![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
171 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description? |
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Reed-Sternberg cells, cervical lymphadenopathy, night sweats |
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Most common form of Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
Nodular Sclerosis
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Bence-Jones proteins, osteolytic lesions, high calcium |
Multiple Myeloma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Translocation 14;18 |
Follicular lymphoma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Translocation 8;14 |
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Translocation 9;22 |
CML (and 15% of adult ALL)
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
“Starry sky” pattern due to phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells |
Burkitt’s lymphoma
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
High hematocrit/Hg, pruritis (esp after hot bath or shower), burning pain in hands or feet |
Polycythemia Vera
|
|
|
Which blood cell pathology matches the following description?
Blood smear (hair-like projections), splenomegaly |
Hairy Cell Leukemia
|
|
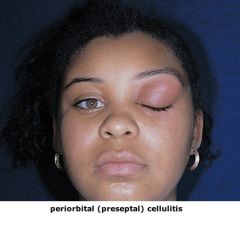
What are the classic features that distinguish orbital cellulitis from periorbital cellulitis?
|
Orbital (postseptal) cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection characterized by fever, painful purple-red eyelid swelling, restriction of eye movement, proptosis, and variable decreased visual acuity. It may begin with eye pain and low-grade temperature. In general, it’s caused by S.pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and S. aureus. It usually arises as complication of ethmoid or maxillary sinusitis. If not treated promptly, it can lead to blindness, cavernous sinus thrombosis, meningitis, subdural empyema, or brain abscess
Periorbital (preseptal) cellulitis usually presents with edema and typically circumferential erythema of the eyelids and periorbital skin, minimal pain, and fever. Proptosis and ophthalmoplegia are NOT characteristic. Usually results from trauma, contiguous infection, or in rare instances, from primary bacteremia among young infants. Common organisms are S aureus and group A Streptococcus. |
|
|
In which pts is bupropion (wellbutrin) contraindicated?
|
Buproprion can lower the seizure threshold & is therefore contraindicated in pts with:
Seizure disorders Eating disorders Benzo or alcohol withdrawal |
|
|
What is the treatment for serotonin syndrome?
|
d/c serotonergic agents: symptoms usually resolve in 24hrs
supportive care to normalize vital signs (mechanical cooling with ice/cooling blankets) |
|
|
How is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnosed? How is it treated?
|
Cause: Dislodged (free-floating) otolith in semicircular canal
Diagnosis: Patients suffering from recurrent spells of vertigo, lasting under several minutes per spell, a/w changes in head position (often provoked by rolling over in bed) Can do Dix-Hallpike maneuver to aid diagnosis Note: The term "positioning vertigo" is more accurate than "positional vertigo" because it is provoked by changes in head position rather than by the maintenance of a particular posture. Treatment: physical therapy → Epley’s maneuver |
|
|
What is the treatment for acute angle-closure glaucoma?
|
Eye drop combination of β-blockers, α-agonists, cholinergic agonists, prostaglandin analogs
Acetazolamide orally IV mannitol |
|
|
What is the antidote to the following toxin?
Anticholinesterases, organophosphates |
Atropine, Pralidoxime
|
|
|
What is the antidote to the following toxin?
Mercury |
Dimercaprol, Succimer
|
|
|
What is the antidote to the following toxin?
Carbon Monoxide |
100% O2, hyperbaric O2
|
|
|
What is the antidote to the following toxin?
Heparin |
Protamine
|
|
|
What is the antidote to the following toxin?
Isoniazid |
B6
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Diastolic murmur heard best at LLSB, that increases with inspiration |
Tricuspid Stenosis
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Late diastolic murmur with opening snap (no change w/ inspiration) |
Mitral Stenosis
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Systolic murmur heard best in second right interspace |
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Systolic murmur heard best in second left interspace |
Pulmonic stenosis
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Late systolic murmur best heard at apex |
Mitral valve prolapse
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Diastolic murmur with a widened pulse pressure |
Aortic regurgitation
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Holosytolic murmur that is louder with inspiration at the LLSB |
Tricuspid regurgitation
|
|
|
What type of murmur fits the following description?
