![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta results in defect collagen type ____.
|
1
|
|
|
Substance A is freely filtered in the glomeruli and reabsorbed in the renal tubules. A healthy volunteer receiving substance A has the following findings:
Inulin clearance: 100 mL/min PAH clearance: 500 mL/min Plasma concentration of substance A: 0.5 mg/mL Tubular reabsorption of substance A: 25 mg/min What is the expected excretion rate for substance A in this volunteer? |
Total filtration rate of substance A = GFR x plasma concentration of A
GFR~Clearance of inulin (neither secreted nor reabsorbed) Total filtration rate of substance A = (inulin clearance)(plasma concentration of substance A) Net excretion rate of substance A= (inulin clearance)(plasma concentration of substance A) - (Tubular reabsorption of substance A) =100x0.5 - 25 = 25 mg/min Note that PAH clearance is irrelevant! |
|
|
What are potassium levels like in someone with DKA?
Why? |
Normal to increased serum potassium levels despite low intracellular potatssium.
Potassium loss occurs via osmotic diuresis induced by glycosuria. Potassium replacement is a crucial step in management of pts with DKA. |
|
|
Draw a cardiac catheterization graph that shows mitral regurgitation.
|
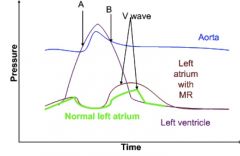
|
|
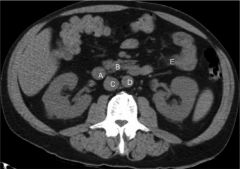
Label
|
A: Descending duodenum
B: Pancreas C: IVC D: Abdominal Aorta E: Loop of jejunum |
|
|
Describe the mechanisms required for calcium influx and efflux of cardiac muscle cells.
|
Influx: Voltage dependent calcium channels which then stimulate ryanodine receptors, which allow for release of a still larger pool of stored calcium within sarcoplasmic reticulum
Efflux: mediated by Ca2+-ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange mechanisms |
|
|
Side effects of nitrates.
|
HEADACHES
Cutaneous flushing Most common at higher doses where nitrates can produce arteriolar dilation. |
|
|
What reaction does urease catalyze?
|
Urea-->CO2 + Ammonia, causing a pH increase
Used to detect H. pylori infection |
|
|
How is vancomycin resistance achieved?
|
Vancomycin binds D-alanyl-D-alanine termini in cell wall peptide precursors to prevent formation of peptidoglycan.
Mechanism of vancomycin resistance results from substitution of D-lactate for D-alanine in synthesis of proteoglycan precursors (altered vancomycin binding site) |
|
|
How is pseudomonas transmitted?
|
Water!
HOT TUB FOLLICULITIS |
|
|
Women who have just delivered babies with neural tube defects are asked about their use of acetaminophen during the first three months of pregnancy.
Women who delivered healthy babies are also asked about their use of acetaminophen during the first three months of pregnancy. What type of study is this? What measure of association is most appropriate? |
Case-control study
People with dz of interest (cases) and people without the diseases (controls) are asked about previous exposure to variable being studied (acetaminophen use). Main measure of assocn is exposure ODDS RATIO (odds of exposure of people with disease (cases))/(odds of exposure of people w/o the dz (controls)) Note: would only use relative risk if had incidence (which can't be measured in case-control studies bc people already have the dz!) |
|
|
How does anorexia result in amenorrhea?
|
Loss of pulsatile secretion of GnRH from hypothalamus. Not due to defect in pituitary or ovaries.
This occurs when level of body fat falls below a certain critical level. |
|
|
Effects of carnitine deficiency.
|
beta-oxidation of fatty acids requires removal of carbons from FA chain by oxidation at beta-carbon (occurs in mitochondria).
