![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is the catalytic triad positioned in chymotrypsin as it is? |
To allow the serine to become a nucleophile & To promote electrostatic associations with the substrate |
|
|
If an atom has a hydrogen nucleus (a proton) drawn away from it: |
Gains a negative charge and becomes a nucleophile |
|
|
The HIV protease is an Aspartyl protease, yet the peptide contains only a single carboxylic acid in the active site. How does this protease therefore function? |
The protein functions as a dimer |
|
|
Which amino acid transfers a hydrogen to His in chymotrypsin? |
Ser |
|
|
What is the role of Asp in the catalytic triad of chymotrypsin? |
To hydrogen bond to the hydrogen of His |
|
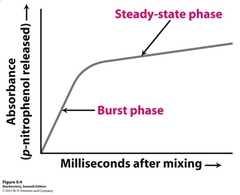
How would the above pattern of color formation differ if color were not produced until the release of the colored product from chymotrypsin? from chymotrypsin? from chymotrypsin? |
The burst phase would be eliminated |
|
|
If the S-1 substrate pocket of chymotrypsin were to be mutated so that two of the original Ala residues were mutated to two phenylalanine residues, what new substrate would you expect to be recognized? |
An Ala as the C-terminal amino acid |
|
|
Where does the hydrogen originally on water end up after one complete cycle of chymotrypsin catalytic activity? |
On the C terminal peptide fragment & On Ser of the catalytic triad |
|
|
A nucleophile is: |
Negatively charged & Able to promote chemical bond formation with another nucleus |
|
|
chymotrypsin, what is the rate limiting step. |
Cleavage by water of the bond between the substrate carbon and enzyme serine. |
|
|
Substrate binding to an enzyme: |
Involves many small forces |
|
|
If a nucleus has extra electrons it: |
Gains a negative charge and becomes a nucleophile. |
|
|
Which of these groups is likely to become a nucleophile in a protease? |

|
|
|
In the formation of chemical bonds as we discussed for chymotrypsin, the nucleophile is able to: |
Attack a carbon |
|
|
What three amino acids are involved in the catalytic triad of chymotrypsin? |
Asp His Ser |
|
|
Where does the hydrogen originally on the Ser of the catalytic triad eventually end up after the full reaction sequence? |
On the peptide fragment that contributes the nitrogen of the peptide bond |
|
|
The oxyanion hole of chymotrypsin contains which active group? |
NH2 |
|
|
If the S-1 substrate product of chymotrypsin were to be mutated so that two Ala residues were mutated to two phenylalanine residues, what new substrate would you expect to be recognized? |
An Ala as the C-containing amino acid |
|
|
In the Aspartyl proteases, what serves as the nucleophile, as the electrophile? |
Asp as the electrophile and another Asp as the nucleophile. |
|
|
HIV, the protease is required to: |
Generate the protein subunits required for viral particle formation |
|
|
The HIV protease has been inhibited, as discussed in class: |
By modeling a molecule to mimic the transition state of the protease |
|
|
Which type of protease discussed in class would be most benefitted in its catalytic activity by lowering the pH? Why. |
Gly (1) Arg (2) Asp (3) Phe (4) Ser (5) Met |
|
|
the above peptide, which bond would most likely be cleaved by chymotrypsin? (Parentheses indicate the bond referred to.) |
4 |
|
|
Answer the above question if the enzyme were trypsin. |
2 |
|

The equation above refers to an enzyme like chymotrypsin. In this enzyme, however, K3 >>> K2. How would this change the kinetics of product release very soon after the reaction begins? Compare to the kinetics seen with chymotrypsin itself shown in the figure below the equation. |
Linear curve for product formation. |
|
|
Chymotrypsin is placed in heavy water (deuterium oxide, where hydrogen is replaced by deuterium) in the absence of substrate and analyzed. Substrate is then added to the reaction and the analysis is repeated. Which member(s) of the catalytic triad would be most likely become more highly associated with deuterium following addition of substrate? Why. |
Serine, because a hydrogen from water will end up on the serines hydroxyl group after one full round of catalysis. |