Holosystolic murmur heard at the apex and radiates to the axilla |
Mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
What is the mneumonic for Stages of Pubertal Development?
|
“GRaB PAM”
GRowth spurt Thelarche (Breast development) Pubarche (growth of pubic hair) Adrenarche (growth of axillary hair) Menarche |
|
|
What is the mean age of menarche in the US?
|
Age 13
|
|
|
In which Tanner stage does thelarche occur, and in which race(s) does this occur earlier than 10.5 years of age?
|
Tanner stage 2
Seen earlier than 10.5yrs in African Americans & Hispanics |
|
|
Does the growth spurt usually occur before or after menarche?
|
Before menarche
|
|
|
What is the definition of precocious puberty?
|
Pubertal changes in girls < 8yrs, or boys < 9years of age
|
|
|
What are some causes of heterosexual precocious puberty?
|
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Exogenous androgens Androgen secreting neoplasms |
|
|
What are some causes of isosexual precocious puberty?
|
CNS lesions
Trauma Thyroid disorders |
|
|
What is the treatment for central precocious puberty?
|
Use GnRH analogs in continuous fashion to suppress gonadotropin release
|
|
|
Which phase of the menstrual cycle is fixed at 14 days, regardless of cycle length?
|
Luteal phase
|
|
|
FSH triggers the release of which hormone from the follicle?
|
Estradiol
|
|
|
What hormonal change causes menstruation?
|
↓ progesterone level = corpus luteum will degrade & menstruation occurs
|
|
|
How is menopause diagnosed?
|
12 mos of amenorrhea in a woman over 45yrs is diagnostic and requires no additional w/u
a woman over age 45 with irregular menses (oligomenorrhea) and menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, mood changes, sleep disturbances) can be assumed to be going through perimenopause ↑ Serum FSH levels in perimenopausal periods and after menopause, but it is of little diagnostic value beyond obtaining a history of menses symptoms if younger than 45, other etiologies for oligo/amenorrhea must be excluded (TSH, serum hCG, prolactin, FSH) |
|
|
What are the pros of hormone replacement therapy for menopause?
|
Pros:
Control of menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, vaginal dryness/atrophy, urinary incontinence, emotional lability) ↓ risk of osteoporosis ↓ risk of colorectal cancer |
|
|
What are the cons of hormone replacement therapy for menopause?
|
Cons:
Not indicated for the prevention of chronic disease, stroke, heart disease, and osteoporosis (can be used in tx of osteoporosis but not first line) HRT doubles risk of Invasive breast cancer (+8 per 10,000) but not noninvasive breast cancer Endometrial cancer Venous thromboemabolism (+8 PEs per 10,000) ↑ risk of stroke by up to 32-41% (+ 8 per 10,000) ↑ risk of heart disease by 29% (+7 per 10,000) however, if taken at ages 50-59, HRT results in less coronary calcification on CT scan (NEJM 2007; 356:2591) This may or may not correlate with less risk of heart disease in women taking HRT during ages 50-59 ↑ risk of biliary disease and need for biliary surgery |
|
|
What non-hormonal options can be used in the treatment of menopausal hot flashes?
|
Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq): 100mg qd. Only non-hormonal FDA drug approved for hot flashes. Also works as antidepressant
Venlafaxine (Effexor): 37.5mg BID ↓ frequency 52-62% and severity 57-67%, and results begin in the first week of therapy. Good choice if any depression, anxiety, fatigue, or isolation. Good first line drug Clonidine (Catapres): ↓frequency 22% and severity 48%. Good choice if BP control is also needed. SE of dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness Gabapentin (neurontin): ~50% reduction seen in small trial. Good choice if insomnia, restless leg syndrome, seizure d/o, neuropathy, chronic pain Time: ~30-50% of women have symptoms improvement within a few months, and most have resolution w/in 4-5yrs Placebo: placebo effect is ~20-25% effective in reducing hot flashes |
|
|
Premature menopause is defined as menopause before what age?
