![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The interconversion between mono and diphoshpate nucleotides if mediated by _____________________________>
|
specific nucleoside monophosphate kinases (one for every base)
|
|
|
The interconversion between di- and triphosphates is mediated by ___________________, called ____________________.
|
a single kinase, nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK)
|
|
|
CTP is created from UTP with which enzyme? how is this enzyme regulated?
|
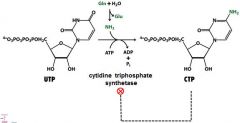
cytidine triphosphate synthetase (cytidylate synthetase), CTP is the feedback inhibitor
|
|
|
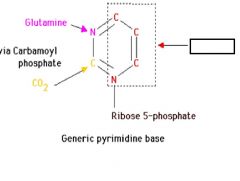
In pyrimidine biosynthesis carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate synthesize ______________ _______________. What is the name of the enzyme? How is it regulated?
|
carbamoylaspartate, enzyme= aspartate transcarbamoylase , regulated by CTP
|
|
|
Where does the amine group on the 4C of CTP come from?
|
Gln, Q
|
|
|
ATCase? what is it? how is it regulated?
|
carbamoyl apartate, makes carbamoyl aspartate from
carbamoyl phosphate, it is down regulated by CTP, upregulated by ATP in the presence of CTP |
|
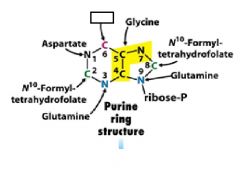
|
CO2
|
|
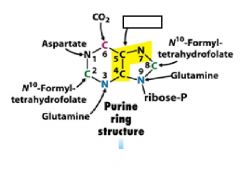
|
Glycine
|
|

|
n10-fomyltetrahyrofolate
|
|

|
glutamine
|
|

|
aspartate
|
|

|
glutamine
|
|

|
n10- formyltetrahydrofolate
|
|

|
glutamine
|
|
|
CO2
|
|
|
Aspartate
|
|
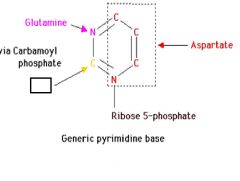
Draw this.
|
|
|
Draw this.
|

|
|

|
PRPP amidotransferase
|
|

|
Gln+H2O ----> Glu + NH3
|
|

|
5-phoshoribosyl-1-amine
|
|

|
committed step
|
|
|
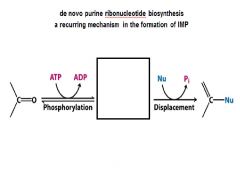
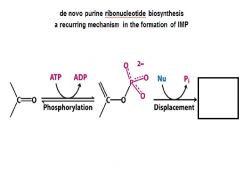
Turning PRPP into 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amine is done by which enzyme? how is it regulated?
|
PRPP amidotransferase
regulation partial- GTP ATP total - GTP & ATP IMP |
|
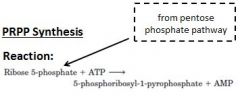
enzyme? regulation?
|
ribose phosphate pyrophosphokinase , downregulated by ADP
|
|
|
Who performed the S & R experiment? what was the main conclusion of the experiment?
|
Griffith, genetic material can be transferred between cells
|
|
|
Who performed the "ase" tests? What was the main conclusion of the experiment?
|
Avery, McLeod, McCarty, DNA is the "transforming principle"
|
|
|
Who performed the virus experiment? What was the main conclusion from the experiment?
|
Hershey, Chase, Solidified that DNA is the genetic material
|
|

|
adenylosuccinate synthetase
|
|

|
inosinate (IMP)
|
|

|
Inosinate (IMP) dehydrogenase
|
|
|
Allosteric feedback regulation of purine ribonucleotide synthesis occurs at four places. Name the enzymes.
|
PRPP synthetase, glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase, adenylosuccinate lyase, IMP dehydrogenase
|
|
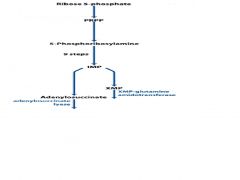
Name the endproducts, missing enzymes, and draw the regulation of this pathway.
|

