![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the smallest viruses that infect mammals?
|
Circoviruses
|
|
|
What are 3 animal important circoviruses that cause disease in animals?
|
PBFD
Chicken Anemia Virus Porcine Circovirus - fetal dz/ still birth in Germany, wasting syndrome of piglets in US |
|
|
Circoviruses and Parvoviruses are Class II viruses. How do these viruses replicate? Do they have a virion-bound enzyme?
|
ssDNA(-) viruses
Do not carry own enzymes - use cellular enzymes. DdRp makes mRNA, DdDp makes DNA Assembled viral products lyse cells (no envelope) |
|
|
How will circoviruses and parvoviruses appear when stained with Acridine Orange?
|
Red intranuclear inclusion against yellow-green nucleus
|
|
|
What general kinds of cells do circoviruses and parvoviruses infect?
|
rapidly dividing cells/ cells with high mitotic index
|
|
|
Name 4 symptoms of PBFD.
|
- Beak abnormalities
- Feather loss - immunosuppression - death |
|
|
Which of the following would NOT appear as a green cytoplasmic inclusion when stained with Acridine Orange?
a) Reovirus b) Birnavirus c) Poxvirus d) Herpesvirus e) Asfivirus |
D - Herpesvirus
It is a dsDNA virus (stains green) but replicates in the nucleus like most DNA viruses |
|
|
Which of the following will appear as a red intranuclear inclusion when stained with Acridine Orange?
a) Parvovirus b) Circovirus c) Rhabdovirus d) Coronavirus e) both A and B |
E
Red indicates single stranded nucleic acids. Both Parvo and Circo are ssDNA viruses. |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about parvoviruses?
a. They persist for long periods in the environment b. Staining with Acridine orange will show red-orange in the nucleus against a yellow-green background of cellular DNA c. They have 2 capsid proteins d. They have non-defective linear ssDNA(-) e. They agglutinate RBCs |
C - They have 2 capsid proteins
They actually have 3 capsid proteins. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a clinical sign observed in canine parvoviral disease?
a. Ataxia b. Diarrhea c. Anorexia d. Dehydration e. Vomiting |
A - Ataxia
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a parvovirus?
a. Infectious Feline Panleukopenia b. Mink Virus Enteritis c. Rheumatoid arthritis in humans d. Alleutian Mink Disease e. Chicken Anemia Virus |
E - Chicken Anemia Virus
it is a circovirus |
|
|
Which of the following correctly describes Feline Panleukopenia?
a. depression, diarrhea, dehydration, death (the 4 D’s) b. Kittens affected after birth develop cerebellar ataxia c. Fever, anorexia, mucopurulent ocular discharge d. All cats showing clinical signs have poor prognosis e. Spread only via direct contact |
A - depression, diarrhea, dehydration, death (the 4 D’s)
|
|
|
True or False: Dogs can be infected subclinically with Feline Panleukopenia and have immunity to canine parvovirus as a result.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Intentionally infecting dogs with feline panleukopenia virus to protect them from parvovirus infections is a good strategy in your clinic.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False: Bovine parvovirus is a major problem on some operations when there are outbreaks of it.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False: Aleutian Mink Disease only affects albino mink.
|
False - it affects them more severely though.
|
|
|
True or False: Porcine Parvovirus causes abortion in sows with no other clinical signs.
|
True
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of canine parvovirus:
a. Worldwide distribution b. Watery, bloody diarrhea c. Malodorus diarrhea d. Highly contagious e. Zoonotic |
E - zoonotic
|
|
|
What are 2 reasons parvoviruses are so resistant to degradation?
|
1) Carries no enzymes
2) No envelope (naked) |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about mink virus enteritis?
a. Infected animals will have bloody diarrhea b. Mink kits infected in-utero may show signs of cerebellar hypoplasia c. It is equivalent to canine parvo in minks d. It is also called Fort Williams Disease |
B
cerebellar hypoplasia is seen in felines infected in-utero |
|
|
Which of the following is correct about circoviruses?
a. They have spherical symmetry b. They are 15-18nm c. They will appear as a green cytoplasmic inclusion with Acridine orange stain d. They carry DdRp e. They are naked |
E - they are naked
|
|
|
True or false: PBFD (Psitticine Beak and Feather Disease) is highly contagious and highly fatal in young birds.
|
True
|
|
|
True or false: Chicken anemia virus affects erythrocytes but not leukocytes.