|
Age 40
|
|
|
What is required for a diagnosis of menopause?
|
1 year of amenorrhea in a woman > 40years
|
|
|
As periods become less frequent during perimenopause, what hormonal changes are occurring?
|
↓ ovarian response to FSH & LH
↑ FSH & LH levels estrogen levels fluctuate |
|
|
What are the non-hormonal options for the treatment of menopausal hot flashes?
|
SNRIs → Venlafaxine (Effexor) & Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)
Clonidine (Catapres) Gabapentin (Neurontin) Time |
|
|
To which menopausal pts should bisphosphonates be given?
|
pts with osteopenia
pts with high risk factors for osteoporosis note: need to supplement all pts taking bisphosphonates with Ca2+ & Vit D! |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of action of OCPs?
|
Inhibit follicle development & ovulation
Change endometrial quality ↑ cervical mucus viscosity |
|
|
OCP use ↓incidence of what type of cancer?
|
Ovarian cancer
|
|
|
What are the side effects of estrogen? Progesterone?
|
Estrogen: weight gain, nausea, breast tenderness, headache
Progesterone: acne, depression, hypertension |
|
|
What are the absolute contraindications to the use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs)?
|
Pregnancy (although accidental use in early pregnancy is not a/w congenital anomalies
h/o thromboembolism (DVT, PE) or inherited thrombophilia h/o estrogen-dependent tumor (endometrial or breast ca) Cerebrovascular disease (h/o stroke) or CAD Poorly controlled HTN *****Smoker > 35yrs Hepatic disease/ neoplasm (adenoma, cancer, hepatitis, cirrhosis) Abnormal vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology *****Migraine with aura, neurologic symptoms, or vascular involvement (↑ risk of stroke) |
|
|
What are the advantages of combined oral contraceptives?
|
Reliable (<3% failure rate)
↓ risk of endometrial & ovarian cancer ↓ incidence of ectopic pregnancy menses more predictable, lighter, less painful |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of combined oral contraceptives?
|
Daily dosing
Does not protect against STDs Breakthrough bleeding Estrogen side effects: bloating, weight gain, breast tenderness, nausea, headaches Progesterone side effects: depression, acne, hypertension ↑ risk of DVT ↑ triglycerides |
|
|
What type of liver pathology is a/w OCP use? (very rare)
|
Reversible liver cholestasis
****Hepatic adenoma - Benign liver tumor which may undergo malignant transformation - Incidence is 3-4 per 100,000 long-term users vs 0.1 per 100,000 in the general population - Development typically requires high-dose estrogen for over 5 years Budd-Chiari syndrome from hepatic vein thrombosisor IVC thrombosis Veno-occlusive disease of the terminal hepatic venules and hepatic sinusoids (similar to Budd-Chiari) Hepatocellular carcinoma Resulting cirrhosis, portal hypertension, or liver failure from one of the above |
|
|
What medications are well known for reducing the effectiveness of oral combination contraceptive pills through changes in liver metabolism?
|
Antibiotics: Rifampin, (griseofulvin to a lesser degree)
Antiepileptics (ie Phenobarbital, Phenytoin (Dilantin), Carbamazepine (Tegretol), Topiramate (Topamax), Oxcarbazapine (trileptal), Primidone (Mysoline) Other: St. John’s wort |
|
|
What are the contraindications for IUD placement?
|
Current vaginal or cervical infection
High risk for STDs/PID including multiple sexual partners or history of recurrent STDs Known pregnancy or desire for pregnancy in the near future Severe uterine distortion (bicornuate uterus, cervical stenosis, fibroids distorting the uterine cavity) Uterine bleeding that has not yet been worked-up Copper allergy or Wilson’s disease → avoid copper IUD Breast cancer → avoid progesterone IUD |
|
|
What are the first steps in the work-up of a female with primary amenorrhea?