To transport fatty acyl-coA from cytosol into mitochondria, cell must first form fatty acyl-CARNITINE intermediate. Reaction catalyzed by carnitine acyltransferase I on outer surface of inner mitochondrial membrane. After molecule transported into mitcodhonria, carnitine acyltransferase II on inner surface of inner mitochondrial membrane catalyzes regeneration of fatty acyl-CoA and free carnitine. KNOWN AS CARNITINE SHUTTLE. Carnitine deficiency reduces ability of FA's to enter mitochondria for beta-oxidation. Beta-oxidation of FA's produces acetyl CoA, a precursor of acetoacetate (a ketone!). Thus, carnitine deficiency causes dec'd formation of acetoacetate. |
|
|
Tumor cell expressing CD31:
Diagnosis Exposure risks Tumor type |
CD31 is PECAM1 (platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule); functions in leukocyte migration through endothelium
Thus tumor arises from vascular endothelial cells. Most likely diagnosis is LIVER ANGIOSARCOMA (rare malignant vascular endothelial cell neoplasm) Carcinogen exposure: arsenic, thorotrase (radioactive contrast medium), polyvinyl chloride (plastic widely used in industry) |
|
|
Papillary thyroid vs Follicular thyroid carcinomas:
Histologic differences |
Papillary: branchinc papillae, cuboidal epithelium, GROUND GLASS APPEARANCE, CONCENTRIC CALCIFIED STRUCTURES (psammoma bodies)
Follicular: consist of follicular cells or large cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (Hurthle cells). |
|
|
Which biochemical processes occur exclusively in the mitochondria?
|
beta-oxidation of FAs
TCA Urea cycle (carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1, ornithine transcarbamoylase) Pyruvate carboxylation (pyruvate carboxylase) |
|
|
Which biochemical processes occur exclusively in the cytoplasm?
|
All reaction of pentose pathway (transketolase)
|
|
|
33 year-old female
Failure to conceive for 1 year h/o purulent urethritis 5 years ago treated with ceftriaxone Diagnosis How could this have been prevented? |
Most common cause of tubal-factor infertility is PID--most commonly caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis.
Need to treat for both! Not just ceftriaxone. Need to add azithromycin or doxycycline. Since not treated correctly, chlamydia allowed to persist and cause asyx infection leading to fallopian tube scarring and subsequent infertility. |
|
|
A cohort study is conducted to assess association between smoking and SCC of esophagus. During 10 years of follow-up, smokers had five times the risk of esophageal carcinoma compared to non-smokers (RR=5.0, 95% CI = 2.9-7.1)
What percent of esophageal carcinoma can be attributed to smoking? |
Attributable risk percent = (risk in exposed - risk in unexposed)/risk in exposed
OR ARP = (RR-1)/RR =(5-1.0)/5.0=0.80 |
|

|
Filtration Fraction = fraction of plasma entering kidneys that filters into renal tubular lumen:
FF = GFR/RPF RPF is amount of plasma that perfuses kidneys per unit time: RPF = (1-HCT)(RBF) Therefore: FF = GFR/[(1-HCT)(RBF)] =0.1/[(1-0.5)(1)] =0.2 |
|
|
8 year-old boy
1 week h/o fever, throat pain Severe dyspnea, tachypnea, inspiratory stridor Worsening dysphagia with solid foods Labs reveal immature hematopoietic cells (blasts) in peripheral smear Diagnosis Pathophys of Syx |
Blast cells in periphery suggestive of leukemia.
Most common pediatric malignancy is ALL. Neoplastic cells of ALL cells arise from either pre-B or pre-T lineage. T-cell ALL more likely to present with large anterior mediastinal mass that can compress great vessels, causing SVC syndrome. Mediastinal mass can also compress esophagus causing dysphagia, while compression of trachea leads to dyspnea, stridor. |
|
|
Effects of doxorubicin on heart function (specific).
|
Cardiotoxicity leading to DILATED cardiomyopathy with SYSTOLIC DYSFN.
|
|
|
What is alcoholic cardiomyopathy?
|
LV dilation (CM)-->systolic dysfn
|
|
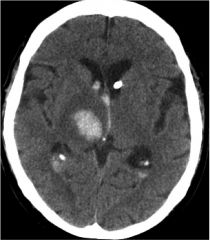
Diagnosis
Pathophys Presentation |
Oval focus of hyperdensity consistent with acute intraparenchymal hematoma.
Most commonly caused by HTN. HTN iduces hyaline arteriosclerosis of arterioles, most commonly in basal ganglia. Vascular walls weaken, prone to dilation. Expansion of arterioles form tiny CHARCOT-BOUCHARD PSEUDOANEURYSMS. THese pseudoaneurysms may rupture and cause small amounts of bleeding or production of hematoma. Presentation: sudden onset of focal deficits |
|
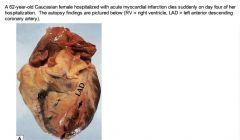
Cause of death?
|
Ruptured LV free wall (complication of STEMI; generally occurs 3-7 days after onset of total ischemia, when coagulative necrosis, neutrophil infiltration, and enzymatic lysis of CT have weakened infarcted myocardium).
