![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
145 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
isoelectric point |
the pH-level at which a particular molecule carries no net electrical charge. it's shortened to "pl". At pH below their pl, proteins carries a net positive charge. |
|
|
alanine |
a-amino acids, it's codons are GCU GCC GCA GCG |
|
|
såpemolekyl |
CH3-(CH2)16-COONa CH3-(CH2)16-COOK |
|
|
2-hydroxypropanal |
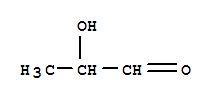
|
|
|
dihydroxyacetenone |
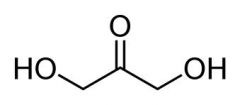
|
|
|
hydroxypropanoic acid |
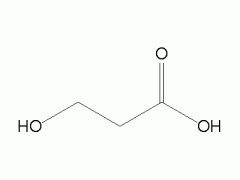
|
|
|
propanal |
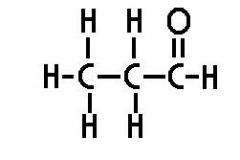
|
|
|
pOH level of pure water |
7 |
|
|
cysteine |
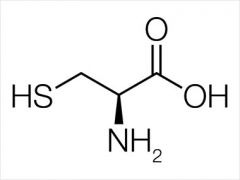
|
|
|
dalton |
enheten u for massen til et atom |
|
|
metalloids |
halvmetaller |
|
|
coordinate covalent bond |
a covalent bond in wich both electrons come fro the same atom |
|
|
electromotive force (emf) |
the induced difference of potential between electrodes emf = E (+) - E (-) force in a galvanic cell |
|
|
acetate can be formed in the reaction of |
glucose with methanol |
|
|
carboxylic acid |
HOOC-COOH |
|
|
At room temperature pH+pOH in water is? |
14 |
|
|
at equilibrium, the rate of product formation is the same as the rate of? |
reactant formation |
|
|
the stronger the acid the lower? |
pKa pKa= -log Ka |
|
|
nitrate (NH3) reacts with water to form? |
alakline (basisk) løsning |
|
|
aminogruppe |
NH2 |
|
|
det enkleste av ketonene? |
acetone, CH3CH3 |
|
|
C5H10O5 |
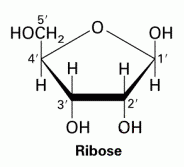
|
|
|
Strukturformel til serine |
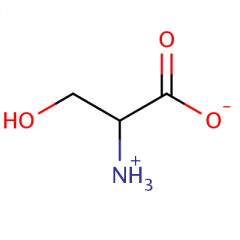
|
|
|
acetic acid (eddiksyre) |
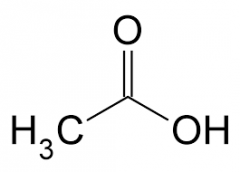
|
|
|
ribose, serine and 2-hydroxypropanoic acid can all react with acetic acid and form? |
ester |
|
|
2-bromo-2-methylbutane with NaOH forms? |
2-methylbut-1-en |
|
|
dioxyribose is an |
aldopentose |
|
|
fats are esters of? |
glycerol and fatty acids |
|
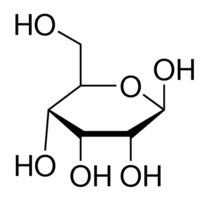
|
cyclic form of aldohexose |
|
|
what make up a N-glycosidic bond? |
it has oxygen replaced with nitrogen |
|
|
Substances containing N-glycosidic bonds are know as? |
glycosylamine E.g. nucleosides like adenosine |
|
|
peptides in water could have the charge? |
positive, negative and 0 |
|
|
-S-S-bonds/disulfide bond effects? |
the shape of the protein
|
|
|
in the dipeptide ala-gly alanine has? |
a free amino group |
|
|
an oligosaccharide is? |
