)
|
|
|
What are the “rule of 2’s” for Meckel’s Diverticulum?
|
Def: remnant of vitelline duct, exists as outpouching of ileum, may contain ectopic tissue
Males 2x more common vs females w/in 2ft of ileocecal valve 2 types of ectopic tissue (gastric or pancreatic) found in 2% of population most complications occur before 2 yrs old |
|
|
What is the differential for Neonatal Jaundice? (HIGH YIELD!)
|
- Physiologic jaundice: (50% of newborns) – starts day 2-3, peaks at <10mg/dL on day 3-5
- Exaggerated physiologic jaundice (aka breastfeeding jaundice) – occurs in 1st wk of life, peaks at 12-15mg/dL, due to dehydration → make sure baby has more than 10 feeds/day - Breast milk jaundice: starts days 4-14 (usually after 1st wk) due to substances in breast milk. May continue for wks-mos while breastfeeding. Improvement with the substitution of formula for 48-72 hrs is diagnostic - Immune related: - ABO incompatibility - Rh (or other antigen) incompatibility (erythroblastosis fetalis) - Trauma, cephalohematoma, bruising - Infection/sepsis (look for signs of infxn such as fever, lethargy, and poor feeding) - Polycythemia - Hereditary disease - G6PD deficiency (more common in black, African, Asian, Mediterranean, and Middle-Eastern males) - Hereditary spherocytosis - Dubin-Johnson (direct/conjugated bili elevation) - Rotor’s (direct/conjugated bili elevation) - Byler’s (direct/conjugated bili elevation) - Biliary atresia: may present after 2wks of age with jaundice and pale stools. Direct bili is more than 20% of the total bili which is usually elevated to 6-12 mg/dL. Early referral to Ped GI for diagnosis (U/S + biliary nuclear imaging +/- biopsy) is important since surgical repair prior to 2 months of age is essential in preventing biliary cirrhosis |
|
|
What antibiotic is contraindicated in neonates with hyperbilirubinemia & why?
|
Ceftriaxone (displaces bilirubin from albumin)
|
|
|
What characteristics might help you identify newborn jaundice as pathological?
|
Any jaundice in 1st 24hrs
Rise in total bili by more than 0.5mg/dL/hr Rise in total bili more than 5mg/dL/day Direct (conjugated) hyperbili greater than 20% of the total bili or >1.5 mg/dL Total bili higher than 13mg/dL in term neonates Jaundice appearing after 2-3 wks of age |
|
|
What are the criteria for failure to thrive (FTT) in a child younger than 2rs of age?
|
Weight <3rd or 5th percentile for gestation corrected age on more than one occasion (make sure to use special growth chart for Down syndrome and Turner syndrome pts)
Weight <80% of ideal weight for age Weight crosses 2 major percentiles downward on a standardized growth chart over time Weight for length ratio <10th percentile Rate of daily weight gain less than that expected for age |
|
|
What would be the common presentation of tracheoesophageal fistula (TE fistula)?
|
Infant that coughs or aspirates during feeds
abdominal distention |
|
|
What are the key characteristics of the H&P of a pt with pyloric stenosis?
|
1-2wk old infant
projectile non-bilious vomiting palpable mass in epigastric area |
|
|
What is seen on biopsy of the colon in a Hirschsprung pt?
|
Absence of enteric ganglia
|
|
|
What are key characteristics in the H&P of a child with intussusception?
|
Currant jelly stool
Sausage-like abdominal maa Barium enema (shows obstruction & may reduce defect) |
|
|
What study can be used to diagnose a 2yo child with painless rectal bleeding?
|
Meckel’s scan (think Meckel’s diverticulum)
|
|
|
What characteristics might help you identify newborn jaundice as pathological?
|
Any jaundice in the 1st 24hrs is pathological
Rise in bilirubin: >0.5/hr, >5mg/day Direct (conjugated) bili: >20% of total bili or >1.5mg Total bili: >13 mg in full-term neonates Jaundice appearing after 2-3wks of age |
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
Deep palpation of RUQ → arrest of inspiration due to pain |
Murphy's sign - Cholecystitis
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
fever, jaundice, RUQ Pain, hypotension, AMS |
Reynolds pentad - Cholangitis
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
RLQ pain on passive extension of the hip |
Psoas sign - Appendicitis
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
RLQ pain on passive internal rotation of the flexed hip |
Obturator Sign - Appendicitis
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
LUQ pain and referred left shoulder pain |
Kehr's sign - Splenic Rupture
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
Ecchymosis of the skin overlying the flank |
Grey Turner's sign - Pancreatitis
|
|
|
What is the name of the sign & what condition is it associated with:
Ecchymosis of skin overlying the periumbilical area |
Cullen's Sign - Pancreatitis
|
|
|
What is the tx for hepatic encephalopathy?
|
Lactulose
Neomycin/ rifaximin Protein restriction |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Budd-Chiari syndrome?
|
Ascites
Hepatomegaly Jaundice +/- RUQ pain Liver failure |
|
|
What is the most widely used screening test for hemochromatosis?
|
Phlebotomy (weekly or biweekly until normal Hct, then 1/mo)
Rarely deferoxamine |
|
|
What distinguishes primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) from primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)?
|
PBC → women, AMA & ANA, other autoimmune disease
PSC → men, pANCA, ulcerative colitis, “beads on a string” on ERCP |
|
|
What is the treatment for primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Ursodeoxycholic acid, colchicine
May need transplant |
|
|
What is the tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma? For colon cancer? For gastric cancer? For pancreatic cancer?
|
HCC → α-fetoprotein (AFP)
Colon Cancer → CEA Gastric Cancer → CEA Pancreatic Cancer → CEA & CA 19-9 Ovarian Cancer → CA-125 |
|
|
What is the most common type of TE fistula?
|
Blind upper esophageal pouch
Lower esophagus attached to trachea |
|
|
What is the classic presenting scenario for necrotizing enterocolitis?
|
Premature or low birth weight infant → then started on tube feeds → subsequently to starting the tube feeds, develop increasing abdominal distention & signs of enterocolitis
|