|
False - it affects both
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Infectious Canine Hepatitis?
|
Jaundice, thirst, tender abdomen, acute disease, often unilateral corneal opacity.
|
|
|
Porcine circoviruses have different clinical manifestations in the United States and Germany. What are these?
|
US = piglet wasting syndrome
Germany = fetal disease and still births |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about papovaviruses?
a. They have class I type replication b. They replicate in the cytoplasm of the host cells c. They have a circular genome d. They are naked and icosahedral e. They are 45-55nm |
B
They replicate in the nucleus like most DNA viruses. |
|
|
True or False: Equine Adenovirus is only a problem in foals with SCID.
|
True
IFN-gamma is needed, which SCID foals cannot produce. SCID = Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. |
|
|
Describe the difference between cytocidal and non-cytocidal interactions. Which is permissive/ non-permissive?
|
Cytocidal/permissive: within species of origin, virus replicates and kills cells
Reductive/non-cytocidal/non-permissive: not in species of origin, virus does not replicate, but instead integrates into host genome and causes transformation of cells into tumors. These cells will produce early antigens (T antigens) in the nucleus, but will later express TSTA (Tumor specific transplantation antigens) on the cell surface. These transformed cells are tumorigenic in species of origin. |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about papillomaviruses?
a. They can be cleared from the system with autogenous vaccines b. They cause warts c. The human papilloma virus causes cancer d. Warts can be cured by surgical removal e. Warts are species-specific |
D
Warts will usually recur if they are surgically removed. |
|
|
True or False: Equine adenovirus is normally found in the Upper Respiratory Tract of all horses.
|
True
|
|
|
The human poliovirus vaccine was made from viruses grown in African Green Monkey kidney cells that were contaminated with SV40 virus. Why were there worries that the polio vaccine would cause tumors in people and why did we not see this happen?
|
The SV40 virus is a vacuolating agent within the family Papovaviridae, a family of viruses that tends to cause tumors in non-species of origin. However, humans may be similar enough to the virus species of origin that this phenomenon did not occur.
|
|
|
What additional precautions are now taken to inactivate viruses for vaccines?
|
Treated with formalin and exposed to UV light
|
|
|
Aside from canine infectious hepatitis and equine adenovirus infections in SCID foals, what other disease(s) can adenoviruses cause? What species are affected?
|
Respiratory infections – cattle, goats, sheep, humans
|
|
|
Name 3 viruses that are permanent once host is infected.
|
Papova, adeno, and herpes viruses
|
|
|
What are episomes?
|
It is a viral DNA floating in the nucleus without being integrated (it is how the virus remains in the body = permanent situation).
|
|
|
True or false: Herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infect all eukaryotic species.
|
True
|
|
|
How is a herpes simplex integrated and what is the cause of the intergration?
|
The episome gets activated by stress (such as UV light, cancer therapy) and travels down the axon and gets integrated at the trigeminal ganglion. This leads to a cold sore or genital lesions.
|
|
|
What are the two types of Herpes simplex?
|
1. HSV1 = oral sores (aka cold sores) (and ocular – can cause blindness)
2. HSV2 = genital herpes |
|
|
Herpesviruses have a core (DNA and proteins), a capsid, and an envelope, which are things that other viruses possess. What else do herpesviruses possess between their capsid and their envelope?
|
Tegument (contains virally-encoded proteins and enzymes involved in the initiation of replication)
|
|
|
What are the two diseases caused by Varicella Zoster (VZV)?
|
1. Chicken pox- Varicella
2. Shingles- Zoster |
|
|
True or False: Herpesviruses replicate exclusively in the nucleus.
|
True
They are typical DNA viruses. |
|
|
What is required for shingles to develop?
|
Previous infection and integration of chicken pox when young, followed by immunosuppression in later life.
|
|
|
List 7 distinguishing characteristics of asfivirus.
|
Class 1
Icosahedral Linear dsDNA with covalently linked ends Enveloped virus Large DNA virus = 170-190nm Infects all swine. |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about the replication of Herpesviruses?
a) Capsid is uncoated in cytoplasm b) Core is uncoated in nucleus c) Transcription and translation use host enzymes d) Assembly occurs in the nucleus e) Virus buds off cell membrane for release. |
E - buds off cell membrane for release
Actually buds off inner nuclear membrane. |
|
|
What is the major asfivirus? And how does it cause disease?
