![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ipratropium
|
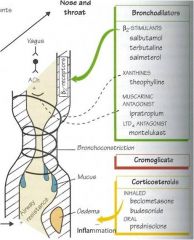
Muscarinic antagonist; block the muscarinic receptors found in the lung that is innervated by parasympathetic nervous system. PNS stimulation causes bronchoconstriction so inhibiting PNS = bronchodilation
|
|
|
Side effects of muscarinic cholinergic antagonists (ipratropium)
|
• Adverse effects of muscarinic antagonists are predictable knowing other muscarinic beds. When given by inhalation these are minimized due to poor absorption through the lungs. Adverse effects include dry mouth, can see palpitations, constipation, blurred vision, dysuria.
|
|
|
Albuterol (immediate peak) and salmeterol (longer duration)
|
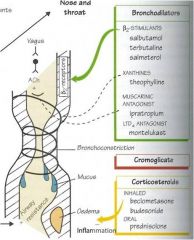
B2 agonists activate adrenergic receptors in lung which respond to epinephrine stimulation to cause bronchodilation; short acting agents are used for symptom relief to relieve acute dyspnea by inhalation of the agent while long acting agents used in combo w corticosteroids by inhalation
|
|
|
Side effects of B2 adrenergic agonists (albueterol, salmeterol)
|
Poor absorption through lungs minimizes side effects when inhaled; more likely to cause systemic adverse effects than muscarinic antagonists administered by inhalation; adverse effects include headache, tremor, palpitations
|
|
|
Beclomethasone
|
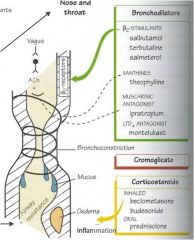
Corticosteroid; relieve dyspnea by anti-inflammatory effects of PMN leukocytes and reverse increases capillary permeability
|
|
|
Side effects of corticosteroids (beclomethasone)
|
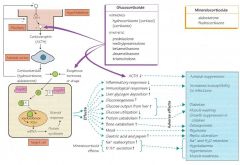
Adverse side effects minimized by inhaled administration; all adverse effects can be caused
|
|
|
Aerobic gram + (haemophilus influenzae) infection
|
Cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone)
|
|
|
Aerobic gram - (Moraxella catarrhalis)
|
Trimethoprim & Sulfamethoxazole, Amoxicillin + Sulbactam (no longer sensitive to penicillins)
|
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (lower respiratory tract)
|
Erythromycin
|
|
|
Chlamydia Pneumoniae (intracellular)
|
Doxycyline
|
|
|
Nicotine
|
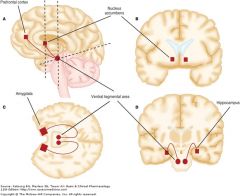
site of action for addiction and cessation of smoking pharmacotherapy – ventral tegmental area of CNS. Mechanism of action for addiction and cessation of smoking pharmacotherapy – neuronal nicotine cholinergic agonist (at α4β2 subtype).
|
|
|
Bupropion
|
SOA is within CNS
MOA: neuronal uptake inhibitor of serotonin, NE, and DA, and this is the presumed MOA in relieving the urge to smoke |
|
|
Varenicline
|
SOA: within CNS, VTA (involved in nicotine addiction)
MOA: Partial neuronal A4B2 nicotinic cholinergic agonist |