|

see above
|
|
|
A 15yo girl comes in for evaluation of primary amenorrhea and on physical exam, a bluish bulge is evident where the vaginal orifice should be. What is the diagnosis?
|
Imperforate hymen
|
|
|
What are the first steps in the work-up of a female with secondary amenorrhea?
|
Serum β-hCG to rule out pregnancy
Thorough history and physical exam Serum prolactin (r/o hyperprolactinemia), serum TSH (r/o thyroid disease), serum FSH (r/o ovarian failure) If signs of hyperandrogenism → serum DHEAS and total testosterone If all of the above are normal or h/o D & C → progestin withdrawal test (r/o Asherman’s) |
|
|
Why are combined hormonal contraceptive regimens not indicated in breastfeeding women?
|
Estrogen can interrupt lactation
|
|
|
Which are the most cost-effective means of reversible birth control?
|
Medroxyprogesterone shots
Implants IUDs |
|
|
Why is the transdermal contraception patch less effective in obese women?
|
Diffusion thru adipose tissue leads to lower blood levels
|
|
|
When can lactational amenorrhea be relied upon as an effective method of contraception?
|
≤ 6mos post-partum, only if breastfeeding every 3-4hrs
|
|
|
What are the non-contraceptive benefits of the progestin-releasing IUD?
|
Amenorrhea & tx for abnormal uterine bleeding
|
|
|
What is the definition of primary amenorrhea?
|
NO menarche by age 13 + NO secondary sex characteristics
NO menarche by age 16 in presence of secondary sex characteristics |
|
|
What’s the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea?
|
Pregnancy
|
|
|
What is the work-up for a pt with amenorrhea?
|
β-hCG
History & Physical Pelvic sonogram Serum testosterone & DHEA-S if signs of hyperaldosteronism Serum prolactin is galactorrhea Karyotype if uterus absent FSH if uterus present |
|
|
HYQ: A female presents with primary amenorrhea, absent secondary sex characteristics, and anosmia. What is the dx?
|
Kallman syndrome
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the initial step in the management of a woman presenting with secondary amenorrhea and new galactorrhea when the β-hCG is negative?
|
First, always check the β-hCG
Then check TSH & prolactin |
|
|
What are the basic components of a work-up for secondary amenorrhea?
|
β-hCG
Prolactin TSH FSH Testosterone & DHEA-S Progestin withdrawal test |
|
|
What lab findings distinguish true precocious puberty from pseudoprecocious puberty?
|
True/central: ↑ LH/FSH
when you give GnRH = further ↑ FSH Pseudo: ↓ LH/FSH No response when you give GnRH |
|
|
What is the definition of premature ovarian failure?
|
Absence of menses for > 6mos in a woman < 40 yrs old
|
|
|
What are some of the causes of pseudoprecocious puberty?
|
Exogenous hormones
Adrenal hormones Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) Hormone secreting tumor McCune Albright syndrome |
|
|
Which hormone level is a/w and ↑ basal body temperature? How is basal body temp increase a/w ovulation?
|
Hormone = progesterone
BBT rises 24-48hrs after ovulation |
|
|
What are 4 different options for emergency contraception?
|
Combination OCPs
Progestin only Copper IUD Selective progesterone receptor modulators |
|
|
What are the absolute contraindications for OCPs?
|
Pregnancy
h/o thromboembolism h/o estrogen-dependent tumor poorly controlled HTN smoker > 35yrs Liver Disease Abnormal vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology Migraines with aura or neurologic symptoms or vascular involvement |
|
|
What medications are known for reducing the effectiveness of combination OCPs?
|
Rifampin
Griseofulvin Antiepileptics St John’s Wort |
|
|
What are the characteristic features of endometriosis?