|
African swine fever (ASF) is the major asfivirus and it is a reportable disease. This virus causes lymph nodes to convert into blood clots, destroying the normal endothelial cells. It is very similar to hog cholera.
|
|
|
How is African Swine Fever diagnosed?
|
1. Use Giemsa stain to distinguish between ASF and hog Cholera.
2. Hemadsorption test Monocytes decorated with RBC all around it indicate ASF infection. 3. Perform Acridine Orange stain test Since asfivirus is a dsDNA, the orange cytoplasm should have green fluorescing intracytoplasmic inclusions indicating the presence of dsDNA. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a tumor disease caused by a herpesvirus?
a) Lymphoma in rabbits b) Marek’s disease in chickens c) Leukemia in cattle d) Infectious mononucleosis in humans e) Burkitt’s Lymphoma in humans |
c) Leukemia in cattle – caused by Retrovirus
|
|
|
What are poxviruses thought to be a link between?
|
Bacteria and viruses
|
|
|
List 7 distinguishing factors of poxvirus.
|
Class 1
Largest animal virus = 320x270nm Can be seen under light microscope under oil immersion Core contains linear covalently bound dsDNA, Brick-shaped Enveloped virus Lateral bodies loaded with enzymes surround the core |
|
|
Which of the following classes of viruses does not cause tumors?
a) Adenovirus b) Herpesvirus c) Papovavirus d) Retrovirus e) Poxvirus |
Trick question: they can all cause tumors!
|
|
|
Name a genomic factor that is unique to lentiviruses.
|
NEF (essential for pathogenicity)
|
|
|
What happens when poxviruses enter the cell?
|
Once the poxviruses enter the cell they become intracytoplasmic inclusions. Poxviruses require host ribosomes to continue. Cellular lysosomes remove the envelope and lateral bodies. The mRNA comes out of the core and looks like flagella. The first mRNA codes for an enzyme that digests the protein coat around the core and it frees the DNA for replication.
|
|
|
What disease does variola cause?
|
Smallpox
|
|
|
12. Reverse transcriptase has important ramifications in feline leukemia virus, human immunodeficiency virus, and other retroviruses. What is its function (describe the mechanism) and what is the significance of this enzyme in terms of disease management?
|
-Reverse transcriptase makes DNA from viral RNA, which is then incorporated into the host cell genome leading to viral protein production. Because eukaryotes never go from RNA to DNA, this enzyme is only found in retroviruses, and is therefore a potential target for therapy. (Eg, AZT).
|
|
|
True or False: Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis causes abortion in cattle.
|
True
|
|
|
What disease does vaccinia virus cause?
|
No disease – used in the development of vaccines.
|
|
|
List 7 Orthopoxviruses:
|
1. Variola (small pox)
2. Vaccinia virus 3. Buffalo pox 4. Cowpox 5. Camel pox 6. Ectromelia (mouse pox) 7. Monkey pox |
|
|
Which disease is not caused by the same genus as the others? What is the genus?
HIV, BLV, CAE, Visna/Maedi- |
BLV
Lentiviruses (Also FIV, SIV, BIV, EIA (equine infectious anemia)) |
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about Equine Rhinopneumonitis?
a) It is the equivalent of IBR in horses b) It causes URIs in foals c) It causes late term abortions in mares d) It is highly contagious e) It is highly fatal |
E - It is highly fatal
It is a rather mild disease. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a pox virus?
a. Smallpox b. Chickenpox c. Cowpox d. Monkeypox e. Buffalopox |
B - Chickenpox
|
|
|
Which disease is not caused by the same genus as the others? What is the genus?
FeLV, FeLSV, Avian Leukosis, EIA |
EIA
Oncornaviruses (Also BLV, murine orncornavirus) |
|
|
Why don’t most universities allow research on Ectromelia (mouse pox)?
|
It is a devastating disease to mice (like smallpox in humans) and can wipe out entire research colonies.
|
|
|
What species does Malignant Catarrhal Fever affect and what are the symptoms of it?
|
Cattle – short febrile inflammation of respiratory and alimentary tracts, keratoconjunctivits, encephalitis, and often death.
|
|
|
What do each of the following enzymes encode:
Gag: Pol: Env: Which are needed for replication? |
What do each of the following enzymes encode:
Gag: Capsid Pol: Enzymes Env: Envelope Which are needed for replication? ALL of them! |
|
|
List 5 classes of poxviruses that are important in veterinary medicine
|
Orthopoxviruses
Parapoxviruses Avipox Capripox Suipox |
|
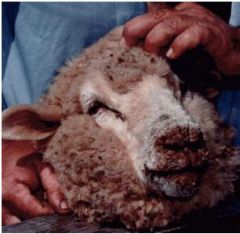
What is wrong with this picture of a lesion on a sheep? What poxvirus might this be?
