![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the relationship between molecular weight and mobility on SDS PAGE? |
Molecular weight and mobility have a linear relationship in SDS-PAGE. This is because secondary structure that might distinguish one protein from another is disrupted by the SDS. |
|
|
What is the purpose of SDS in PAGE? |
SDS denatures the protein and gives it a uniform negative charge. SDS by itself does not break disulfide bonds. This requires a sulfhydryl reagent like DTT which reduces the disulfide bond the S-S bond breaks it into two S-H groups. |
|
|
SDS PAGE is commonly used to purify enzymes in preparation for enzymatic analysis. True or False |
False |
|

If you added a relatively short molecule with an isoelectric point of 10 to a two dimensional gel as described in class, where would it appear? |
Lower right |
|

Which would be pelleted first during centrifugation? |
Whole nuclei are largest and would pellet first, followed by nuclei, microsomes and finally polyribosomes. Microsomes are small membrane bounded vesicles that pre-exist in the cell or are formed during homogenization. |
|
|
How is HPLC different than normal chromatography? |
Because the beads are smaller with more surface area a higher pressure is required to force the sample through the column, but the separation is much more efficient with HPLC compared to traditional column chromatography. HPLC is applicable to all forms of chromatography, including size exclusion and ion exchange. |
|

Which of these peptides would emerge first from a size exclusion column? |
(Remember “d” stands for “Daltons” and is the molecular weight of a larger molecule.) The largest amino acid (10,000d) would emerge first. |
|

How are tightly bound peptides most often released from an ion exchange column? |
As explained in the video, increasing salt concentrations are normally used to release bound proteins. It might be possible to use pH, but this is not normally the case. The correct answer is increasing salt. The salt displaces the protein bound to the charged groups on the chromatographic resin. |
|

What living cells are required for the preparation of a monoclonal antibody? |
A tumor cell and an antibody producing cell |
|

Western blotting: |
All of the above |
|

NMR has the capacity to determine what? |
NMR is able to determine which hydrogen molecules are associated together in the native protein. It would therefore be useful to determine secondary and tertiary and even quaternary structure of a protein. It would not be useful to determine amino acid sequence, which can be determined with a Mass Spec. Sadly, we did not have time to discuss this concept in class. |
|

X-ray crystallography requires what? |
X-ray crystallography requires that the proteins form into a crystalline lattice. It is the structures within this lattice, which produces the needed diffraction of the x-ray beam. |
|

In a mass spec analysis, if a protein is broken exactly in half one half the time by the electron beam, what would you expect to see. |
There would be two peaks. One of these would be the intact protein, and the other would be the two halves of the protein. Because this occurs half the time, the intensity of the two peaks would be equal. |
|

Which would pellet first in differential centrifugation? |
Nuclei |
|

The difference between HPLC and conventional chromatography is: |
The amount of surface area of resin in contact with solution |
|

The difference between SDS PAGE and gel filtration chromatography is: |
The relative appearance of differently sized molecules |
|

What are you able to change with dialysis? |
A & B |
|

Which of the above peptides would be retained by a negatively charged ion exchange column at neutral pH. |
Poly lysine MW= 2000 d |
|
|
Which would be retained at pH 13? |
None |
|
|
Which would emerge first from a polyacrylamide gel run as described in the presence of SDS? |
C Poly glutamic acid MW=1000 d |
|

What is the effect of SDS on a protein |
B & C |
|

You have a peptide with a single cysteine residue that you are separating by gel filtration (size exclusion) chromatography. The peptide presently elutes from the column much earlier than you expected. How might you enable this peptide to emerge from the column at a position reflective of its primary structure? |
Add a dithiothreitol, a sulfhydryl reagent. |
|

According to our discussion in class, monoclonal antibodies are not normally used for the following purposes: |
X-ray diffraction studies to determine protein 3 dimensional structure. |
|

Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are similar in the following way(s). |
Binding of two antigen molecules |
|

ELISA |
None of the above |
|

In western blotting: |
An antigen is identified with a tagged antibody |
|

The name for solid phase peptide synthesis comes from: |
The fact that the growing chain is attached to a small particle |
|
|
In a mass spectrometry only volatile molecules, generally with molecular weights lower than 10,000 d can be analyzed. True or False |
False |
|

SDS is added to proteins prior to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the following reason(s). |
To denature the protein |
|

Differential centrifugation is useful for: |
Separation of nuclei from polyribosomes |
|

A polyclonal antibody differs from a monoclonal antibody for the following reason(s): |
The monoclonal antibodies recognize the same region on the antigen, while polyclonal antibodies may recognize many sites on the antigen. |
|
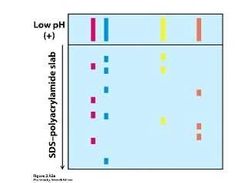
Where would you expect the following peptide to be found in the above two-dimensional gel electrophoresis? {Arg-Pro-Val-Ala-Gly} |

Bottom right |
|

How are SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and molecular exclusion chromatography similar? |
Both separate proteins according to size |
|

If bacteria were grown in medium composed of Nitrogen 15 for many generations (the DNA would thus be maximally dense) and then transferred to medium containing only nitrogen 14 for one full generation, how would you describe the density of the resulting DNA? |
All would be intermediate density |
|

Above is a DNA sequence that is to be used as a template. What would be the sequence of the newly synthesized DNA? (Remember, DNA s always written with the 5’ end first) |

NOT A CHANGE |
|
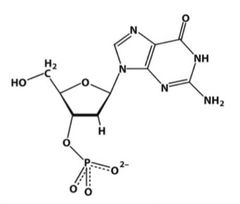
What is the proper name of the above molecule? |

3’ Deoxyguanine monophosphate |

