![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Three Ketone Bodies |
Acetone Acetoacetate Beta-Hydroxybutyrate |
|
|
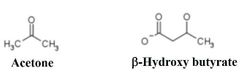
Structure of Acetone |
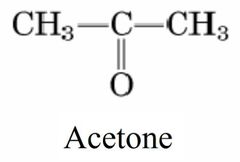
|
|
|
Structure of Acetoacetate |

|
|
|
Structure of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate |
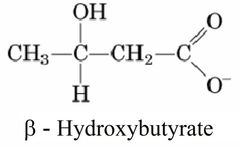
|
|
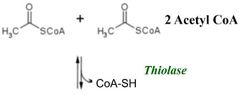
Step 1 |

|
|
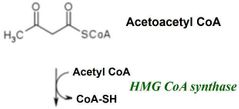
Step 2 |
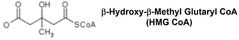
|
|
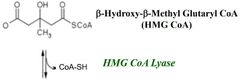
Step 3 |
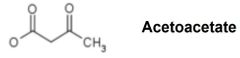
|
|
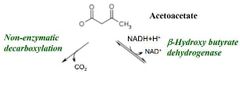
Step 4 |
|
|
|
Acyl vs Acetyl |

|
|
|
Pathway of Acetone to Lungs |

|
|
|
How is acetone formed? |
Spontaneous decarboxylation of Acetoacetate |
|
|
Which ketone body is least common in the body? |
Acetone.
It is highly volatile, consequently it is produced in very small quantities.
It cannot be converted back to Acetyl-CoA so it is excreted in urine and lungs. |
|
|
What is responsible for fruity breath of a person in Ketosis? |
Acetone. |
|
|
How much ATP is produced from a single cycle of Beta-Oxidation? |
5 ATP per cycle |
|
|
Which organ cannot breakdown Ketone Bodies? |
The Liver! |
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for oxidizing Acetoacetate to Acetoacetyl-CoA? |
Succinyl CoA-acetoacetate CoA Transferase |
|
|
Which is bigger, Acyl-CoA or Acetyl-CoA? |
Acyl-CoA is bigger. |
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for regulating the entry of long chain fatty acids into the Mitochondria? |
Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1) |
|
|
CPT-1 activity... |
Low in fed state (decreased FA oxidation) High in starvation (increases FA oxidation) |
|
|
What regulates CPT-1? |
Malonyl CoA |
|
|
What enzyme forms Malonyl CoA and from what? |
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase forms Malonyl CoA. It is formed from Acetyl-CoA during the fed state. |

