![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
34 year-old woman
Nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness after minor surgical procedure 1 year h/o chronic corticosteroid therapy BP 70/40 Pulse 120 Pathophys of presentation |
Exogenous glucocorticoids suppresses HPA axis (low CRH, low ACTH, low cortisol)
During stressful situations (infections or surgery), normal individuals experience 3 to 9 fold increase in endogenous glucocorticoids. In a suppressed HPA axis, this stress response is lacking and adrenal crisis ensues. In such cases, a higher "stress dose" must be given to compensate. |
|
|
What are the effect of atrial natriuretic peptide?
|
Atrial natriuretic peptide
ANP lowers BP through peripheral vasoDILATION, natriuresis (dilates afferent arterioles-->increasing GFR and urinary excretion of Na/H2O; limits sodium reabsorption in PCT and inhibits renin secretion) Diuresis (inhibits aldosterone secretion-->inc'd sodium and water excretion) |
|
|
45 year-old male
MVA resulting in pelvic fracture Unable to void, complains of sensation of full bladder Foley attempted, but procedure only yields blood without urine Pathophys |
Inability to void despite sensation of full bladder suggests urethral trauma.
Foley should not have been attempted. Pelvic fractures commonly cause hematoma below the prostate with upward displacement of the gland. This affects the posterior urethra (prostatic end of urethra). |
|
|
Vitamin C vs Vitamin K Deficiency:
Presentation |
Vitamin C:
Hemorrhages Subperiosteal hematomas Bleeding into joint spaces Gingival swelling Secondary periodontal infection Anemia Papular rashes Impaired wound healing Weakened immune response to local infection Vitamin K: Susceptibility to bleeding, as in gums (minor trauma causes bleeding)--not associated with painful gums Note: Vitamin C accelerates hydroxylation of prolyl and lysyl hydroxylase precursors--both necessary for hydroxylation of procollagen |
|
|
In a developing nation, advocating early empiric use of penicillin in treatment of clinically diagnosed bacterial pharyngitis would decrease what sequelae?
|
Early treatment of strep pharyngitis can prevent many cases of rheumatic fever.
Repeated stimulus of B cells against Group A Strep (s. pyogenes) that are homologous to self antigens in heart and CNS. Recurrent untreated GAS pharyngitis will lead to a more rapid onset and increased severity of rheumatic valvular disease. Eradication of infective streptococci from pharynx prevents subsequent episodes of RF. Drug of choice is PCN. No PCN resistant strains of S. pyogenes have been detected yet. |
|
|
Which calcium channel blockers result in vasodilation but have no effect on AV conduction?
|
Nifedipine!!
|
|
|
Which calcium channel blockers slow conduction through the AV node?
|
Verapamil
Diltiazem These are both CARDIAC secific |
|
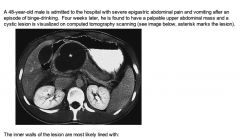
|
CT image shows pancreatic PSEUDOCYST--a potential complication of pancreatitis.
Proteolytic enzymes may disrupt walls of pancreatic ducts and cause leakage of pancreatic secretions into peripancreatic space. This fluid has a high pancreatic enzyme content and induces an inflammatory reaction. Resulting in the formation of GRANULATION tissue, encapsulating the fluid collection and forming a pseudocyst. NOTE: Unlike true cysts, PSEUDOcysts are not lined by epithelium. |
|
|
List the different immunoglobulins and whether they exist as monomers, dimers, or pentamers.
|
IgG = monomers
IgM = pentamers IgA = monomers in serum, dimers in mucus, tears, saliva, COLOSTRUM IgE = monomers |
|
|
40 year-old man
DM I, end-stage renal disease Prolonged bleeding after replacing dialysis catheter Has not been dialyzed for several days Provide values for PT, PTT, PLT count, Bleeding Time Provide reasoning |
Hasn't been dialysed in several days, patient is likely uremic.