|
|
|
In the purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis pathway ribose 5-phosphate is converted to PRPP. Name the enzyme, and the regulation.
|
PRPP synthetase, downregulated by ADP
|
|
|
In the purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis pathway PRPP is converted to 5-Phosphoribosylamine. Name the enzyme, and the regulation.
|
glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase,
regulation partial- GTP ATP total - GTP & ATP IMP |
|
|
In the purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis pathway IMP is converted to AMP. Name the regulated enzyme, and the regulation.
|
adenylosuccinate synthetase, down regulated by AMP
|
|
|
In the purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis pathway IMP is converted to GMP. Name the regulated enzyme, and the regulation
|
IMP dehydrogenase, downregulated by GMP
|
|
|
Name the enzyme reponsible for converting ribonucleotides into deoxyribonucleotides.
|
ribonucleotide reductase
|
|
|
Ribonucleotide reductase use _________________________ as substrates.
|
ribonucleoside diphosphates
|
|
|
Ribonucleotide reductase catalyzation involves a _______________ reduction. The source of these electrons is ___________________.
|
2 electron, NADPH
|
|
|
The regulation of ribonucletoide reductase maintains a balance of ______________________ ______________________.
|
deoxynucleotide concentrations
|
|
|
Regulation of _________________ ________________ maintains a balance of deoxynucleotide concentrations.
|
ribonucleotide reductase
|
|
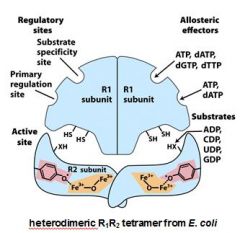
Name this enzyme. What does it do?
|
Ribonucleotide reductase
converts RNA to DNA |
|

|
Substrate specificity site - top
Primary regulation site - bottom |
|

|
active site
|
|

|
ATP, dATP, dGTP, dTTP
|
|
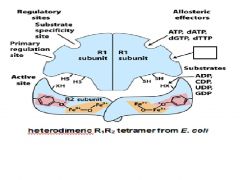
|
ATP, dATP
|
|

|
ADP, CDP, UDP, GDP
|
|
|
The primary regulation switch on ribonucleotide reductase is an ON/OFF switch regulated with ATP, dATP. Which substrate in on, off?
|
on-ATP
off-dATP |
|
|
The primary regulation switch on ribonucleotide reductase is an _________ - _________ switch.
|
on/off
|
|
|
The primary regulation switch on _______________ _______________ is an ON/OFF switch regulated with ATP, dATP. Which substrate in on, off?
|
ribonucleotide reductase
on-ATP off-dATP. |
|
|
The primary regulation switch on ribonucleotide reductase is an ON/OFF switch regulated with what substrates?
|
on-ATP
off-dATP |
|
|
The substrate specificity site on ribonucleotide reductase works by ________________ regulation.
|
reciprocal
|
|
|
The substrate specificity site on ribonucleotide reductase works by reciprocal regulation. Explain.
|
If a purine is in the substrate specificity site than a primidine is in the active site and vica versa.
|
|
|
The reaction in the active site of ribonucleotide reductase occurs via a ____________ _____________. Which is pointed out because there are not many of these in the human body.
|
radical intermediate
|
|
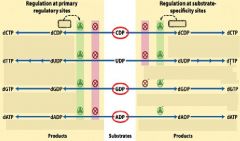
draw the regulation for Ribonucleotide reductase.
|

|
|
|
dTMP is derived from d_______.
|
UMP
|
|

|

|
|
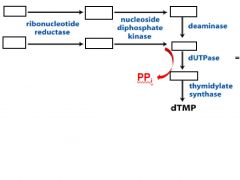
Fill in the blanks of this pathway for dTMP.
|