|
Pelvic pain (most severe during menses, 2-7 days prior to menses and possibly ovulation)
3 D’s: Dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, and dyschezia (painful defecation during menses) difficulties with fertility Physical findings: Localized tenderness in the cul-de-sac or uterosacral ligaments (esp at the time of menses) Palpable tender nodules in the cul-de-sac, uterosacral ligaments, or rectovaginal septum Pain with uterine movement Tender, enlarged adnexal masses Adhesion causing a fixe or retroverted uterus |
|
|
What are the treatment options for treating endometriosis?
|

see above
|
|
|
What is the first-line treatment for a young, infertile female with obvious signs and symptoms of endometriosis?
|
Laparoscopy
|
|
|
What is the tx of choice for primary dysmenorrhea?
|
#1 NSAIDs
#2 OCPs |
|
|
What meds are effective in the treatment of PMS & PMDD?
|
Vit B6
NSAIDs OCPs Progestins SSRIs +/- Alprazolam (Xanax) |
|
|
In any woman of childbearing age with abdominal pain, what must be ruled out/
|
Ectopic pregnancy (check β-hCG)
|
|
|
Where are the most common locations outside the uterus for endometrial implants?
|
Ovaries & broad ligament
|
|
|
What are the “3 D’s” of the presentation of endometriosis?
|
Dysmenorrhea
Deep dyspareunia Dyschezia |
|
|
What is the 1st line treatment for endometriosis?
|
Continuous (monophasic) combined OCPs
(or Nuvaring continuously) |
|
|
Basic evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (5 star topic)
|

see above
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
|
Anovulatory bleeding
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
(+) β-hCG + intrauterine preg + closed os |
Threatened abortion
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Enlarged uterus + menometrorrhagia for months |
Fibroids, molar pregnancy, adenomyosis
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Bleeding a/w severe menstrual pelvic pain |
Endometriosis or adenomyosis
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Menorrhagia + perimenopausal |
Endometrial hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
AUB started with menarche |
Bleeding diathesis (vWD)
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
(+) β-hCG + severe pain + no fetus in uterus on U/S |
Ectopic Pregnancy until proven otherwise
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Metrorrhagia esp after intercourse + no pain + normal sized uterus |
Polyp (endometrial or cervical)
|
|
|
What is the most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)?
Depression + constipation + AUB |
Hypothyroidism
|
|
|
What medication options are available for controlling severe menorrhagia?
|

see above
|
|
|
What medications are used in the treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)?
|

see above
|
|
|
What volume or duration of bleeding is considered abnormal uterine bleeding?
|
> 80mL /cycle (menorrhagia)
> 7 days bleeding (menorrhagia) < 24 hour day cycle (polymenorrhea) > 35 day cycle (oligomenorrhea) |
|
|
What is the most common clotting disorder that can cause menorrhagia? What lab values are abnormal?
|
Dx: von Willebrand’s disease (vWD)
Labs: ↑ bleeding time & abnormal PTT |
|
|
What is the most common cause of irregular heavy uterine bleeding?
|
Anovulation
|
|
|
What is the laboratory work-up for abnormal uterine bleeding?
|
Preg test
Pap smear (r/o cancer) Wet prep GC prob CBC Bleeding time PT/PTT/INR TSH +/- Endometrial biopsy |
|
|
For which type of cancer are women with PCOS at an ↑ risk and why?
|
Endometrial & breast cancer
Secondary to ↑ endogenous estrogens |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hirsutism in the US? What lab findings are used to make the diagnosis?
|
Mcc: PCOS
Findings: ↑ LH (LH : FSH > 3:1) ↑ total testosterone ↑ DHEA (normal DHEA-S) ↑ androstenediol |
|
|
What are the diagnostic features of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
|

see above
|
|
|
What is the treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
|

see above
|
|
|
What are the different types & treatment options for Pelvic Prolapse?
|

see above
|
|
|
With which kinds of vaginitis is it recommended to treat the sexual partner as well?