Bleeding associated with uremia is a QUALITATIVE PLATELET defect: the PLT count, PT, and PTT are normal. Bleeding time is prolonged. |
|
|
Protease Inhibitors:
AEs |
Lipodysrophy--inc'd deposition of fat on back and abdomen, dec'd adipose tissue on extremities ("buffalo hump" appearance)
Hyperglycemia due to inc'd insulin resistance Inhibition of P-450 |
|
|
Zidovudine:
AEs |
Bone marrot toxicity resulting in ANEMIA
|
|
|
Acyclovir:
AEs |
Renal toxicity
|
|
|
Foscarnet:
AEs |
Renal toxicity
Electrolyte disturbances: hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia |
|
|
What diseases are prone to developing hypercalcemia secondary to high levels of active vitamin D (calcitriol)?
|
Sarcoidosis
Granulomatous diseases: -Tuberculosis -Hodgkin's -Non-Hodgkin's |
|
|
Keratin is a marker of ______ cell origin.
|
Epithelial
|
|
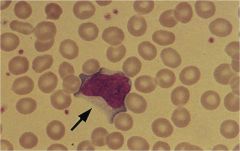
|
Downy Cell--EBV
Risk Burkitt's Lymphoma, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma |
|
|
Ulcer in distal duodenum
|
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome:
Increased gastrin release causes increased gastric acid secretion by parietal cells Majority of these tumors located in pancreas Diarrhea may also occur bc pancreatic and intestinal enzymes are inactivated by gastric acid, so body can't properly digest nutrients Also note that this may appear with multiple ulcers, ulcers refractory to tx, and recurrence of ulcers after acid-reducing surgery |
|
|
Chronic gastritis with antral sparing
|
Autoimmune gastritis
|
|
|
Antral-predominant gastritis
|
H. pylori infection
|
|
|
Ulcer in proximal duodenum
|
Peptic Ulcer Disease; gastric ulcers most commonly located at lesser curvature
|
|
|
Motor innervation of tongue
|
Hypoglossal
|
|
|
Sensation of tongue:
General vs Gustatory |
General:
Anterior 2/3: Mandibular of Trigeminal Posterior 1/3: Glossopharyngeal Posterior area of tongue root: Vagus Taste: Anterior 2/3: Chorda tympani of Facial Posterior 1/3: Glossopharyngeal Posterior area of tongue root and taste buds of larynx/upper esophagus: Vagus |
|
|
Anti-HTN drug associated with depression
MOA |
Reserpine:
blocks storage of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin into vesicles, leaving the NTs vulnerable to degradation by MAO within the cytoplasm while the synaptic vesicles remain empty. Associated with depression and suicidal ideation due to NE and 5HT depleting effects |
|
|
21 year-old male
Sickle Cell Disease Presents with gross hematuria, which he's never experienced before Diagnosis Pathophys Other causes Pathologic findings |
Renal papillary necrosis due to obstruction of renal vessels by sickling-->ischemia
Can also be caused by analgesics (NSAIDs inhibit renal flow by decreasing PG synthesis), DM (non-enzymatic glycosylation causing changes in vascular walls), acute pyelonephritis, UTI (edema compressing medullary vasculature) Will see gray-white or yellow necrosis of tips of renal pyramids; microscopically exhibit coagulative infarct necrosis Note: dark, rust-colored or bloody urine and acute, colicky pain are common syx and are due to acute ureteral obstruction from sloughed papillae |
|
|
20 year-old male
Intermittent self-resolving jaundice Liver biopsy shows abundant pigment inclusions in lysosomes of normal hepatocytes Pigment composed of epinephrine metabolites Diagnosis What type of bilirubinemia would you expect? Pathophys |
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome:
Defect in hepatic excretion of BILIRUDIN GLUCURONIDES across canalicular membrane Presents with CONJUGATED chronic hyperbilirubinemia, NOT A/W hemolysis Icterus is evident, but most pts asyx This is a benign condition |
|
|
Outline homocysteine metabolism
|
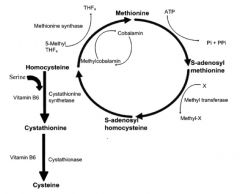
|
|
|
What molecular events occur when a ribosome encounters:
AUG UAA |
AUG-->codes for methionine (this is a start codon)
UAA (or UAG, or UGA) is a stop codon-->stop codons do not code for amino acids. INstead RELEASING FACTORS bind to ribosome and stimulate release of polypeptide chain and dissolution of ribosome-mRNA complex. |
|
|
What are the two methods by which radiation therapy kills cancer cells?