(image from wikimedia commons) |
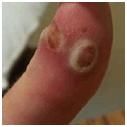
This is a classic presentation of Orf or Contagious Pustular Dermatitis in sheep caused by a parapox virus. This is a zoonotic disease and can cause pustular lesions on human skin (anywhere you touch yourself after touching such a lesion on a sheep)! The person in the picture should be wearing gloves.
(image from CDC) |
|
|
Describe the alteration made to SIV/HIV that reduces pathogenicity.
|
The NEF gene is partially deleted. Because the NEF gene transfers pathogenicity, the NEFless strain has potential in antiretroviral immunizations.
|
|
|
Which of the following is TRUE of Malignant Catarrhal Fever?
a) High morbidity b) High mortality c) Short incubation period d) Known to wipe out entire herds e) Found predominantly where cattle and equids graze together |
B High mortality
sporadic infections, long incubation period (4-20 weeks), usually only a few individuals in a herd that get it, found often where cattle graze with sheep or blsck wildebeest |
|
|
Describe the acute and chronic forms of Equine Infectious Anemia
|
- Acute: With acute infection the horse The acute form of EIA is manifested with fever, depression, and lack of appetite leading to the death of approximately one third of infected horses within a month.
Chronic: The chronically infected horse will have recurring acute bouts of symptoms along with weight loss, ventral (dependent) edema (swollen belly and legs) and anemia. These horses will be positive on a EIA test (Coggins or Immunodiffusion Test. |
|
|
Why are canarypox viruses being used in the production of human vaccines?
|
When injected into humans, they express their proteins, but do not assemble into infectious viruses, so they are a safe vector for recombinant vaccines.
|
|
|
What is the hallmark of retroviruses?
|
Virion bound RdDp (reverse transcriptase)
|
|
|
Which produce a stronger antibody response: linear epitopes or conformational epitopes?
|
-Confirmational epitopes are what is directly recognized by T-cells.
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about retroviruses?
a. They have an icosahedral capsid b. They have an envelope with glycoprotein spikes c. They have one +ssRNA strand. d. They carry a virion-bound enzyme e. Their name means “backward” in Latin |
C - They have one +ssRNA strand.
They are DIPLOID – 2 identical +ssRNA. |
|
|
Name five Lentiviruses.
|
HIV, SIV, FIV, EIA, CAE (Immunodeficiency viruses, Equine infectious anemia, and Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus)
|
|
|
Name 3 Oncorna viruses.
|
FSV, FeLV, BLV (Feline sarcoma and leukemia viruses, and bovine leukemia virus)
|
|
|
What is easier to produce in a lab, a desired linear epitope or a conformational epitope?
|
-because it is difficult to predict the 3-d shape a protein or nucleic acid will take, synthesizing vaccines that will conform to a particular conformation is very difficult.
|
|
|
True or false: Spumaviruses cause foamy cytopathic lesions in their hosts.
|
False: They do in tissue culture, but have never been associated with any disease.
|
|
|
Which of the following is TRUE:
a. C particles look like donuts b. A particles are likely precursors to viral envelopes c. B particles are budding viruses d. B particles have an eccentrically located nucleoid and are seen with mammary tumor viruses e. We discussed D particles and they are extremely important |
D - B particles have an eccentrically located nucleoid and are seen with mammary tumor viruses
|
|
|
Why does the concept of confirmational epitopes negatively impact the effectiveness of vaccinating using a G-protein synthtetic peptide vaccine?
|
-In a virus, the G-protein is bound to other components of the virus, and thus a vaccine of free G-protein will present different isotopes than the real vaccine might have.
|
|
|
True or false: Lentiviruses like HIV and FIV are easy to diagnose from electron micrograph.
|
True - Instead of having a centrally located nucleoid, nucleoid looks conical (like cat eye)
|
|
|
Many viruses can be attenuated by as much as 10% by deleting a single gene. Which of the following are genes that can be attenuated to greatly reduce pathogenicity:
A. TK B. NEF C. IFN D. TSTA E. All of the above F. A, B, and D G. A and B only |
G - A and B only
|
|
|
True or false: The +ssRNA genome of retroviruses is infectious.
