![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dendrite |
Before cell body and carried message towards cell body |
|
|
Axon |
After cell body carries messages away |
|
|
Sensory neuron |
Takes msg from receptor to CNS, long dendrite and short axon |
|
|
Motor neuron |
Takes msg away from CNS to effectors, short dendrite long axon |
|
|
Intermeuron |
Found only in CNS (brain/spinal cord) |
|
|
Nerve impulse transmission |
How impulse moves along neuron, when threshold energy is reached neuron fires all or nothing response |
|
|
All or nothing response |
When nerve responds to stimulus independent of strength of stimulus |
|
|
Resting potential |
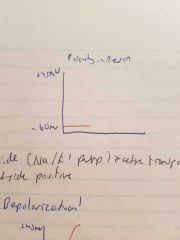
Na outside k inside through pumps (active transport), outside + inside - |
|
|
De polarization (action potential) |

Na flows in through gates, inside + outside - |
|
|
Repolarization (action potential) |
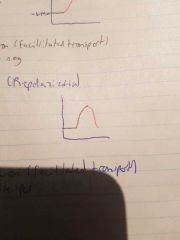
K+ flows out of neuron through k gates, inside - outside + |
|
|
Refractory period |
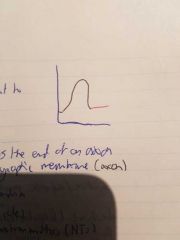
Na/k pump return na+ to outside and k+ to inside (active transport) |
|
|
Synapse (end of axon) |

Ca2+ release, contractor proteins attached to vesicles contract, vesicles pulled towards members, vesicles release NTs by exocytosis(active), NT diffuse across synapse, NT stimulate receptors on dendrite, enzymes are released to neutralize NTs |
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system |
NTs release adrenaline that is broke down by monamine oxidase |
|
|
Parasympathetic nervous system |
Acetylcholine is broken down by acetycholinesterase |
|
|
Soltatory Conduction |
Produces myelin sheath to insulate neuron, depolarization only occurs at nodes of ranvier, increase impulse speed |
|
|
Reflex arc |
Quick involuntary response that doesnt get processed by brain, receptor starts response, sensory neuron takes message to CNS, only one interneuron which makes impulse travel quickly, motor neuron takes impulse away from CNS to effector |
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Controls heartrate, breathing, swallowing |
|
|
Thalamus |
Relay station for sensory input, decides what's important |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Muscular coordination |
|
|
Corpus collosum |
Connects two hemispheres |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Neuro endocrine control, controls pituitary |
|
|
Cerebrum |
High thinking and consciousness |
|
|
Frontal cerebrum |
Voluntary muscle movement and problems solving |
|
|
Periatal |
Pain and temp |
|
|
Temperal |
Hearing, smelling, musical memories |
|
|
Ocipital |
Vision combined with other senses |
|
|
Neuroendocrine control |
Hypothalamus controls hormones, control of adrenaline, nerve runs directly from hypothalamus to adrenal medulla, stimulated by fight or flight response |