What other cells are likely to be affected by this? |
Radiation induces cell death by:
1) DNA double strand breakage 2) Formation of free radicals. ROS are formed by ionization of water; these oxygen free radicals are then able to cause cellular death and DNA damage This damage is most pronounced in cells that are rapidly dividing, such as malignant cell, bc they have less of an ability to repair DNA damage induced by radiation. Bowel mucosa and skin are affected severely bc they are also rapidly dividing. |
|
|
46 year-old female
Diagnosed with SAH on CT 4 days later develops right arm and leg weakness Diagnosis Pathophys Prevention |
More than half of patients with SAH develop secondary arterial vasospasm. This occurs in vessels surrounding the ruptured aneurysm; causes cerebral ischemia, which presents as new-onset confusion and/or focal neurological deficit 4-12 days after initial insult.
Nimodipine, a selective CCB, is often prescribed to prevent this vasospasm. |
|
|
43 year-old male
Muscle weakness in his hips and shoulders Muscle biopsy reveals MHC class I molecule over-expression on sarcolemma and CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration Diagnosis Pathophys Relevant Antibody |
Polymyositis--likely triggered by viral antigens; it's hypothesized that injury causes release of muscle autoantigens that are taken up by macs, presented to CD4+ helper cells. This leads to inflammation.
Inc'd expression of MHC proteins by muscle cells is then presented by myocytes (along with autoantigen) and recognized by CD8+ cells. This results in muscle inflammation, necrosis, and fibrosis. A/w Anti-Jo-1 Elevated creatine kinase |
|
|
45 year-old male
Penile lesion First began as papule Then several draining ulcers formed Inguinal pain Cell scrapings show inclusion bodies Diagnosis |
Chlamytdia trachomatis: this is classic for chlamydia: small papule on genital mucosa contains cell infected with C. trachomatis; papule is followed weeks later by swollen, painful inguinal nodes which coalesce, ulcerate, and rupture.
Lymph nodes will demonstrate granulomatous inflammn; this can cause lymphatic obstruction and strictures. |
|
|
75 year-old male
Vision problems MRI reveals multiple, small lobar hemorrhages in right occipital and left parietal areas MRI from 1 year ago reveals small, lobar hemorrhage in left frontal area Diagnosis Pathophys |
Recurrent lobar hemorrhages in elderly most likely result from CEREBRAL AMYLOID ANGIOPATHY; this occurs when beta-amyloid is deposited into arterial wall, resulting in weakening of the wall and predisposition to rupture
a/w advanced age and is not related to systemic amyloidosis |
|
|
Male patient with fevers, chills
Dull pain above left knee No joint effusion X-ray reveals soft tissue swelling, bone destruction, periosteal reaction over lower end of femur Diagnosis How would cause differ by age? |
If child-->hematogenous osteomyelitis due to Staph aureus
If adult-->due to predisposition for bacteremia such as IVDU or dialysis |
|
|
Describe the four type of renal stones by:
Chemical content Frequency (general) Radiolucency Microscopic appearance/shape |
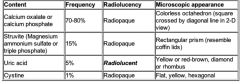
|
|
|
Depolarizing vs Nondepolarizing neuromuscular junction blocking drugs:
MOA Speed of Onset (General) Residual Effects Examples |
Depolarizing NMJ blocking drug, often a rapid onset (within 60 seconds); pt will exhibit residual muscle paralysis even after -stigmine (anticholinesterase) administered to reverse action of a NON-depolarizing agent such as vecuronium.
