![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enzyme for Fatty Acid Chain |
Thiolase |
|
|
Enzyme for Acyl-CoA (fatty acyl-CoA) |
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (AD) |
|
|
Enzyme for Trans-Delta^2-Enoyl-CoA |
Enoyl-CoA Hydratase (EH) |
|
|
Enzyme for 3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA |
3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (HAD) |
|
|
Enzyme for Beta-Ketonacyl-CoA |
Beta-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase (KT) |
|
|
Product of Thiokinase |
Acyl-CoA (fatty acyl-CoA) |
|
|
Product of Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (AD) |
Trans-delta^2-Enoyl-CoA |
|
|
Product of Enoyl-CoA Hydratase (EH) |
3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA |
|
|
Product of 3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA-dehydrogenase (HAD) |
Beta-Ketonacyl-CoA |
|
|
Product of Beta-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase (KT) |
Fatty Acyl-CoA (2 C atoms shorter)
and
Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
Structure of Acyl-CoA (Fatty Acyl-CoA) |

|
|
|
Structure of Trans-delta^2-Enoyl-CoA |
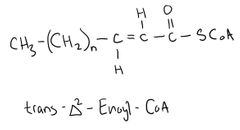
|
|
|
Structure of 3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA |

|
|
|
Structure of Beta-Ketonacyl-CoA |
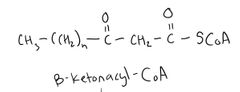
|
|
|
Structure of Fatty Acyl-CoA and Acetyl-CoA |

|
|
|
What does activation of a fatty acid mean? |
It means that ATP and CoASH came together turn the FFA into an Fatty Acyl-CoA. |
|
|
What enzyme requires FAD? |
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase |
|
|
What enzyme consumes H20? |
Enoyl-CoA |
|
|
What enzyme requires NAD+? |
3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase |
|
|
What enzyme consumes a CoA? |
Thiolase |
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for the activation of fatty acids, from Fatty Acyls to Fatty acetyl-CoA? |
Thiokinase |
|
|
What is cAMP? |
A second messenger, responsible for the phosphorylation cascade that promotes glycogen breakdown to glucose. Insulin inactivates (fed state) this molecule, promoting the glycogen synthesis. |