|
False
|
|
|
Describe how retroviruses replicate their genome.
|
+ssRNA converted to -ssDNA with RdDp, complementary DNA strand made from –ssDNA to form dsDNA with RdDp, then host DdRp makes progeny ssRNA
|
|
|
SIVhyIFN is an altered SIV virus that is very highly attenuated. Name two ways in which SIVhyIFN differs from SIV.
|
-It is missing the NEF gene and made to express IFN. It is drastically more attenuated than SIV(delta)nef.
|
|
|
Match the Rous Sarcoma Virus components with their function.
Gag Pol Env Src LTR Envelope Capsid protein Responsible for transformation Makes polymerase, protease, and integrase Promoter for gene expression, integration into host genome |
Gag - Capsid protein
Pol - Makes polymerase, protease, and integrase Env - Envelope Src - Responsible for transformation LTR - Promoter for gene expression, integration into host genome |
|
|
The Rous Sarcoma Virus is also known as the _______ sarcoma virus.
|
avian
|
|
|
Leukemia viruses lack the ______ gene.
|
Src
|
|
|
There is a major shortage of organs for human transplant. What is a key gene that scientists could alter to reduce rejection of xenografts?
|
-Scientists are working to engineer organs such as lungs and hearts in animals that express human MHC.
|
|
|
18. Long Terminal Repeats (LTRs) are important for all of the following except:
a. Polyadenylation b. Initiation of synthesis c. Integration of dsDNA into host genome d. Promotion of gene expression e. Encodes integrase protein |
E - encodes integrase protein
|
|
|
When a virus kills a cell in vitro, many changes are evident. First, the cells “round out,” (become spherical) and the nucleus becomes pyknotic. Next, the cell loses attachment to the surface they were sitting on (“floaters.”) What is the term virologists use to describe these events?
|
CPE or cytopathic effect.
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of priming?
a. Priming is when there is a strong primary immunologic response to a vaccine followed by an equally strong anamnestic response. b. Priming is when there is a weak or undetectable primary immunologic response to a vaccine followed by a strong immunologic response upon challenge with a second vaccine c. Priming is when there is a weak primary immunologic response to a vaccine but a strong immunologic response to the pathogen. d. DNA vaccines were developed because they were thought to have a good priming effect. e. DNA vaccines cannot be used as priming vaccines. |
B - Priming is when there is a weak or undetectable primary immunologic response to a vaccine followed by a strong immunologic response upon challenge with a second vaccine
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of DNA vaccines?
a. Chemically stable b. Cheaper to produce c. No hypersensitivity reactions d. Effective when used alone e. No reversion to virulence |
D. Effective when used alone
|
|
|
There are two kinds of BVD - cytopathic and noncytopathic.
T/F: noncytopathic BVD is causes no pathogenesis in a normal cell. |
-False: noncytopathic BVD won’t kill the cell, but it can still have pathogenic effects such as immune suppression.
|
|
|
What are 4 general mechanisms by which viruses can harm host cells?
|
1. Shut down of cellular macromolecular synthesis
2. Release of enzymes from lysosomes 3. Inclusion bodies 4. Cell fusion |
|
|
What is the purpose of homologous viral interference?
|
To keep the virus from killing the host cells – moderates rate of replication of the virus.
|
|
|
What is a concern with culturing vaccines in live cell cultures regarding cytophatic effect (or lack thereof)?
|
It is very difficult to know if a cell culture has a noncytopathic virus; when culturing a virus in a cell, it’s possible that you will extract the virus you intended AND another virus; this virus may be harmful in the new host.
|
|
|
Which of the following is TRUE about homologous interference?
a. All viruses have defective interfering particles except for vaccinia virus b. B particles have a greater affinity for RdRp c. T particles are not used in vaccines because they cause disease d. T particles infect T lymphocytes and B particles infect B lymphocytes e. Viruses expressing T and B particles are more pathogenic than viruses consisting of only B particles. |
A - All viruses have defective interfering particles except for vaccinia virus
|
|
|
True or False: An example of heterologous interference is the inability of cells infected with rubella to be infected with NDV.
|
True
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a characteristic of prion diseases?
a. CNS amyloid deposition b. Non-inflammatory c. Long incubation period d. Progresses to death e. Antibodies produced, but ineffective |
E - Antibodies produced, but ineffective
Usually no antibody response |
|
|
What is one of the most important characteristics exhibited by normal cells that is lost in cancerous cells, according to Dr. Yilma?
|
Contact inhibition!
