![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA and protein |
What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? |
|
|
Biochemists had identified them as a class of macromolecules with great heterogeneity and specificity of function, essential requirements for the hereditary material. Nucleic Acids seemed too uniform. |
Why did researchers originally think that protein was the genetic material? |
|
|
There was a pathogenic strain and a nonpathogenic strain. The pathogenic strain turned some nonpathogenic pathogenic even when dead. |
Distinguish between the virulent and nonvirulent strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae studied by Frederick Griffith. |
|
|
To develop a vaccine against pneumonia |
What was the purpose of Griffith's studies? |
|
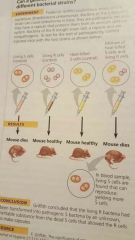
|
Use this figure to summarize the experiment in which Griffith became aware that hereditary info could be transmitted between two organisms in an unusual manner. |
|
|
Transformation |
A change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell. |
|
|
DNA |
what did Oswald Avery determine to be the transforming factor? |
|
|
He broke open the heat-killed pathogenic bacteria amd extracted its contents. He inactivated DNA, RNA, and protein and tested each sample for its ability to transform live nonpathogenic bacteria. |
Explain Oswald Avery's experimental approach. |
|

|
Sketch a T2 bacteriophage and label its head, tail sheath, tail fiber, and DNA. |
|
|
Phage genes enter the host cell and code for an enzyme that degrades the host's DNA. |
How does a bacteriophage destroy a bacterial cell? |
|
|
Sulfur- Protein bc protein contains sulfur. Phosphorus- DNA bc DNA contains Phosphorus |
How did Hershey and Chase "label" viral DNA and viral protein so that they could be distinguished? Explain why they chose each radioactive tag in light of the chemical composition of DNA and protein. |
|
|
They tagged DNA and protein and allowed the phages to infect E. Coli. They then tested the samples to see which molecule had entered the cells. DNA injected by phages must be the molecule carrying the genetic information that makes cells produce new viral DNA and proteins. |
Describe the means by which Hershey and Chase established that only the DNA of a phage enters an E. Coli cell. What conclusions did these scientists draw based on these observations? |
|
|
1. The base composition of DNA varies from one species to another. 2. The Number of adenines= the number of thymines and the number of cytosines= the number of guanines. 3. All species contain adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. |
What are Chargaff's rules? |
|
|
He analyzed the base composition of DNA from a number of different organisms. |
How did Chargaff arrive at his rules? |
|
|
nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and phosphate group |
List the components of a nucleotide |
|
|
Watson and Crick |
Who built the first model of DNA and shared the 1962 nobel Prize for discovery of its structure? |
|
|
She produced an xray diffraction image of DNA through xray crystallography. She came up with the double helix shape with sugar phosphates on the outside. She came up with the details that allowed watson and crick to build thei model. |
What was the role of Rosalind Franklin in the discovery of the double helix? |
|
|
Purines have two organic rings, pyramidines have one. Because one is a purine and the other is a pyramidine, together they are the perfect length. |
Distinguish between the structure of pyramidines and purines. Explain why adenine bonds only to thymine. |
|
|
It showed that only A partners with T and only G with C. It helped explain why by showing how they fit together. |
How did Watson and Crick's model explain the basis for Chargaff's rules? |
|