|
Trichomonas vaginalis & recurrent bacterial vaginosis
|
|
|
What drug is usd to tx both bacterial vaginosis & Trichomonas?
|
Metronidazole (Flagyl)
|
|
|
What substance is responsible for causing toxic shock syndrome? what is the tx?
|
Staph aureus endotoxin
Tx: remove source of bacteria (ie tampon) + supportive care Clindamycin or Penicillinase resistant β-lactamase antibiotics or Vancomycin for MRSA |
|
|
What is the complication of gonorrhea or chlamydia that infects the capsule of the liver?
|
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (perihepatitis)
|
|
|
What drugs are no longer used for gonorrhea due to resistance?
|
Fluoroquinolones
|
|
|
What are the potential symptoms of gonorrhea and chlamydial infections?
|
Often asymptomatic (esp in women)
Dyspareunia ***Bleeding after intercourse Purulent vaginal discharge Urethritis with purulent discharge Dysuria |
|
|
What are the diagnostic features of PID?
|
Lower abdominal pain + cervical motion or adnexal tenderness
Leukocytosis, new or purulent vaginal discharge, WBCs on wet prep, Temp > 101°F, Elevated ESR/ CRP |
|
|
What are the treatment options for PID?
|
Outpatient: Ceftriaxone + metronidazole + doxycycline
(Rocephin + Flagyl + doxy) Inpatient: IV Cefoxitin + doxycycline (then oral clindamycin + gentamycin) Ampicillin-sulbactam (Unasyn) + doxycycline (then oral doxycycline + metronidaxole) |
|
|
What is the treatment for genital warts?
|
Podophyllin, TCA, topical 5-FU, α-interferon injection, cryotherapy, laser therapy
|
|
|
Which STD can be mistaken for IBD due to its association with fistula formation?
|
Lymphogranuloma venereum
|
|
|
A sexually active woman presents with the classic symptoms of cystitis. Gram stain of the urine shows no organisms. What organism do you suspect is the cause of this pt’s symptoms?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
How is the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease made?
|
Lower abdominal pain + cervical motion tenderness or adnexal tenderness
Leukocytosis, new or purulent vaginal discharge WBCs on wet prep, Temp > 101°F, ↑ ESR/CRP |
|
|
What meds are used in the tx of PCOS?
|
OCPs
Progesterone Spironolactone (Aldactone) Statins (ie Simvastatin) Metformin (Glucophage) or clomiphene (Clomid, serophene) Exercise, weight loss |
|
|
What is the most common cause of female infertility?
|
Endometriosis
|
|
|
HYQ: When is an endometrial biopsy a necessary part of the work-up for abnormal uterine bleeding?
|
↑ bleeding in a woman > 35years old or with multiple risk factors
|
|
|
What is the treatment for gonorrhea? Chlamydia?
|
Gonorrhea: Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
Chlamydia: Doxycycline (Doxy) or azithromycin (Z-pack) |
|
|
What are the complications of PID?
|
Infertility, adhesion formation, chronic pelvic pain, tubo-ovarian abscess, ↑ risk of ectopic pregnancy
|
|
|
What is the presentation of the various stages of syphilis?
|
latent: asymptomatic
1°: solitary chancre ~ 3 weeks after exposure 2°: headache, malaise, fever, rash (palms/soles), lymphadenopathy, up to 12 weeks 3°: gummas, tabes dorsalis, proprioceptive ataxia, (+)Romberg sign, Argyll Robinson pupils |
|
|
What medications can be used in the treatment of syphilis?
|
Penicillin G, Doxycycline, Tetracycline
|
|
|
What are the distinguishing features of bacterial vaginosis, Candida vaginitis, and trichomonas infections?
|
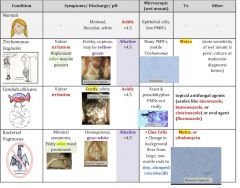
see above
|
|
|
What is the most important factor in endometrial cancer?