Free wall rupture causes cardiac tamponade-->limits diastolic filling-->venous return reduced -->PROFOUND SYSTEMIC HYPOTENSION -->pulseless electrical activity |
|
|
Osteoblasts vs Osteoclasts:
Serum markers |
Osteoblasts: alkaline phosphate
Osteoclasts: Tartrate-resistance acid phosphatase, urinary hydroxyproline, urinary deoxypyridinoline (urinary deoxypyridinoline is most reliable of the three) |
|
|
Symptoms of MEN syndromes.
|
MEN1: parathyroid, pancreas, pituitary
MEN2A: medullary thyroid, pheo, parathyroid MEN2B: medullary thyroid, pheo, mucosal neuromas Note MEN2A/2B both have germ-line RET proto-oncogeneamll |
|
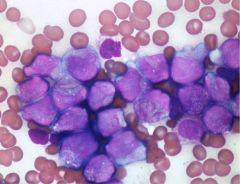
Diagnosis
What would these stain positively for? |
Auer rods-->AML M3
Auer rods indicate myeloid differentiation, they are deformed azurophilic granules and will stain positively for MYELOPEROXIDASE. |
|

Verapamil administration would have what effect?
|
Phaso 0 depolarization (rapid upstroke following slow phase 4 depolarization) mediated by calcium ion influx into cells of the SA and AV nodes.
Verapamil is a CCB and will slow phage 0 depolarization, which decreases the rate of SA node firing and slows AV node conduction. Impulse conduction from SA node through AV node to ventricular myocardium all occurs during diastole; thus, verapamil slows diastolic depolarization. |
|
|
65 year-old female
Progressive dyspnea and cardiomegaly Occasional dysphagia Enlargement of what heart structure accounts for her symptoms? |
Cardiovascular dysphagia can result from pressure on esophagus from dilated left atrium.
LA commonly enlarged in patients w/Mitral Stenosis and LV failure. |
|
|
What heart structures are most anterior/posterior?
|
Most anterior: RV
Most posterior: LA |
|
|
Describe the steps by which chronic hypertension contributes to pulmonary hypertension.
|
Chronic HTN-->LV diastolic dysfn
Dec'd LV diastolic compliance-->rise in LV fill pressure -->Rise in LA pressure -->Rise in Pulmonary venous pressure -->Pulmonary venous congestion -->Rise in hydrostatic pressures cause capillary leak and subsequent pulmonary edema -->Alveolar collapse -->Dec'd ventilation -->REACTIVE VASOCONSTRICTION -->Pulmonary arterial HTN (-->Pulmonary arterial HTN-->increase in afterload-->RHF) |
|
|
Describe the events that occur once phospholipase C is activated.
|
Phospholipase C takes phospholipids and converts them into IP3 and DAG
IP3 increases intracellular calcium which, along with DAG, activates Protein Kinase C PKC then phosphorylates proteins to do its thang. |
|
|
What is the role of 16S rRNA in prokaryotic ribosomes?
|
Prokaryotic 16 rRNA contains a sequence complementary to Shin-Dalgarno sequence on mRNA (located 10 bases upstream from AUG start codon)
This allows initiation of protein translation. |
|
|
Hypnotic drug with anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant actions
Drug class Specific MOA |
Benzodiazepines
Modulate GABA-A receptor CHLORIDE channel in CNS, increasing its frequency of firing. This increase in Cl- permeability hyperpolarizes and stabilizes the membrane, rendering it less excitable. |
|
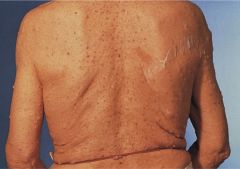
Diagnosis
Mode of Inheritance Other symptoms |
Multiple small cutanoues lesions = Neurofibromas assocd w/NF1
Presents with: Café-au-lait spots Lisch nodules in iris (pigmented hamartomas; benign) MENINGIOMAS |
|
|
Most common cause of pneumonia in ALL ADULTS.
|
Step pneumo
|
|
|
CSF shows:
Gram positive Lancet shaped diplococci |
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
CSF shows:
Gram positive Cocci in clusters |
Staph aureus
|
|
|
CSF shows:
Gram positive Cocci in chains |
Strep agalactiae (Group B Strep)
|
|
|
CSF shows:
Bean shaped diplococci |
Neisseria meningitidis
|
|
|
Etoposide:
Specific MOA |
Specifically inhibit TOPOISOMERASE II's ability to seal strand breaks it induces, causing chromosomal breaks to accumulate and eventual cell death.