Acetylcholinesterases do not reverse action of depolarizing NMJ blockers and may enhance them. Example of depolarizing NMJ = succinylcholine |
|
|
When is dantrolene used?
|
Dantrolene relaxes skeletal muscle by reducing Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Used to treat MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA after surgery requiring anesthetic.
|
|
|
Which adrenergic receptors are present in the uterus?
What is the effect of their stimulation? Specific drugs that would do this? |
Adrenergic receptors of uterus belong to beta-2 group whose stimulation leads to uterine relaxation (an effect called tocolysis)
Used in obstetrics to defer premature labor Need to use adrenergic beta-2 agonists such as TERBUTALINE and RITODRINE |
|
|
Cimetidine side effects (2)
|
Gynecomastia
Inducer of Cyp450 |
|
|
66 year-old male with PD
Taking levodopa/carbidopa Complains of increased motion restriction Patient is highly compliant Possible cause? |
Patient is likely takin a multivitamin, which almost always contain B6.
B6 should not be taken by those on levodopa, because B6 increases peripheral metabolism of levodopa and decreases its effectiveness. The more peripheral conversion of levodopa, the less levodopa enters the CNS. |
|
|
59 year-old female
Facial swelling, difficulty breathing Patient recently began taking captopril Diagnosis Pathophys |
This is angioedema (a symptom of anaphylaxis)--involves swelling of tongues, lips, or eyelids. Patients can also experience laryngeal edema and difficulty breathing.
Believed to be due to bradykinin accumulation. |
|
|
Assuming continuous infusion, how long does it take for a drug with first-order kinetics to achieve steady state concentration?
|
4-5 half-lives
|
|
|
In RHD, what physiologic changes occur solely to mitral stenosis?
What findings might indicate an additional process? What could that process be? |
In isolated mistral stenosis, diastolic pressure in the LV is normal. Only pressures PROXIMAL to the mitral valve are elevated.
When a patient with suspected MS is also found to have an increased LVEDP, an additional lesion is likely. Possibilities include rheumatic involvement of the aortic volve (which typically causes aortic stenosis AND regurgitation) or infective endocarditis superimposed on aortic valve deformed by RHD. in RHD, mitral valve alone is sole site of involvement in up to 70% of cases. |
|
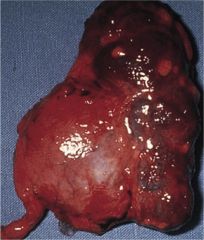
Diagnosis
Pathophys |
Significantly enlarged kidney with dilatation and deformation of the calices and renal pelvis-->HYDRONEPHROSIS
Due to obstruction of urine flow. Most common cause of urinary tract obstruction (in elderly male) is BPH. Other causes include nephrolithiasis, anatomic abnlty, pregnancy, neurogenic bladder |
|
|
Linear vs Lumpy granular deposits of IgG/C3
|
Linear = Goodpasture's
Lumpy = PSGN |
|
|
Describe the events of intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis.
|
Extrinsic:
TNF bound to TNF receptor 1 or Fas ligand to Fas Pro-caspase molecules brought into close proximity Caspases are activated and cleave aspartate residues (note caspases contain cysteine; it's the c in caspase) Intrinsic: UV light, heat, hypoxia, toxins, etc display intrinsic apoptotic signals Balance of pro-apoptotic (Bak, Bax, Bim) and anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2, Bcl-x) proteins is pushed toward Bak, Bax, Bim. Mitochondria becomes permeable and releases cytochrome c into cytoplasm Cytochrome c activates caspases Caspases cleave aspartate residues |
|
|
Moldy grains:
Risks Specific mutation |
Specific strains of Aspergillus grow on foods such as corn, soybeans, and peanuts, producing AFLATOXINS
High levels of dieatary aflatoxin exposure is associated with G to T mutation in p53 Increases risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
Painless gross hematuria
|
Bladder cancer
|
|
|
What is the effect of CO on the oxygen-dissociation curve for hemoglobin?
|
Leftward ***** (inc'd affinity)
|
|
|
What is primary biliary cirrhosis?