|
Name the 5 nitrogenous bases. |
|
|
A pairs with T. G pairs with C. |
Explain the base pairing rule. |
|
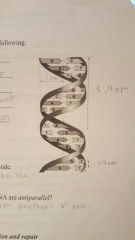
1nm .34 nm 3.4 nm sugar and phosphate nitrogenous bases |
Describe the structure of DNA relative to each of the following. Distance across molecule distance between nucleotides distance between turns components of the backbone components of the "rungs" |
|
|
The numbers assigned to the carbons in the sugar ring |
Explain what is meant by the 5' and 3' ends of the nucleotide. |
|
|
The 5' end matches up with another's 3' end. |
What do we mean when we say the two strands of DNA are antiparallel? |
|
|
When a double helix replicates, each of the two new daughter molecules will have one old strand, derived from the parent molecule and one newly made strand. |
What is the semiconservative model of replication? |
|
|
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl |
Who performed the experimenrs that elucidated the correct mechanism of DNA replication? |
|
|
They cultured the bacteria in a heavy isotope and then put them in a lighter isotope |
How did Meselson and Stahl create "heavy" DNA for their experiments? |
|
|
The bacteria was cultured in 15N and then transferred to medium containing 14N. Then the DNA was centrifuged after 20 and 40 min. They got light and hybrid DNA, proving the semiconservative model. |
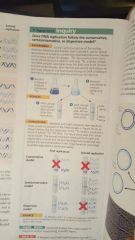
Use this to explain how Meselson and Stahl confirmed the semiconservative mechanism of DNA replication. |
|
|
origins of replication |
Short stretches of DNA having a specific sequence of nucleotides; Where replication begins. |
|
|
The leading strand is the DNA strand made by DNA pol III nesting in the replication fork and adding nucleotides. 5'-3' direction. The lagging strand is the strand created as DNA Pol III works away from the template. |
Distinguish between the leading and lagging strands during DNA replication. |
|
|
5'-3' |
What is the direction of synthesis of the new strand? |
|
|
Segments of the lagging strand. Using DNA Pol I. |
What are Okazaki fragments? How are they welded together? |
|
|
Helicase |
Which enzyme untwists and separates strands? |
|
|
single stranded binding proteins |
Which enzyme holds DNA strands apart? |
|
|
primase |
Which enzyme synthesizes RNA primer |
|
|
DNA polymerase III |
Which enzyme adds DNA nucleotides to new strand? |
|
|
Topoisomerase |
Which enzyme relieves strain caused by unwinding? |
|
|
DNA Ligase |
Which enzyme joins DNA fragments together? |
|
|
DNA Pol I |
Which enzyme removes RNA primer and replaces with DNA |
|
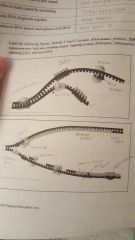
|
Look at the following figures of replication |
|
|
1. primase joins RNA nucleotides into a primer. 2. DNA pol III adds DNA nucleotides to the primer, forming okazaki fragment I. 3. After reaching the next RNA primer to the right, DNA pol III detaches. 4. After fragment 2 is primed, DNA pol III adds DNA nucleotides until it reaches the fragment I primer and detaches. 5. DNA pol I replaces the RNA with DNA, adding to the 3' end of fragment 2. 6. DNA ligase forms a bind between the newest DNA and the DNA of fragment I. 7. The lagging strand in this region is now complete. |
Make a detailed list of the steps that occur in the synthesis of a new strand. |
|
|
It proofs each nucleotide against its template and removes mistakes. Helps fill in gap left by nuclease |
Explain the roles of DNA Polymerase in DNA proofreading and repair. |
|
|
cuts out the damaged strand of DNA |
Explain the role of Nuclease in DNA proofreading and repair. |
|
|
it fills in the gap left by nuclease with nucleotides |
explain the role of ligase in DNA proofreading and repair. |
|
|
it repairs genetic damage caused by ultraviolet rays of sunlight |
explain the role of repair enzymes in DNA proofreading and repair |
|
|
The covalent linking of thymine bases that are adjacent on a DNA strand. Causes the DNA to buckle and interfere with DNA replication. Damage by UV rays Repaired by DNA repair enzymes in our skin cells. |
What is a thymine dimer? How might it occur? How is it repaired? |
|

|
Look at the telomeres |
|
|
Telomeres become shorter during every round of replication |
Explain telomere erosion |
|
|
Telomerase catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells, restoring their length, compensating for shortening |
Explain the role of telomerase |
|
|
They have unlimited cell division and telomerase activity. Telomerase is not active in body cells |
Why are cancer cells immortal but most body cells have a limited life span? |
|
|

|
|
|
Heterochromatin- Interphase chromatin visible as irregular clumps with a light microscope. less accessible. Euchromatin- Less compacted, more dispersed. DNA is accessible to cell machinery so its genes can be expressed. |
Distinguish between heterochromatin and euchromatin. |
|
|
c |
In his work with pneumonia-causing bacteria and mice, Griffith found that a. the protein coat from pathogenic cells was able to transform nonpathogenic cells b. heat killed pathogenic cells caused pneumonia c. some substance from pathogenic cells was transferred to nonpathogenic cells, making them pathogenic d. the polysaccaride coat of bacteria caused pneumonia e. bacteriophages injected DNA into bacteria |
|
|
d |
E. Coli cells grown on 15N medium are transferred to 14N medium and allowed to grow for two more generations (two rounds of DNA replication). DNA extracted from these cells is centrifuged. What density distribution of DNA would you expect in this experiment? a. one high density and one low density band b. one intermediate density band c. one high density and one intermediate density band d. one low density and one intermediate density band e. one low density band |
|
|
b |
A biochemist isolates and purifies molecules needed for DNA replication. When she adds some DNA, replication occurs, but each DNA molecule consists of a normal strand paired with numerous segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. What has she probably left out of the mixture? a. DNA polymerase b. DNA ligase c. nucleotides d. okazaki fragments e. primase |
|
|
c |
What is the basis for the difference in how the leading and lagging strands of DNA molecules are synthesized? a. the origins of replication occur only at the 5' end b. helicases and single strand binding proteins work at the 5' end. c. dna polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of a growing strand d. dna ligase works only in the 3'-5' direction e. polymerase can work on only one strand at a time |
|
|
b |
In analyzing the number of different bases in a DNA sample, which result would be consistent with the base paring rules? a. A=G b. A+G=C+T c. A+T=G+T d. A=C e. G=T |
|
|
d |
The elongation of the leading strand during DNA synthesis a. progresses away from the replication fork b. occurs in the 3'-5' direction c. produces okazaki fragments d. depends on the action of DNA polymerase e. does not require a template strand |
|
|
a |
The spontaneous loss of amino groups from adenine results in hypoxanthine, an uncommon base, opposite thymine in DNA. What combination of molecules could repair such damage? a. nuclease, DNA polymerase, dna ligase b. telomerase, primase, and dna polymerase c. telomerase, helicase, single strand binding protein d. dna ligase, replication fork proteins, adenylyl cyclase e. nuclease, telomerase, primase |
|
|
c |
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around a. polymerase molecules b. ribosomes c. histones d. a thymine dimer e. satellite dna |

