![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of RNA polymerases?
Functions? |
I: forms ribosomal RNA in nucleolus; always active--loosely regulated
II: synthesizes mRNA; tightly regulated III: transcribes DNA to form small RNA molecules such as tRNA, snRNPs (snurps); few regulatory factors |
|
|
Genetic predisposition for Alzheimer's:
Early vs Late Onset |
Early: Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin gene mutations promote beta-amyloid
Late-onset familial AD: apolipoprotein E-4 (ApoE4)-->senile plaques |
|
|
Familial hypercholesterolemia:
Pathophys |
Defective LDL receptors-->dec'd hepatic LDL uptake and severe elevation in total cholesterol and LDL levels
|
|
|
Buspirone:
Indications MOA |
Generalized ANXIETY disorder
5HT1a agonist |
|
|
Fluoxetine:
MOA |
SSRI
|
|
|
Opioid tolerance:
Mechanism |
Chronic tolerance involves inc'd adenylyl cyclase activity OR inc'd NO levels
|
|
|
Morphine tolerance:
Mechanism |
Glutamate binds, activates NMDA receptors-->inc'd phosphorylation of opioid receptors-->inc'd NO levels-->morphine tolerance
|
|
|
Ketamine:
MOA |
NMDA receptor antagonist--blocks actions of glutamate and blocks morphine otlerance
|
|
|
Chronic dry cough
Low-grade fever, malaise CXR shows pulmonary infiltrates severe in appearance (more so than would be expected from symptoms) Diagnosis Growth requirements on agar |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Requires cholesterol for growth on agar |
|
|
Currant jelly sputum
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae
|
|
|
Chocolate agar
|
H influenzae (supplemented with factor X (hematin) and V (NAD+))
|
|
|
Most common in southwest US and northern Mexico
|
Coccidoides immitis
|
|
|
Ground glass infiltrates on CXR
|
Pneumocytsis jiroveci
|
|
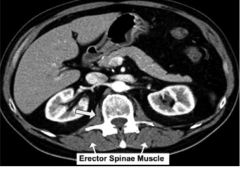
Label muscle groups.
|
|
|
|
Psoas:
Action |
Flex thigh
|
|
|
Erector Spinae:
Action |
Extend spine
|
|
|
What activities/events can lower glucose levels in a diabetic?
|
Exercise
|
|
|
What activities/events can elevate glucose levels in a diabetic?
|
Infection
Pain Sleep deprivation Stress ALL INC GLUCOSE LEVELS (via catechols) |
|
|
Why is glucagon used in type 1 DM?
|
Glucagon can increase production of glucose from the liver in times of hypoglycemia.
Done via inc'd glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen) and inc'd gluconeogenesis (production of glucose from non-carb source) Note: Glucagon stimulates insulin secretion from pancreas, but pts w/DM I have diminished beta cells. |
|
|
With defective immunoglobulin isotype switching, what immunoglobulin will be overproduced?
|
IgM
|
|
|
These cells require insuline for glucose uptake.
|
Muscle cells
Adipocytes Note: Without insulin, receptor is in cytoplasm. With insulin, receptor integrates into cell membrane (receptor = GLUT4 transporter) |
|
|
Precipitating factors for isolated atrial fibrillation in healthy patients.
Specific EKG findings. |
Binge alcohol consumption
Inc'd sympathetic tone Pericarditis Absent P waves (no coordinated atrial contractions) Irregular QRS complexes |
|
|
RBF vs RPF:
Equations Include equation for clearance. |
Renal Blood Flow = PAH clearance/(1-HCT)
Renal Plasma Flow = PAH clearance Clearance = (Ux x V)/Px |
|
|
Describe the reactions that require tetrahydrobiopterin.
|
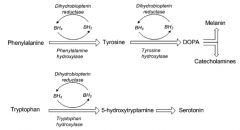
Note: tetrahydrobiopterin = BH4
|
|
|
Where is aqueous humor produced?
Describe its path. How does narrow-angle glaucoma arise? |
Formed by epithelial cells of ciliary body
Excreted into posterior chamber and transferred through pupil into anterior chamber Passes through trabecular meshwork of anterior chamber ANGLE into Schlemm's canal Schlemm's canal drains into espiscleral and conjunctival veins When the anterior chamber narrows, the trabecular meshwork is obstructed and results in narrow-angle glaucoma. Manifests acutely with HA and eye pain. |
|
|
How does timolol treat glaucoma?
|
Timolol and other non-selective beta-blockers diminish secretions of aqueous humor by ciliary epithelium.
|
|
|
How does acetazolamide treat glaucoma?
|
Decreases aqueous humor secretion by ciliary epithelium.
|
|
|
How does latanoprost treat glaucoma?
|
PG agonist-->increases outflow of aqueous humor and thus decreases intraocular pressure
|
|
|
How is glycogen degradation coupled with skeletal muscle contraction?