Antibody? |
Autoimmune disease of the liver causing progressive destruction of the small bile ducts (bile canaliculi) within the liver.
When these ducts are damaged, bile builds up in liver (cholestasis) and over time damages the tissue. This can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Can lead to xanthoma! (Collection of cholesterol in skin, esp around eyes) Anti-Mitochondrial Antibody (AMA) |
|
|
58 year-old male
Diffuse gallbladder calcification Diagnosis Risks |
Porcelain gallbladder; up to 33% of patient population will develop gallbladder carcinoma
|
|
|
18 year-old male
Right-sided chest pain, dyspnea Tall, thing patient in acute distress Right chest is hyperresonant to percussion, lacks audible breath sounds Diagnosis Pathophys |
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax
Thought to result from rupture of apical subpleural blebs--blebs are continuous, distended airspaces and sometimes form cyst-like sacs. Blebs may spontaneously rupture, usually while pt is at rest, causing a pneumothorax. Tall, thin males around age of 20 are most commonly affected. |
|
|
Describe the role of carbonic anhydrase in RBCs.
|
CO2 produced by tissue respiration enters RBCs and via carbonic anhydrase is hydrated to form HCO3 and H2O.
Many bicarb ions diffuse out of RBC into plasma. To maintain electrical neutrality, Cl- ions diffuse into the RBC to take place of HCO3. THis process is called "chloride shift", and it the reason RBC Cl- content is higher in venous blood. |
|
|
B. anthracis:
Toxins and effects What other bacterium exhibits a similar toxin effect? |
Edema factor--causes increase in cAMP concentration within host cells; important for suppression of nphil fn and accumuln of fluid with and between cells (leading to edema)
Bordetella pertussis also produces an edema factor-like exotoxin called "extracellular adenylate cyclase"; causes dramatic increase in cAMP levels leading to nphil dysfn just as edema factor does Note: B anthracis also has an antiphagocytic poly-gamma-D-glutamic acid capsule |
|
|
45 year-old female
Severe pruritis at night Elevated alkaline phosphatase Diagnosis |
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
|
|

|
For parallel circuits:
1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3...1/Rn Therefore: 1/Rtotal = 1/2 + 1/2 +1/2 +1/2 = 2 Rtotal = 0.5 mmHg/ml/min |
|
|
30 year-old male
Exertional dyspnea Liver biopsy shows PAS-positive intracellular inclusions Diagnosis Pathophys |
Homozygous for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency which inhibits proteolytic enzyme
Will develop panacinar emphysema secondary to DESTRUCTION of alveolar walls May also develop cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma due to granules of unsecreted alpha-1 antitrypsin building up in hepatocytes. |
|
|
What is the best kind of question to ask patients (in order to elicit most important information)?
|
Open-ended questions:
"What brings you in today?" "Tell me more." "How can I help you?" |
|
|
30 year-old male
HIV positive IVDU Presents with abdominal distention, anorexia, ascites CT reveals large mass surrounding small intestine Biopsy reveals uniform, round tumor cells with basophilic cytoplasm Ki-67 fraction (mitotic index) >99% Diagnosis Cause Specific mutation |
This is Burkitt lymphoma--most strongly associated with Epstein-Barr virus.
Crucial step in transformation is balanced t(8;14) translocation which causes overexpression of c-MYC (a transciptional regulator that controls cell proliferation) Chronic EBV infection increases B cell proliferation and increases risk of C-myc translocation High proliferation index represented by Ki-67 (approaching 100%)--in addition to a starry sky appearance--is classic for Burkitt's |