|
|
|
_____________ ______________ catalyzes the last step in dTMP pathway, the reaction uses THF as the cofactor to add a ____________ ____________ to C5. It converts d_____ to dTMP.
|
Thimidylate Synthase
methyl group |
|
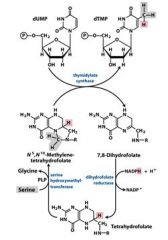
This pathway is the target for several ___________ and ______________ drugs.
|
cancer, autoimmune
|
|
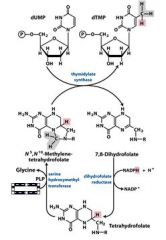
____________ aa residue methylates Tetrahydrofolate.
|
Serine
|
|
|
Many types of cancers are defined by _____________ ___________ cells.
|
rapidly dividing
|
|
|
Cell division requires replication of ____________ ________, thus cancer (or rapidly dividing cells have a heightened need for _______________.
|
genomic DNA, nucleotides
|
|
|
Failure to replicate DNA during the cell cycle is detected by the DNA replication checkpoint resulting in _____________ _____________ ___________ and/or ______________.
|
cell cycle arrest, apoptosis (programmed cell death)
|
|
|
Because cancer is often rapidly dividing, blocking ___________ precursors is an effective strategy to arrest the cell cycle and/or cause apoptosis.
|
nucleotide precursors
|
|
|
Two specific strategies of blocking nucleotide precursors to eliminate cancer are?
|
1. Block (Q) PRPP amidotransferase by using Q analogs, halting purine production
2. Block thymidylate synthase, stopping dTMP production. |
|
|
Describe how Fluorouracil halts nucleotide metabolism.
|
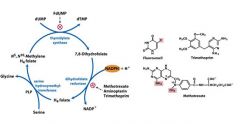
Fluorouracil becomes FdUMP though the de novo pyrimidine pathway covalently binding to thymidylate synthetase halting the production of dTMP.
|
|
|
Describe how Methotrexate inhibiits nucleotide metabolism.
|
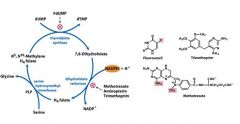
Methotrexate halts the methylation of THF that produces N5,N10 methylene THf. It does this by having a higher binding affinity for dihydrofolate reductase than it's substrate. Thus halting the production of dTMP.
|
|
|
Name the two cancer treatment drugs that inhibit dTTP production.
|
Fluorouracil
Methotrexate |
|
|
Name the two cancer treatment drugs that inhibit purine biosynthesis.
|
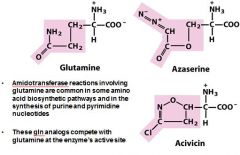
azaserine
avicin |
|
|
Free __________ and ___________ bases can be salvaged from degraded DNA and RNA.
|
purine, pyrimidine
|
|
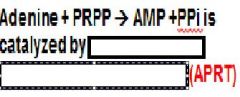
In the salvage pathway for purines.
|
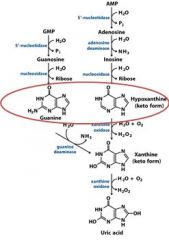
Adenosine phosphoriboysltransferase
|
|
|
In the salvage pathway for purines Guanine or (hypoxyanthine) + PRPP --> GMP or XMP + PPi is catalyzed by ______________ _______________________(H/GPRT).
|
hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltranferase.
|
|
|
the best studied are ___________ salvage pathways which use specific __________________________ to join PRPP to free purine bases to form nucleotide monophosphates.
|
purine, phosphoribosyltransferases
|
|
|
In the catabolism and salvage of nucleotides pathway, guanylate and adenylate have a shared breakdown product in _______________.
|
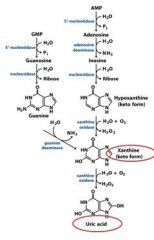
xanthine
|
|
|
In the catabolism and salvage of nucleotides pathway, _______________ and ______________ have a shared breakdown product in xanthine.
|
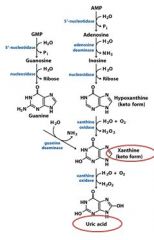
guanylate and adenylate
|
|
|
In the catabolism and salvage of nucleotides pathway, guanosine cleavage from ribosyl produces the free base ____________, which is then deaminated to form ____________.
|
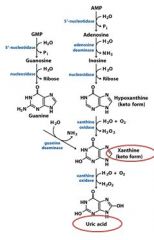
guanine, xanthine
|
|
|
In the catabolism and salvage of nucleotides pathway, adenosine is deaminated to form ___________. Separation from ribose yields _______________, which is oxidized to form _____________.
|
inosine, hypoxanthine, xanthine
|
|
|
The end product of the degradation of purines is?
|
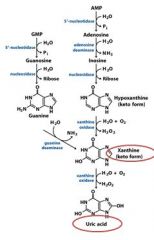
uric acid
|
|
|
________ is the swelling of joints resulting from a build-up of urate in the form of sodium urate crystals.
|
Gout
|
|
|
Gout is the swelling of joints resulting from a build-up of ________ in the form of __________ __________ crystals.
|
urate, sodium urate
|
|
|
Gout is caused by the ________________ of uric acid.
|
undersecretion or overproduction
|
|
|
Gout, which is caused by undersecretion of uric acid is the result of a genetic defect. This defect is not known but is likely related to improper _______________ balance.
|
purine
|
|
|
What drug is used in the treatment of gout?
|
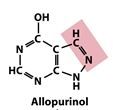
Allopurinol
|
|
|
The gout treatment drug Allopurinol is an anolog to _________________.
|
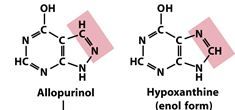
Hypoxyanthine
|
|
|
Allopurinol metabolizes to ____________, it is catalyzed by xanthine oxidase. ____________ binds tightly to ____________ ____________ effectively blocking the active site.
|
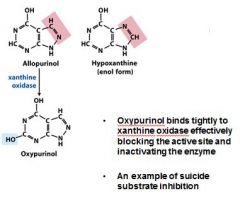
oxypurinol, xanthine oxidase
|
|
|
The cancer treatments and gout treatments talked about in class are called _____________________________. (general name)
|
mechanism based inhibition or suicide substrate inhibition
|
|
|
Define phenotype?
|
the observable characteristics of an organism
|
|
|
Define gene?
|
a chromosomal segment that codes for a single functional polypeptide chain or RNA molecule
|
|
|
Define chromosome?
|
a single large DNA molecule and its associated proteins (contains many genes)
|
|
|
Define karyotype?
|
the number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species
|
|
|
Define genome?
|
all the genetic information encoded in a cell or virus
|
|
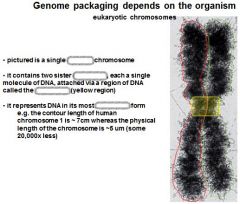
|
m-phase, chromatids, centromer, condensed
|
|
|
What is the c-value enigma?
|