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of prions?
a. Resistant to formalin inactivation b. Resistant to nucleases and irradiation c. Resistant to SDS and trypsin d. Extremely hydrophobic e. Proteinaceous infectious particle |
C - Resistant to SDS and trypsin
They are proteins and can be broken down by the sames things that degrade protein. |
|
|
T/F: The immune system is very good at detecting TSTA antigens in a cell.
|
-FALSE. TSTA is viral antigen produced when DNA of many viruses is integrated into the genome of the host cell. It is expressed on the surface of cells, but is not usually recognized by the immune system. If we could get the immune system to recognize these antigens, it would be an effective way of preventing viral propagation for many viruses.
|
|
|
Which of the following is FALSE about prions?
a. Prion proteins encoded by cellular DNA are referred to as PrPc b. Prion proteins found in scrapie lesions are referred to as PrPsc c. PrPc has an alpha helix conformation and PrPsc has a beta pleated sheet conformation d. PrPc has a beta pleated sheet conformation and PrPsc has an alpha helix conformation e. PrPsc is both hereditary and infectious |
D - PrPc has a beta pleated sheet conformation and PrPsc has an alpha helix conformation
|
|
|
True or false: Transgenic mice lacking PrPc are resistant to prion diseases.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F: A promising technique for combating HIV is to educate the immune system to respond to T antigen or TSTA.
|
HIV does not produce either T antigen or TST antigen.
|
|
|
True or False: Scrapie can be seen in sheep under one year of age.
|
False
|
|
|
How do prions cause disease?
|
Pathogenic prions (PrPsc) convert endogenous prions (PrPc) from their alpha helix conformation to a beta pleat conformation. These abnormally folded proteins accumulate in the CNS as amyloid deposits. The amyloid causes spongiform disruption of brain tissue (histologically brain has lots of vacuoles and looks like a sponge) and the normal functioning of the brain is impaired causing a slow degenerative encephalopathy.
|
|
|
Which of the following diseases are NOT caused by prions?
a. Scrapie b. TSE c. CWD d. ASF e. Kuru |
D - ASF
|
|
|
True or False: feline sarcoma virus can't grow without feline leukemia virus
|
True
All sarcoma viruses except Rous virus are deficient, meaning they lack a viral factor essential to replication (such as gag, pol, and env) |
|
|
What would be the result of putting fsv on a culture of fibroblasts? (Would the fibroblasts become oncotic or not?)
What about leukemia virus? |
FSV: Instant tumors! Feline sarcoma virus contains the SRC gene, which is an oncogene.
Leukemia: Nothing will happen; the process of induction of oncosis via leukemia virus is slow an inefficient. |
|
|
True or False - A cat with leukemia virus most likely has sarcoma virus as well
|
False - other way around
|
|
|
What is the oldest known disease of sheep?
|
Scrapie
|
|
|
True or False-- Viral src genes contain introns
|
False
|
|
|
True or False- scrapie is a piece of protein, not a virus
|
True
|
|
|
True or False-- Viral src genes cointain only exons and were taken directly from cellular DNA
|
False
Viral SRC gene was stolen from the host mRNA and incorporated into the virus. mRNA genes have had the introns spliced out, and only the exons remain. (If you have a hard time remembering which is which, remember EXpressed versus INtervening.) |
|
|
How does the Long Terminal Repeat (LTR) of FeLV cause cancer in host cell?
|
The LTR sequence inserts randomly into the genome, but because it lacks SRC gene, it does not automatically induce a tumor. However, it will frequently insert into a control segment upstream of the host SRC gene or other oncotic genes, disrupting the regulation and resulting in constitutive expression. (Example: some factors normally are expressed inhibiting cell growth, but in response to a laceration, the control factor is blocked, and the cell grows. If the regulating factor has an insertion disrupting its function, the growth factor will be constitutively expressed.
|
|
|
T/F: both sarcoma virus and leukemia virus insert randomly into host genome
|
true- but sarcoma virus causes cancer independent of location, whereas leukemia only causes cancer if it’s located in a control region upstream of an oncogene!
|
|
|
Compare and contrast PrPsc and PrPc
|
• They both have the same amino acid sequence however PrPsc (the disease form) takes on the Beta sheet form; PrPc (normal/non-diseased form) takes on an alpha helix form.