Used in testicular cancer and small cell lung cancer. |
|
|
Topoisomerase I vs II
|
Topoisomerase I makes single-stranded nicks to relieve negative supercoiling
Topoisomerase II induces transient breaks in both DNA strands simultaneously to relieve both positive and negative supercoiling |
|
|
First-line treatment for patients with acute gouty arthritis
|
NSAIDs--dec'd PG synthesis
|
|
|
When are xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosuric drugs used in gout?
|
to PREVENT future gouty arthritis attacks. not for use in acute gouty arthritis
|
|
|
Hypoxemia
Petechial rash Acute neurologic abnormalities Long bone fracture |
Fat embolism syndrome
|
|
|
Which cell cannot utilize ketones for energy? Why?
|
RBCs--don't have mitochondria
Hepatocytes--don't have succinyl CoA-acetoacetate CoA transferase (thiophorase), which is required to convert acetoacetate to acetoacetyl CoA |
|
|
What is MCHC?
Diagnostic utility? |
MCHC = mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
In hereditary spherocytosis, MCHC is inc'd because of mild dehydration of the RBC |
|
|
3 year-old male
Jaundice, pallor Anemia, reticulocytosis, increased indirect bilirubin RBCs are dysmorphic without central pallor Diagnosis |
Hereditary spherocytosis
Diagnosis is best confirmed by osmotic fragility testing |
|
|
45 year-old female
h/o pruritis, fatigue Pale stool Liver biopsy reveals granulomatous destruction of interlobular bile ducts Diagnosis Pathophys |
Primary biliary cirrhosis--autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts and cholestasis
May also present with steatorrhea, portal HTN, osteopenia Will see heavy portal tract infiltrate of macs, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils |
|
|
Vertical diplopia:
When is it triggered? Cause? |
When reading (eyes look toward nose) or walking downstairs
Trochlear Nerve Palsy (CN IV) |
|
|
CN innervations of the extraocular muscles.
|
LR: CN6
SO: CN4 R: CN3 |
|
|
30 year-old male
Neck lump PMH pheochromocytoma FMH of thyroid cancer Diagnosis Histologic Findings Gene mutation involved |
Patient likely has MEN 2A/B syndrome
Expect medullary thyroid cancer (mutation to RET proto-oncogene); arises from parafollicular calcitonin-secreting C cells Histology shows uniform polygonal or spindle-shaped cells w/extracellular amyloid deposits. Amyloid stains with Congo red. |
|
|
What step of the TCA provides a phosphate source for energy?
|
GTP production occurs in SuccinylCoA-->Succinate
Energy sed to convert phosphoenolpyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
|
|
Laparotomy reveals chalky white lesions in mesentery.
Histology reveals fat cell destruction and calcium deposition. Diagnosis Pathophys |
Acute pancreatitis:
Starts as acute interstitial pancreatitis (duct obstruction-->stasis-->digestions of adipose cells by lipase) Areas of focal necrosis and calcium precipitation induce an inflammatory rxn If inflammatory process continues, blood flow to pancreas is compromised as a result of edema and ischemia damages the acinar cells-->RELEASES TRYPSIN Trypsin activates other proteolytic enzymes and initiates autodigestion of pancreatic tissue Acute necrotic pancreatitis develops Destruction of blood vessel walls can cause hemorrhage into necrotic areas. |
|
|
Neuroendocrine markers of small cell carcinoma.
|
Chromogranin
Synaptophysin Neurofilaments |
|
|
High Potency vs Low Potency Antipsychotics:
Examples AE Differences |
High potency:
Haloperidol, fluphenazine, pimozide Low potency: Chlorpromazine, thioridazine High potency agents more likely to cause EPS and less likely to cause anticholinergic/antihistamine f/x Low potency agents more likely to cause antichol/antihistamine side effects |