|
|

|
Telomeres
|
|

|
Centromere
|
|
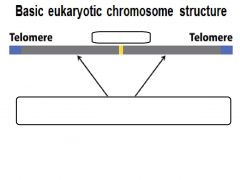
|
genes, repeats, origins of replication
|
|

|

|
|
|
Current estimates are that ______% of the genome codes for genes. ______% is noncoding.
|
30 , 70
|
|
|
Of the 30% that encodes for genes, only _____% is actually coding sequence, the remaining ______% consists of ___________ which are removed after transcription.
|
1.5 , 28.5 , introns
|
|
|
Approximately ____% of our genome is transposons.
|
45%
|
|
|
Evidence for non-coding, repeated elements in the DNA comes from?
|
FISH analysis, Cot curves, Genome sequencing
|
|
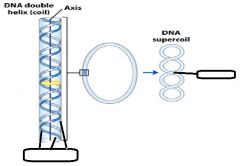
In DNA supercoiling these two are called?
|
twist and writhe
|
|
|
For B-form dsDNA any deviation from a helical twist of 10.5bp/turn represents a ____________ ____________.
|
strained conformation
|
|
|
Most dsDNA in a cell is _______________ resulting in writhe.
|
underwound
|
|

In supercoiling, _________ is the number of turns of the DNA double helix.
|

twist
|
|
|
In supercoiling, ______________ is the munber of times a dsDNA molecule is coiled or crosses over itself.
|
writhe
|
|

|

|
|
|
Why is it that many circular DNA molecules remain supercoiled when extracted from cells and free of protein and other cellular components?
|
because the dsDNA is underwound
|
|

|

|

