![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What specific embryonic germ layer gives rise to the GU system?
|
Intermediate mesoderm
|
|
|
Describe the embryonic development of the cloaca.
|
Cloaca, at first, is a common opening between the GU and GI tracts.
A URORECTAL septum forms and divides the cloaca into GU sinus (becomes urinary bladder) and anorectal canal (forms rectum) |
|
|
What is the specific embryonic germ layer origin of the urorectal septum?
|
Splanchnic LPM
|
|
|
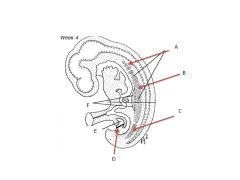
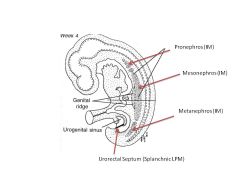
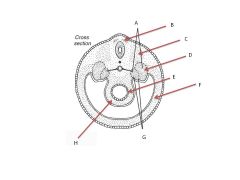
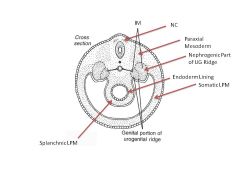
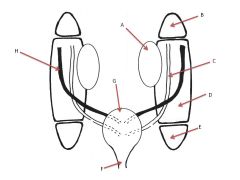
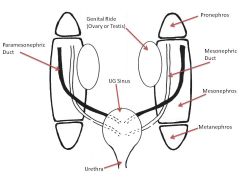
What structures comprise the urogenital ridge?
|
Genital Portion
Nephrogenic portion (Pronephros, Mesonephros, Metanephros) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Describe the embryonic development of the following structures in males:
-Genital portion of UG Ridge -Pronephros -Mesonephros -Metanephros -Mesonephric Duct -Paramesonephric Duct |
In Males:
-Genital portion of UG Ridge: Testis -Pronephros: Never becomes functional in mammals; leaves behind pronephric duct -Mesonephros: Functions as early kidney for a few weeks -Metanephros: Develops into excretory structures of adult kidney: DCT, PCT -Mesonephric Duct: Becomes Wolffian Duct; Drains into Developing Bladder; forms URETERIC BUD (extends into metanephros) which forms collecting ducts of kidney (ureters, renal pelvis, major/minor calyxes) ALSO becomes Epidydymis, Vas Deferens, SVs, Ejaculatory Duct (Hugs Testis) -Paramesonephric Duct: Becomes Mullerian Duct; doesn't drain into anything. DEGENERATES. |
|
|
Describe the embryonic development of the following structures in females:
-Genital portion of UG Ridge -Pronephros -Mesonephros -Metanephros -Mesonephric Duct -Paramesonephric Duct |
In Females:
-Genital portion of UG Ridge: Becomes Ovary -Pronephros: Never becomes functional in mammals; leaves behind pronephric duct -Mesonephros: Functions as early kidney for a few weeks -Metanephros: Develops into all excretory structures of adult kidney (PCT, DCT)--Induction by Ureteric bud from Mesonephric Duct -Mesonephric Duct: Drains into developing bladder; forms Ureteric Bud; initially forms Wolffian Duct but in absence of testosterone, DEGENERATES -Paramesonephric Duct: Hugs Ovary; gives rise to fimbrae, fallopian tube, uterus, proximal vagina |
|
|
What does the ureteric bud connect? What effect does it have on the latter structure?
|
Ureteric Bud connects Mesonephric Duct and Metanephric Cap
Bud induces metanephric cap to form nephrons and then form collecting system |
|
|
Describe the development of the following structures in relation to the bladder in males:
Paramesonephric Duct Mesonephric Duct Urerteric Bud |
Bladder Growth incorcoporates part of Mesonephric Duct and Ureteric bud into Bladder Wall
Paramesonephric Duct Degenerates Mesonephric Duct moves inferiorly toward urethra over Ureteric Bud |
|
|
Describe the development of the following structures in relation to the bladder in females:
Paramesonephric Duct Mesonephric Duct Urerteric Bud |
Bladder Growth incorporates part of Mesonephric Duct and Ureteric Bud into Bladder Wall
Mesonephric Duct DEGENERATES Paramesonephric Ducts FUSE and form Vaginal Plate (forms distal vagina) Paramesonephric Duct and Vaginal Plate grow and move inferiorly toward Urethra |
|
|
How might a double uterus occur?
|
Formation of uterus requires fusion of paramesonephric ducts followed by resorption of the partition between the two ducts to form a single uterus. Lack of fusion of the paramesonephric ducts results in two uteruses.
|
|
|
What threat would an unresorbed uterine septum pose to a developing embryo?
|
If embryo implants itself in septum (rather than uterine wall), would be difficult for fetus to acquire adequate blood supply.
|
|
|
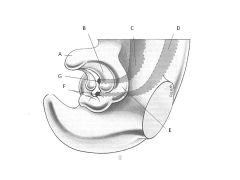
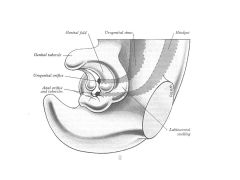
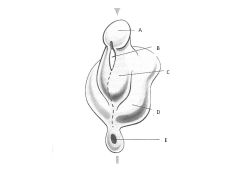
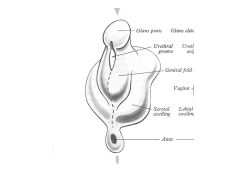
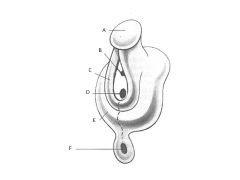
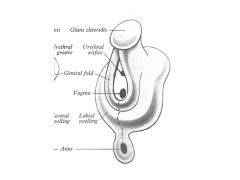
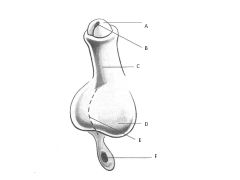
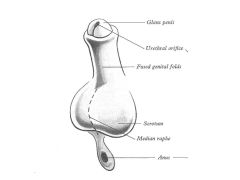
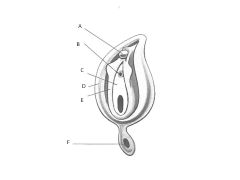
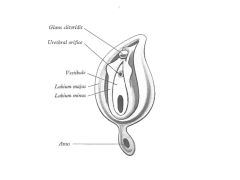
How does the developmental anatomy of the external genitalia differ in males and females?
|
In males:
Genital tubercle-->Glans Penis Genital Fold FUSES Labioscrotal swelling-->Scrotal Swelling-->Scrotum Females: Genital Tubercle-->Glans Clitoris Genital fold-->Labium Minus Labioscrotal swelling-->Labial Swelling-->Labium Majus |
|
|
1What are the male/female external genitalia homologs?
|
Fused Genital Folds in Males = Labium Minus
Scrotum = Labium Majus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List the erectile tissues of the male and female external genitalia. Which are homologs?
|
Female:
Corpus Spongiosum: forms bulb of vestibule and bulb of penis (contains urethra) Corpus Cavernosum: forms crura (left and right crus) of clitoris and crura (left, right) of shaft of penis |
|
|
List the muscles that overly the erectile tissues of the female and male external genitalia.
|
Bulbospongiosus muscle over corpus spongiosum
Ischiocavernosus over corpus cavernosum |