a saccaride polymer containing a small number of monosaccharides. They are commonly found on the plasma membrane of animal cells where they can play a role in cell-to-cell recognition. Glycoproteins contains oligosaccharides. |
|
|
C7H60 |
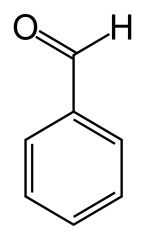
benzenaldehyd |
|
|
C6H60 |
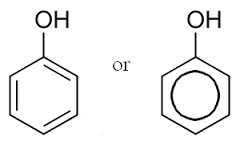
phenol |
|
|
C6H6 |
benzene |
|
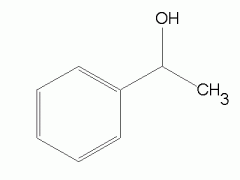
|
phenylethanol |
|
|
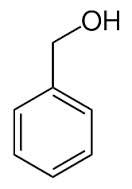
phenylmetanol |
|
|
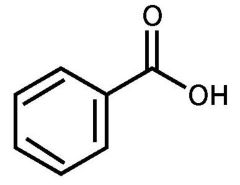
benzoic acid |
|
|
CH3COOH, pH? |
acetat |
|
|
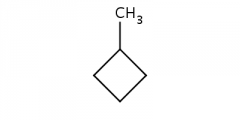
methylcyclobutane |
|
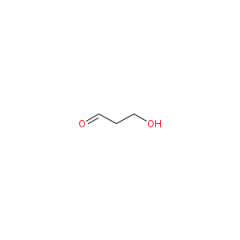
C3H6O2 |
3-hydroxypropanal |
|
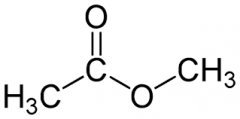
|
methyl acetate |
|
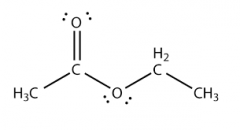
|
ethyl formate |
|
|
amphoteric substance |
an oxide of an element that acts both as an acid and base E.g. water |
|
|
heterocyclic |
a cyclic compound with at least two different elements as members of it's ring E.g. the DNA bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine |
|
|
CH3CH(NH2)COOH |
alanine |
|
|
lysine |
amino acid |
|
|
AAA, AAG are codons to the amino acid? |
lysine |
|
|
glycine |
amino acid |
|
|
GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG are codons to? |
Glycine |
|
|
cysteine |
amino acid |
|
|
UGU UGC are codons to which amino acid? |
cysteine |
|
|
lipides will hydrolyse in NaOH-solution and form? |
glyserol and sodium salts of fatty acids |
|
|
Fe2(SO4)3 |
iron(III)sulfate(IV) |
|
|
Calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with water to give? |
hydroxides |
|
|
ethanol are isomer to? |
dimethyl ether |
|
|
glucose are isomer to? |
fructose |
|
|
acetic acid are isomer to? |
methyl methanoate |
|
|
propanoic acid are isomer to? |
methyl acetate |
|
|
[H+] = [OH-] [H+] + [OH-] = 2x10-7M Kd < 10-7 pH in water in these conditions are? |
7 |
|
|
ethanothiol and cysteine both contains? |
sulfur |
|
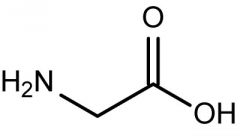
C2H4NO2 |
glycine |
|
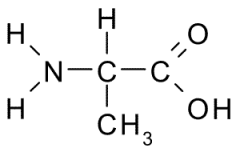
C3H7NO2 |
alanine |
|
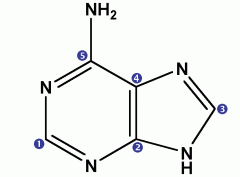
C5H5N5 |
adenine |
|
|
Ketones are oxidation products of? |
secondary alcohols |
|
|
substitution reaction |
a reaction where one functional group is replaced by another |
|
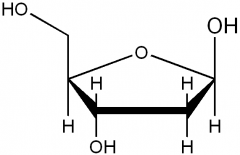
|
deoxyribose |
|
|
potassium |
kalium |
|
|
1L = ?cm3 |
1000cm3 |
|
|
sodium |
natrium |
|
|
sodium carbonate |
Na2CO3 |
|
|
kjemisk formel for glukose og fruktose? |
C6H12O6 |
|
|
A product of the addition of an alcohol to a ketone. Which product is this?