• PrPSC has been adapted from sheep to mice and hamsters • Amyloid deposits can cause a conformational change in normal PrPC converting it to the Beta sheet conformation ( PrPsc) |
|
|
T/F: virtually every mammal has endogenous viruses
|
True
|
|
|
List three mechanisms by which a normal cell can be transformed into a cancer cell.
|
1. Overexpression of oncogenes. (Oncogenes are so named not because they typically cause cancer, but because their overexpression results in cancer. Oncogenes are very common and serve to promote physiological growth.)
2. Loss of a tumor suppressor gene (eg, leukemia virus) 3. Introduction of a viral SRC gene (ie, FSV) |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT true about prions?
a. They are inactivated by protein denaturing agents b. They are inactivated by nucleic acid denaturing agents (formalin) c. Are the agents for the disease scrapie d. Can be isolated from the brains of infected animals e. All of the above are true about prions |
B - they are resistant to formalin (not inactivated by formalin), which only degrades nucleic acids and not the prions, which are proteins.
|
|
|
Define ectopic.
(in relation to retroviruses which are transmitted vertically) |
(ECO)- If you were to isolate them, they could only replicate in their host
|
|
|
Name a TSE of cattle.
|
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy of cattle = Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
|
|
|
Define Xenotropic
(in relation to retroviruses that are transmitted vertically) |
isolate of this virus could only replicate in a non-host species
|
|
|
Define Amphotropic
(in relation to retroviruses that are transmitted vertically) |
can replicate anywhere (Word hint: amphi means both/both sides: amphipathic=both lipid and polar, amphibian=both land and water, amphoteric=both acid and base)
|
|
|
Which of the following diseases is transmissible to humans: Scrapie or BSE?
|
BSE can be transmitted to humans by eating the meat of an infected animal.
|
|
|
What is the name of a slowly progressive, fatal human disease caused by eating the infected brain of another human (primarily affecting cultures who ritually eat the brains of deceased relatives)?
|
Kuru
|
|
|
Match the Classifications and types of Interferons.
1. IFN-alpha 2. IFN-beta 3. IFN-gamma a) leukocyte interferon b) Immune or type II (there must be an immune response to induce) c) Fibroblast, non-immune, type I |
ANSWER: 1=a 2=c 3=b
|
|
|
Interferon is antigen specific. True or false?
|
False
|
|
|
Name 3 types of Interferon Assays; describe what they measure
|
1. Biological: [inhibition of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV) or EMCV)] measures how much antiviral state you have.
2. Quantitative: [ELISA] Measures how much protein (IFN = protein) you have. 3. Anti-proliferative: [ anti-cellular assay] measures its anti-tumor activity. |
|
|
T/F: Interferon is generally species-specific
|
True
With rare exceptions, the cytokine receptors for interferon differ with species. (Sheep IFN receptors are an exception, and respond to interferons from many species.) |
|
|
Interferon is induced by double-stranded RNA; explain why the common flu elicits an antibody response, despite having an ssRNA genome.
|
Regardless of the genome, one strand of RNA will serve as a template for another at some point in the life cycle of a virus. With rare exceptions, these strands are free in the host cytoplasm and thus pairing of complimentary strands to produce dsRNA is not uncommon.
|
|
|
Would measuring the inhibition of a virus after application of serial dilutions of an antiviral best be termed a biological, quantitative, or anti-proliferative assay?
|
Biological
|
|
|
Name a test that quantifies the amount of protein present in a sample. Does this test tell you whether the sample will have antiviral activity?
|
ELISA
No—it does not directly measure biological activity. |
|

Match the interferon with its characteristics
|
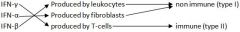
|
|
|
What are two mechanisms of antiviral action?
|
1. Protein Synthesis- (In response to IFN, cells produce a protein kinase that, in the presence of double-stranded RNA and ATP, inactivates eIF-2 (by phosphorylation).eIF-2 is responsible for protein synthesis initiation, and so infected cells are not able to produce proteins in the presence of interferon)
2. Viral RNA degradation- (In response to IFN, cells also produce an enzyme called 2-5A synthetase.This combines with dsRNA and ATP to produce a LMWIT (low molecular weight oligonucleotide) which, activates an endonuclease that degrades viral mRNA and rRNA.) |
|
|
What two things must be present in a cell for interferon to work by either mechanism (protein synthesis inhibition or viral RNA degradation)?