|
Grade > depth of myometrial invasion
|
|
|
What are the current recommendations for pap smears if pt has h/o NO abnormal pap smears?
|
Initiate screening at age 21 or 3 years after the onset of sexual activity
Frequency of pap smears: At least every 3 years (USPSTF) Annually in women under age 30+ years of age (ACS & ACOG) or every 2 years if using liquid based testing (aka thin-prep) Every 2-3 years if 30+ years of age and 3 consecutive normal pap smears (ACS and ACOG) or every 3 years if receiving pap smear +HPV testing Screening may be stopped at age 65 (USPSTF), 70 if adequate recent normal paps (ACS) or on an individual basis (ACOG) If hysterectomy for benign disease, there is no need to screen for cervical cancer |
|
|
What are the general treatment strategies for squamous cell cancer of the vagina?
|
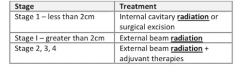
|
|
|
What is lichen sclerosis? How to manage/ tx?
|
Chronic inflammatory condition of the anogenital region, most commonly affecting postmenopausal women
Classic late findings – ivory or porcelain-white macules and plaques with pruritis Tx: low threshold for punch biopsy to r/o SCC; steroids (clobetasol) or pimecrolimus |
|
|
What are the tx options for fibroids?
|
Medications
Myomectomy Thermal destruction Endometrial ablation Hysterectomy |
|
|
Which type of endometrial cancer has a worse prognosis?
|
Type II (non-estrogen dependent)
|
|
|
What are the indications for an endometrial biopsy?
|
> 35 yrs: menometorrhagia or post-menopausal bleeding
< 35 yrs: menometorrhagia AND significant risk factors for cancer |
|
|
What is the treatment for endometrial cancer?
|
TAH/BSO + lymph node sampling
To preserve fertility, tx temporarily with progesterone until fertility is finished (only if cancer is caught early & responds well to treatment) |
|
|
What is the tx for a lesion found to be HGSIL on biopsy?
|
Repeat colposcopy every 6 months
If finished with fertility, consider excision with LEEP, cold knife conization, laser ablation |
|
|
What is the most common type of ovarian tumor?
|
Epithelial
|
|
|
Which kind of ovarian tumor has three or more different tissue types within the tumor? Are they benign or malignant?
|
Dx: Teratoma
Generally benign, but 1-2% can undergo malignant transformation |
|
|
Which type of ovarian tumors can cause precocious puberty through secretion of estrogen? Which cause virilization thru secretion of androgens?
|
Precocious puberty: granulose-theca cell tumors
Virilization: Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors |
|
|
What ultrasound findings are consistent with benign ovarian tumors? With malignant ovarian tumors?
|
Benign → cystic mass, smooth lesion edges, few septa
Malignant → irregularity, nodularity, many septa or thick septa, pelvic extension |
|
|
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
|
Often asymptomatic until late stage
Abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss Adnexal mass Changes in bowel habits Menstrual irregularities Ascites |
|
|
Which age group is most at risk for lichen sclerosis? What is the management of disease?
|
Age group: post-menopausal women
Tx: Topical steroids, pimecrolimus, punch biopsy |
|
|
What is the most common cause of a breast mass in a pt younger than 25 years old? What is the tx?
|
Dx: Fibrocystic breast change
Tx: eliminate caffeine, use OCPs |
|
|
What findings are suspicious on a mammogram?
|
Hyperdense regions & calcifications
|
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of gynecomastia?
|
Puberty (resolves spontaneously in 6mos – 2 years)
Medications: Spironolactone (Aldactone), Digitoxin, Cimetidine, Amiodarone, Ketoconazole, Haloperidol (Haldol), HIV HAART therapy Drugs: alcohol, marijuana, heroin, anabolic steroids Herbal agents: tea tree oil, lavendar oil Cirrhosis Hypogonadism (Klinefelter’s, hyperprolactinemia) Testicular germ cell tumor Hyperthyroidism Hemodialysis patients |
|
|
What is the work-up for a fibroadenoma appearing breast mass in a woman younger than 35 years of age?
