![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Divergent Evolution
|
related species becoming more dissimilar
|
|
|
convergent evolution
|
unrelated species become more similar as they adapt to similar environment
|
|
|
species
|
most basic level of classification
|
|
|
specication
|
descendants evolve from ancestor
|
|
|
biological species concept
|
groups of individuals that interbreed but are reproductively isolated
|
|
|
problems with fossils as biological secies
|
cannot observe interbreeding
|
|
|
allopatric
|
complete reproductive isolation
|
|
|
parapatric
|
partial reproductive isolation
|
|
|
sympatic
|
separation occurring with in a population with no reproductive isolation
|
|
|
allopatic
|
if species becomes separated by a barrier
|
|
|
classification
|
clustering organisms in natural groups
|
|
|
phylogeny
|
identifying ancestor-descendant relationships
|
|
|
Classification and phylogeny principle
|
classification should reflect phylogeny
|
|
|
anagenesis
|
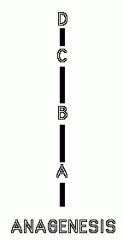
linear evolution cladistics
|
|
|
cladogenesis
|
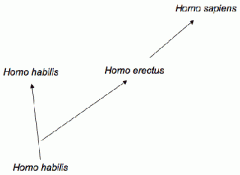
|
|
|
linnaen taxonomic system
|
hierarchical system shows relative relationship between all living things. Starts broad and gets increasingly specific
|
|
|
cladisitcs
|
shared derived characterisitcs
|
|
|
evolutionary systematic
(aka phylogenies) |
-incorporated time aspects
-ancestor- descendant relationships shown in phylogenies |
|
|
cladistics
|
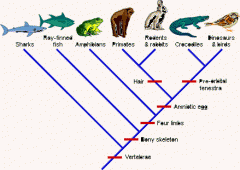
defines groups based on recentness of a common ancestor
*based on order of speciation |
|
|
ancestral traits in caldisitcs
|
-shared widely
-relatively ancient -common ancestory of distant relatives -not useful for tracing descent |
|
|
derived traits in cladisitics
|
-shared norrowly
-relatively recent -close relationships -useful for tracing descent |
|
|
general trends in primate evolution
|
1)big brain
2) five digits 3)grasping hands and feet 4)upright posture 5)Increased reliance on vision decreased reliance on olfaction 6) omnivorous 7)group living 8)generalized diet and teeth |
|
|
The Arboreal Theory
|
primates adapted to trees and fruit is scarce and ephemeral
*Matt Cartmill disproved theory |

