![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enzyme 1: Citrate Synthase |
Citrate (A) |
|
|
Enzyme 2: Aconitase |
Isocitrate (B) |
|
|
Enzyme 3: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
a-Ketoglutarate (C) |
|
|
Enzyme 4: a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase |
Succinyl-CoA (D) |
|
|
Enzyme 5: Succinyl-CoA Synthetase |
Succinate (E) |
|
|
Enzyme 6: Succinate Dehydrogenase |
Fumarate (F) |
|
|
Enzyme 7: Fumarase |
L-Malate (G) |
|
|
Enzyme 8: Malate Dehydrogenase |
Oxaloacetate (H) |
|
|
Enzyme 20: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase |
Acetyl CoA (Y) |
|
|
Oxaloacetate (H) + Acetyl CoA (Y) = |
Citrate (A) |
|
|
Irreversible Reactions |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (20) Citrate Synthase (1) Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (3) a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (4) |
|
|
Reactions that produce CO2 |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (20) Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (3) a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (4) |
|
|
Structure: Pyruvate (X) |

|
|
|
Structure: Acetyl-CoA (Y) |

|
|
|
Structure: Citrate (A) |
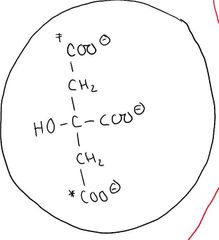
|
|
|
Structure: Isocitrate (B) |

|
|
|
Structure: a-Ketoglutarate (C) |

|
|
|
Structure: Succinyl-CoA (D) |

|
|
|
Structure: Succinate (E) |

|
|
|
Structure: Fumarate (F) |

|
|
|
Structure: L-Malate (G) |

|
|
|
Structure: Oxaloacetate (H) |

|
|
|
Reactions that require CoASH |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (20) a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (4) |
|
|
Reactions that produce CoASH |
Citrate Synthase (1) Succinyl-CoA Synthetase (5) |
|
|
Reactions that require NAD+ (Produce NADH + H) |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (20) Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (3) a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (4) Malate Dehydrogenase (8) |
|
|
Reactions that require FAD (Produce FADH2) |
Succinate Dehydrogenase (6) |
|
|
Reactions that produce GTP (sometimes ATP) |
Succinyl-CoA Synthetase (5) |
|
|
ATP yield per NADH |
2.5 ATP |
|
|
ATP yield per FADH2 |
1.5 ATP |
|
|
ATP yield per Acetyl-CoA |
10 ATP ____________________ 3 NADH = 7.5 ATP 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP 1 GTP = 1 ATP |
|
|
ATP yield of Glucose (6 C's) |
32 ATP |
|
|
ATP yield of 16 C Fatty Acid chain |
108 ATP |
|
|
ATP yield per C from Fatty Acid Chain |
6.8 ATP per C |
|
|
ATP yield per C from Glucose |
5.3 ATP per C |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
The two substrates for Citrate synthesis... |
Oxaloacetate and Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
What "Global Hormone" interacts with Pyruvate Dehydrogenase? |
Insulin |
|
|
Total ATP yield of a molecule of Glucose |
32 ATP |
|
|
Which reaction has a very high delta G? |
Malate Dehydrogenase. + 33.5 Kj
This very high delta G means that a exceptionally large concentration of reactant (Malate) must be present in order to drive the reaction forward towards the formation of Oxaloacetate (product). |
|
|
What two forms of regulation govern Pyruvate Dehydrogenase? |
Product (NADH and Acetyl-CoA) Inhibition
Covalent Modification |
|
|
Product Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase |
This occurs naturally when there is a very high concentration of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase's products (NADH). Once the cell has enough the products they will allosterically bind to the enzyme effectively inhibiting it. |
|
|
Covalent Modification of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase |
Controlled by Insulin. |
|
|
How many sub reactions does PDH undergo? |
PDH is actually a multi enzyme complex. It is comprised of 5 different reactions. |
|
|
PDH: Rxn. 1 |
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP) - bound to E1 - decarboxylates pyruvate, yielding a hydroxyethyl-TTP carbanion. |
|
|
PDH: Rxn. 2 |
Lipoic Acid - covalently linked to a Lys on E2 (lipoamide) - accepts the hydroxyethyl carbanion from TTP as an acetyl group. |
|
|
PDH: Rxn. 3 |
Coenzyme A (CoA) - substrate for E2 - Accepts the acetyl group from lipoamide. |
|
|
PDH: Rxn. 4 |
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD) - bound to E3 - Reduce to Lipoamide. |
|
|
PDH: Rxn. 5 |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) - Substrate for E3 - Reduced by FADH2. |