|
hemiketal |
|
|
carboxylic acids are oxidation products of? |
aldehydes |
|
|
P4O10 reacts with water to give? |
phosphoric acid H3PO4 |
|
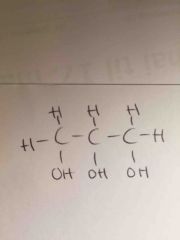
|
glyserol |
|
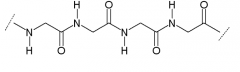
|
α-peptide |
|
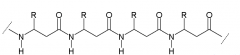
|

|
|
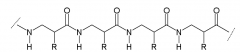
|

|
|
|
sulfuric acid, ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen sulfid in increasing acidic strength order |
NH4OH, H2S, H2SO4 |
|
|
NH4HSO4 |
ammonium hydrosulfate |
|
|
sulfur |
svovel |
|
|
NH4HCO3 |
ammonium bicarbonate |
|
|
MnO4- |
permanganate |
|
|
which solution is being decolorized by all organic compounds with double og triple bounds between the C-atomes? |
bromide solution |
|
|
the addition reaction between pent-1-en + Br2 gives? |
1,2-dibrompentane |
|
|
carboxylic group |
-COOH |
|
|
DNA is composed of? |
deoxyribose, heterocyclic bases, phosphate |
|
|
arene substitution pattern |
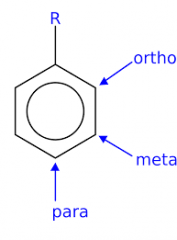
orto, meta para |
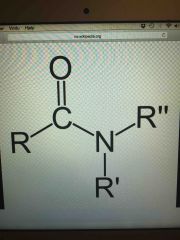
|
|
the functional group amide |
|
|
NH2 |
the functional group amino |
|
|
α-carbon |
the first carbon atom that attaches to a functional group |
|
|
β-carbon |
the second carbon atom that is attached to the functional group and is directly attached to the α-carbon. goes on with gamma, delta epsilon. |
|
|
how are the amino acids in proteins connected? |
with peptide bonds |
|
|
glucose could form a ?? ring |
hexa-membrered ring |
|
|
simple lips are esters of? |
fatty acids and glyserol |
|
|
name two monosaccharides |
glucose and ribose |
|
|
name two disaccharides |
sucrose and lactose |
|
|
name a polysaccharide |
starch |
|
|
pH level in NaCl and why |
7,because Na+ comes from a strong base, and Cl- from a strong acid |
|
|
pH level in glucose |
7 |
|
|
ribose is an? |
aldopentose |
|
|
which amino acid has a free amino group in the tripeptide: Ala-Gly-Tyr |
alanine |
|
|
pH level to Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 is? |
8,1 |
|
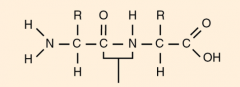
|
peptide bond/link |
|
|
what does a glycosidic bond? |
joins carbohydrate molecule to another group |
|
|
K2SO4 |
potassium sulfate |
|
|
KHSO4 |
potassium hydrosulfate |
|
|
(NH4)2SO4 |
ammonium sulfate |
|
|
1 u |
1,66*10-27kg |
|
|
NaC2H3O2 |
sodium acetate |
|
|
CnH2n+2 |
the general formula for alkanes |
|
|
CnH2n |
the general formula for alkenes |
|
|
CnH2n-2 |
the general formula for alkynes |
|
|
CnH2n+1 |
the general formula for alkyl group |
|
|
CnH2n |
the general formula for cycloalkanes |
|
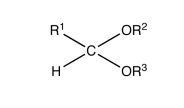
|
acetal |
|
|
ortho |
two substitutes that occupy adjacent (next to) positions on an aromatic ring |
|
|
soap contains of a ? chain and a ? head |
hydrophobic carbon chain and hydrophilic polar head |
|
|
the final product of the hydrolysis of starch is? |
glucose |
|
|
same element but different number of neutrons in the nucleus i called |
isotopes |
|
|
common stable polyatomic ions are |
carbonate CO3 -2 nitrate NO3 - sulfate SO4 -2 hydroxide OH - phosphate PO4 -3 ammonium NH4 + hydronium H3O + |
|
|
what does the binary acids contain? |
hydrogen and a non-metal e.g. HCl |
|
|
oxoacids contains |
hydrogen, oxygen and at least one non-metal e.g. H2SO4 |
|
|
NaOH |
sodium hydroxide |
|
|
Ca(OH)2 |
calcium hydroxide |
|
|
NH4OH |
ammonium hydroxide |
|
|
NaCl |
Sodium chloride |
|
|
K2S |
potassium sulfide |
|
|
CaSO4 |
calcium sulfate |
|
|
Fe(NO3)3 |
irion(III)nitrate of ferric nitrate |
|
|
(NH4)3PO4 |
ammonium phosphate |
|
|
the maximum oxidation number of the non-metal cannot exceed the number of the? |
group it's in |
|
|
sulfuric acid, carbonic acid and phosphoric acid are all? |
oxoacids |
|
|
H2SO4 |
sulfuric acid |
|
|
H2CO3 |
carbonic acids |
|
|
H3PO4 |
phosphoric acid |
|
|
C3H5OH3 |
glyserol |
|
|
deamination |
the process by which amino acids are broen down if there i an excess of protein intake |
|
|
hypertonic solution |
a solution with a higher concentration of solute, than som other, specific solution. (and therefore a higher osmotic pressure than the other solution) |
|
|
hypotonic solution |
the solution with a lower concentration of solute than another |
|
|
isotonic solution |
a solution whit the same concentration as some other solution. iso- means equal |