|

|
|
|
A 34yo F presents with a smooth, mobile breast mass. On FNA, it is found to contain clear, non-bloody fluid. What is the diagnosis & management?
|
Dx: Fibrocystic breast change
Management: reassurance & f/u in 1 month |
|
|
A woman presents with bloody nipple discharge upon stimulation and a mass behind the areola. What is the management of the condition?
|
Excision or core biopsy
Intraductal lavage Surgical excision |
|
|
What does “orange peeling” of the skin on the breast indicate? New nipple retraction? Dimpling?
|
Peau d’ orange: Lymphatic obstruction
New nipple retraction: lactiferous duct involvement Dimpling: suspensory ligament involvement |
|
|
What is the next step in management of non-palpable calcified lesions identified on mammogram?
|
Ultrasound-guided needle localization for open biopsy
CXR |
|
|
What is the most common site for breast cancer?
|
Upper outer quadrant of the breast
|
|
|
How are most breast cancers detected in the US?
|
Screening mammography
|
|
|
A woman presents with breast tenderness, erythema, and orange peeling. Antibiotics for cellulitis fail to improve her symptoms. What do you suspect and what is the next step if this is the case?
|
Dx: Inflammatory carcinoma
Management: mastectomy, radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy |
|
|
Once you have ruled out invasive cancer, what is the management of LCIS? Why is drug therapy so effective?
|
Observation
+/- tamoxifen (Nolvadex/soltamox) or raloxifene (evista) optional bilateral mastectomy |
|
|
When is radiation therapy performed for invasive carcinoma of the breast?
|
Tumors > 5 cm, in conjunction with mastectomy
|
|
|
Why are core biopsies typically preferred over FNAs?
|
FNA carry 20% chance of false negative, so any false negative FNA requires a biopsy
|
|
|
HYQ: What is the most likely cause of bloody nipple discharge?
|
Intraductal papilloma
|
|
|
What is the most common breast cancer?
|
Invasive ductal carcinoma
|
|
|
Which type of breast disease matches the following?
Often p/w serous or bloody nipple discharge |
Intraductal papilloma
|
|
|
Which type of breast disease matches the following?
Most common mass in pts 35-50 |
Fibrocystic change of the breast
|
|
|
Which type of breast disease matches the following?
Most common tumor in teen and young women |
Fibroadenoma
|
|
|
Which type of breast disease matches the following?
Breast mass accompanied by redness, pain & warmth |
Inflammatory carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for endometrial cancer?
|
Exogenous estrogen
High fat diet PCOS, Diabetes, HTN, age Obesity, colon cancer, nulliparity |
|
|
What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer?
|
Ovulation
Nulliparity Family history (BRCA) |
|
|
What serum marker may be elevated in cases of endometrial cancer? Ovarian cancer?
|
Endometrial cancer → may CA-125
Ovarian cancer → usually CA-125 |
|
|
What is the next step in the management of CIN 2 cervical lesion identified on biopsy in a woman who has completed fertility?
|
Excision with LEEP
Conization Laser ablation |
|
|
What is the next step in the management of an ASCUS pap smear with a negative HPV test? A (+) HPV test?
|
(-) HPV → repeat pap smear
(+) HPV → colposcopy |
|
|
What is the next step in the management of an AGUS pap smear?
|
Colposcopy with endocervical curettage
If > 35years or risk factors for endometrial cancer → EMB |
|
|
What type of ovarian tumor is a/w psammoma bodies? Estrogen excess? Androgen secretion?
|
Psammoma bodies → serous cystadenoma
Estrogen excess → Granulosa cell tumor Androgen excess → Sertoli-leydig cell tumor |
|
|
What is the tx for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast?
|
Lumpectomy, with or without radiation
|

