![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Estrous |
Most animals Endometrium is absorbed by the uterus Sexual receptivity is limited, called heat Length and freq of estrous cycle varies: bear and wolves=1 a year, elephants = several a year, rats=throughout the year |
|
|
Difference appearance of reproductive structures but similar in function |
Glans of penis and clitoris Scrotum and the labor majora Skin on penis and the labia minora |
|
|
2 reactions in sexual response in both genders |
Vasocongestion: filling of tissue with blood Myotonia: increased muscle tension, smooth and skeletal muscles may show sustained or rhythmic contractions Includes 4 phases: excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution |
|
|
Excitement phase |
Vasocongestion: enlargement of penis and clitoris, testicles, labia, and breast and vaginal lubrication Myotonia: May result nipple erection or tension in arms and legs |
|
|
Plateau phase |
Excitement responses continue as a result of direct stimulation In females, vasocongestion of outer third of vagina, expansion of inner two thirds vagina and elevation of uterus to receive sperm Autonomic nervous system increases breathing and heart rate |
|
|
Orgasm |
Involuntary contraction Shortest phase In male, emission is the contraction of glands and ducts of reproductive tract, forced semen into urethra In female, uterus and outer vagina contract but inner 2/3 do not |
|
|
Resolution |
Competes cycle and reverses the response of earlier stages Vasocongestion organs return to normal size, muscle relax Changes are completed in 5 minutes but some can take as long as an hour |
|
|
Refractory period |
Last anywhere from a few min to an hour No orgasm or erection Females get multiple orgasms |
|
|
Copulation |
2-5 mL of sperm transferred with 70- 130 mIllion sperm Semen coagulates to keep in place until sperm reaches cervix Cervix had anticoagulants that liquefy semen |
|
|
Conception |

Fertilization of egg by sperm Occurs in oviduct 24 hours later, zygote begins to divide by mitosis (cleavage) 3-4 days later, blastocyst reaches uterus and implants in endometrium |
|
|
Gestation |
Pregnancy Humans: 266 days / 38 weeks Rodents: 21 days; cows:270, elephant: 600 Correlates with body size and maturity of young at birth |
|
|
First trimester |
Time of most radical change Embryonic stage begins after implantation and lasts 8 wks Secretes human chorionic gonadatropin (hCG) which acts like LH to maintain secretion of progesterone and estrogen for first few months (hCG in urine to detect pregnancy) |
|
|
Twins in First trimester |
Splitting of embryo during first month (monozygotic twins vs dizygotic twins where two follicles release and implant |
|
|
First trimester continued |
During first 2-4 wks, embryo obtains nutrients directly from endometrium Trophoblast combines with endo to form placenta (allows for nutrients, gas exchange, immune protection) Blood travels through arteries in umbilical cord to the placenta and returns to embryo via umbilical vein |
|
|
Fetal blood flow 4 th week |
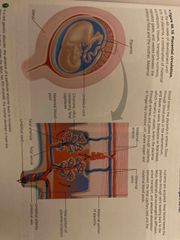
Maternal arteries to umbilical arteries to umbilical veins to maternal veins |
|
|
First trimester and organ development |
Wk 3: brain, heart, blood cells, circ system, spinal cord, digestive system Wk 4: bones, face limbs cont heart and brain, nervous system Wk 5: eyes, nose, kidneys lungs, cont heart(valves), brain, nervous system Wk 6: hands feet digits, cont heart, brain, circ system |
|
|
Second trimester |
Fetus grows and is active (can feel it move) Uterus grows and pregnant is obvious Hormonal levels stabilize as hCG declines, corpus luteum deteriorates, placenta takes over secretion of progesterone to maintain pregnancy |
|
|
Third trimester |
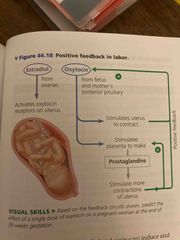
Fetus grows and fills space Moms organs compress, frequent urinate and digestive blockages Labor is regulated by prostaglandins and hormones: estradiol and oxytocin |
|
|
Lactation |
Hypothalamus signals AP to secrete prolactin and PP oxytocin |
|
|
Foreign offspring |
Women’s body does not reject (half dna from dad) May be due to suppressed immune system (symptom of arthritis become less severe during pregnancy) |
|
|
Contraception |
Deliberate prevention of pregnancy Achieved in number of ways that fall into 3 categories: 1.Preventing release of eggs and sperm 2. Keeping sperm and egg apart 3. Preventing implantation of an embryo |
|
|
Rhythm method |
Natural family planning Refrain from intercourse when conception is most likely Pregnancy rate is 10-20% |
|
|
Coitus interruptus |
Withdrawal method Unreliable |
|
|
Barrier method |
Block fertilization with a pregnancy rate less than 100% Condoms Diaphragm Cervical caps Sponges |
|
|
Intrauterine devices IUD |
Inserted into uterus and interfere with fertilization and implantation Less than 1% pregnancy Increase levels of progesterone thickens wall of uterus which prevents sperm entry in cervix |
|
|
Birth control pills |
Rate less than 1% Progesteron-high levels prevents pregnancy by negative feedback (decrease GnRH, decrease FSH and LH). This inhibits follicle development (no increase in estradiol so no surge in LH) prevents ovulation Inhibits sperm from penetrating through cervix by making mucus that blocks cervix Estradiol levels control bleeding through FSH and LH |
|
|
3 types of birth control |
Oral estrogen/progesterone levels mimics pregnancy (inhibits ovarian cycle)-daily Progesterone only-implants or patch Continuous extended use injections 3 months to weeks Vaginal ring monthly |
|
|
Sterilization |
Tubal ligation: tie off oviduct Vasectomy: tie off vas deferens Abortion: termination Spontaneous abortion: miscarriage, in 1/3 of pregnancies Drug U486 (mifepristone): terminates a pregnancy non surgically within the first 7 weeks |
|
|
Morning after pills |
Emergency contraceptive 2 types interrupt uterine: 1. Preven: series of synthetic progesterone pills that disrupts normal cycle making implantation difficult for 72 hours 2. RU486: mifepristone is a progesterone receptor antagonist blocking in uterus so endo is sloughed off Plan B: prevents fertilization by inhibition of ovulation and thickening of cervical mucus for 72 hours |
|
|
Intravaginal ring |
New device Prevents pregnancy Releases low doses of an antiretroviral drug that reduces risk of HIV and herpes infection |
|
|
Phexxi |
Spermicide Contains: lactic acid, citric acid, bitartate, pH 3.4-4.5 Mechanism: after sex, pH of vagina rises to keep sperm alive. This lowers pH killing sperm 86% effective |
|
|
Detecting disorders |
Ultrasound imaging Amniocentesis n chorionic villus sampling (genetic analysis) Sample of maternal blood: contains fetus DNA (genome) |
|
|
Infertility |
Causes vary STIs can cause infertility and are most preventable In vitro: embryos are implanted at 8 cell stage |
|
|
Gamete intrafallopian transfer |
Mix egg and sperm solution |