|
Increased calcium in cytosol-->activates phosphorylase kinase
-->phosphorylates (activates) muscle phosphporylase -->breaks down glycogen for use by muscle |
|
|
What are the direct and indirect effects of alpha-1 receptors?
|
Direct effects:
-Contraction of vascular smooth muscle -Inc'd cardiac contractility -Mydriasis (via contraction of pupillary dilator muscle) Indirect effects: -Inc'd systemic BP due to inc'd vasoconstriction stimulates baroreceptors in carotid sinus and aortic arch-->inc'd vagal influence on heart Causes decreased heart rate (REFLEX BRADYCARDIA), dec'd conductance in AV node Note: indirect vagal influence overwhelms direct cardiac effects of alpha-1 receptor |
|
|
What are the direct effects of alpha-2 receptors?
|
CNS mediated decrease in BP
Dec'd aqueous humor fluid production from ciliary body Inhibition of adrenergic and cholinergic NT release |
|
|
This microbe produces dextrans from glucose.
|
Viridans streptococci (mutans, sanguis)
Producing dextrans from glucose assists in colonization of host organisms. |
|
|
What drugs are associated with agranulocytosis?
How would you monitor this? |
C^3:
Clozapine Colchicine Carbemazapine Requires periodic CBC with differential. |
|
|
Clozapine:
Use MOA AE |
Antipsychotic, used in schizophrenia
Blocks D4 receptors (unlike most antipsychotics, which act on D2 receptors)--less likely to cause pseudoparkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia, hyperprolactinemia AGRANULOCYTOSIS; need CBC SEIZURES |
|
|
Ptosis
Down and out gaze Normal light and accommodation reflexes Diagnosis Pathophys |
Diabetic mononeuropathy of CN III
Due to ISCHEMIC nerve damage, only somatic nerve fibers affected. Parasymp fibers oc CNIII retain function. |
|
|
What nerve is responsible for pupillary response to light and accommodation?
|
CN III (parasymp fibers)
|
|
|
Risperidone:
Use MOA AE |
Anti-psychotic used for schizophrenia
D2 receptor antagonist AE: hyperprolactinemia-->inhibition of GnRH release-->amenorrhea (via PL) |
|
|
First step of suspected child abuse.
|
Contact child protection services IMMEDIATELY.
Do not confront parents, do not call for a consult. |
|
|
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria:
Pathophys Effects |
Deficiency of CD55 and CD59-->disallows inactivation of complement
Results in thrombosis: -Recurrent venous thrombosis -Budd-Chiari Syndrome Also results in hemolytic anemia! Also associated with pancytopenia since it is a stem cell disorder. |
|
|
72 year-old male
Headaches Visual deterioration Resolves with prednisone Diagnosis Pathophys |
Temporal cell arteritis (Giant cell arteritis); because it is GIANT CELL, must be granulomatous inflammation of temporal artery
Also presents with facial pain, jaw claudication |
|
|
Describe the metabolism of fructose. How does this differ in essential fructosuria?
|
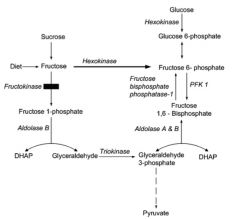
Essential fructosuria = fructokinase deficiency
|
|
|
What antigens are produced by HBV?
How do they differ in terms of structure/function? Which indicate high infectivity? |
HBcAg = nucleocapsid core; resides within hepatocytes and assembles virion. Marker of high infectivity.
HBeAg = nucleocapsid core; marker of high infectivity. Resides within hepatocyte, assemblres virion. HBsAg = noninfective envelope that forms spheres and tubules. Infected hepatocytes may secrete this (often a lot more than amount of HBcAg produced). |
|
|
Blowing holosystolic murmur best heard at apex
High-grade fever Dyspnea Fatigue Erythematous macules on sole of foot Diagnosis Pathophys |
Mitral regurgitation secondary to bacterial endocarditis
Lesions on foot = Janeway lesions; are the result of septic embolization from infected cardiac valve vegetations |
|
|
Epithelium of ovary
|
Simple cuboidal
|
|
|
Epithelium of fallopian tube
|
Simple columnar
|
|
|
List 4 direct dopamine agonists.
Which dopamine receptor do they bind? |
Bromocriptine
Pergolide Pramipexole Ropinerole All act on D2 receptor |
|
|
What are fatty streaks?
How are they formed? When do they become apparent? |
Fatty streaks are the earliest lesion of atherosclerosis
Composed of intimal, lipid-filled foam cells, derived from macs that have engulfed lipoproteins May progress to atherosclerotic plaques later in life, but do not predict occurrence or location of atheromatous plaques later in life Present in all individuals after age 10 |
|
|
Burning sensation in a dermatomeal distribution
Followed by erythematous rash 2-3 days later Transforms into vesicles Diagnosis Histologic features of vesicle |
Herpes Zoster
Vesicle will feature intranuclear inclusions in keratinocytes and multinucleated giant cells |
|
|
Clathrin:
Role |
Mediates endocytosis
|