|
ATP and dsRNA
|
|
|
What do you call a culture of cells freshly obtained by using chemicals to dissociate them from an organ or tissue?
|
primary culture
|
|
|
What is a cell excretion essential for signaling cells to grow in culture?
|
conditioned medium; when cell density is high enough, the concentration of conditioned media spurs the culture to grow.
|
|
|
Give an important signal that limits cell growth when they reach a certain density.
|
contact inhibition
|
|
|
Describe a mechanism for attenuating a virus that used to be used very commonly, and is still used today (though it is much less important.)
|
passage through cells of another species. (Scientists can infect the cells of a nonhuman species with a viral pathogen, collect the resulting viral progeny, and inject them into another set of cells from that species. After this is done enough times, the cells will have adapted to grow in the new host, and their virulence factors will become selective for the nonhuman host. When the virus is no longer pathogenic to humans, it is said to be attenuated.)
|
|
|
What is so darn special about Madin-Darby Bovine Kidney Cells? Are they anchorage dependent?
|
they are karyotypically normal cells that can be “passed” an indefinite number of times without dying off; they are a continuous cell line widely used in biology laboratories. They are not cancerous and do not lose contact inhibition. They are anchorage dependent.
|
|
|
What do you call a cell line that has lost contact inhibition? Are these cells anchorage dependent?
|
Transformed. They are no longer anchorage dependent; they can be grown in suspension and don’t need to be attached to a solid surface. They do not grow in a smooth monolayer, but cluster together and participate in other unruly cell behavior.
|
|
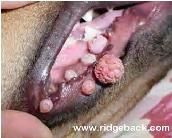
An owner brings in a dog to your small animal clinic with a mouth that looks like this. What is the most likely etiological agent? Is this tumor likely to be malignant? Would you recommend removal of the tumor?
|
Canine Papilloma virus – “Infectious papillomatosis is a self-limiting disease, although the duration of warts varies considerably. A variety of treatments have been advocated without agreement on efficacy. Surgical removal is recommended if the warts are sufficiently objectionable. However, because surgery in the early growing stage of warts may lead to recurrence and stimulation of growth, the warts should be removed when near their maximum size or when regressing. Affected animals may be isolated from susceptible ones, but with the long incubation period, many are likely to have been exposed before the problem is recognized.” –Merck Veterinary Manual
|
|

Match the cell culture to its description
|

(But note that any cell in suspension or prevented from anchoring, eg, with EDTA added, will form spheres naturally.)
|
|
|
What 2 antigens are produced by Papova viruses and where are they expressed?
|
T (tumor)antigen – Intranuclear
TSTA – Tumor Specific Transplantation Antigen – Cell surface |
|
|
What virus type causes warts?
|
Papilloma
|
|
|
What virus could likely be the cause of a dog’s unilateral corneal opacity?
|
Canine Adenovirus; cause of Infectious Canine Hepatitis
|
|
|
Which of the following is TRUE of Adenoviruses?
a) They are icosahedral enveloped viruses b) They have receptor-binding antigens sticking out from the corners of the capsid c) They have class II replication d) They are dsRNA viruses e) They replicate in the cytoplasm of the host cell |
B - They have receptor-binding antigens sticking out from the corners of the capsid
|
|
|
Pseudorabiesis also known as _______________.
|
Mad Itch
|
|
|
What does the human papilloma virus cause?
|
Cervical Carcinoma in women
|
|
|
Pseudorabies is a herpesvirus that affects the CNS, causes intense pruritis, and is 100% fatal. Which of the following species is not affected by pseudorabies?
a) Cattle b) Foxes c) Piglets d) Ferrets e) Dogs f) Cats g) Sheep h) Humans |
H Humans
|
|
|
True or False: Adult pigs have mild or inapparent signs of pseudorabies.
|
True
|
|
|
Canine herpes causes ____________________ in adult dogs and _________ in puppies < 3 weeks.
|
tracheobronchitis/bronchopneumonia
death |
|
|
Feline Rhinotracheitis causes ____ in young cats and has a (high/low) mortality.
|
URI
High |
|
|
Marek’s disease is also known as ____________________ of chickens.
|
Neurolymphomatosis
|
|
|
There are three forms of Marek’s Disease – what are they?
|
Neural
Ocular Visceral |

