![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
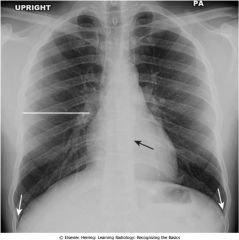
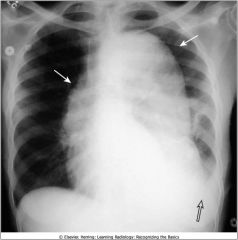
Normal chest; vertebral bodies visible through shadow of mediastinum (black arrow); costophrenic angles (white arrows) where diaphragm arises from ribs
|
|
|
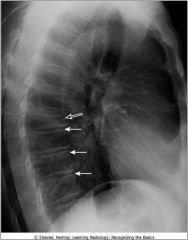
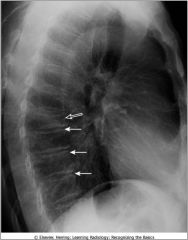
Kyphosis; note abnormal curvative and compression fracture
|
|
|
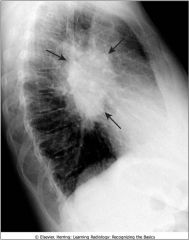
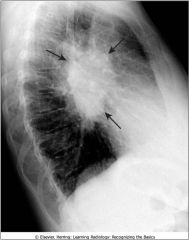
Hilar mass; bilateral hilar adenopathy from sarcoidosis
|
|
|
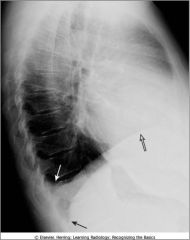
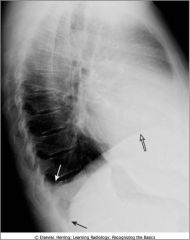
Blunted costophrenic sulcus by a small pleural effusion; left lateral view
|
|
|
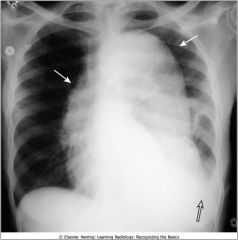
Aortic Dissection; widened mediastinum and left pleural effusion
|
|
|
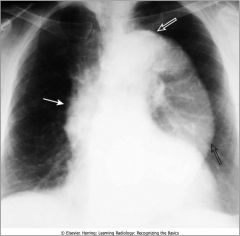
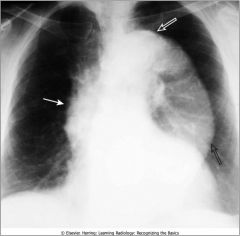
Aortic Aneurysm; ascending aorta visible on right heart border; descending thoracic aorta swings far away from spine and is normally not this visible
|
|
|
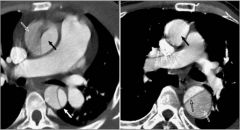
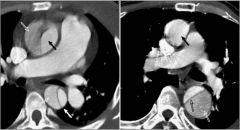
Aortc Dissection; intimal flap
|
|
|
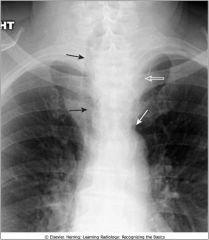
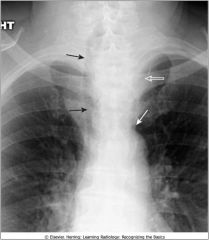
Widening of the mediastinum; substernal thyroid mass; displaced trachea (black arrow) characteristic
|
|
|
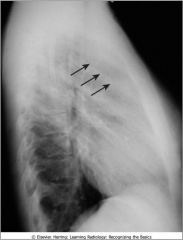
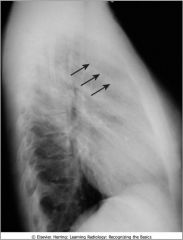
Anterior medistinal lymphadenopathy; normally there is a clear space behind the sternum; this is a pt with lymphoma, adenopathy = most frequent reason that retrosternal clear space is obscured
|
|
|
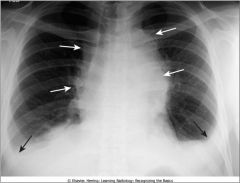
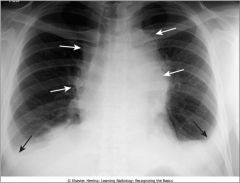
Mediastinal adenopathy from Hodgkins dz; lobulated border due to conglomeration of enlarged lymph nodes that produce the mass
|
|
|
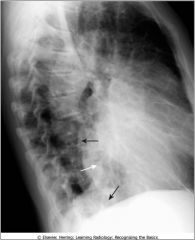
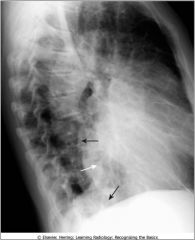
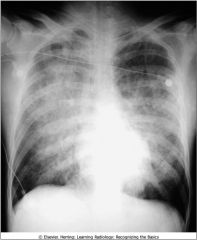
Enlargement of the cardiac silhouette, left lateral position; Poisterior border of hrt does not usually overlap the thoracic spine
|
|
|
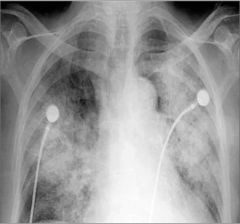
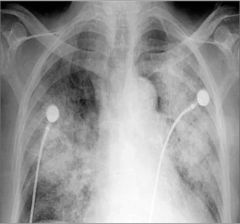
Acute pulmonary aleveolar edema; fluffy, bilateral, perihilar airspace dz with indistinct margins sometimes described as bat wing or angel wing configuration
|
|
|
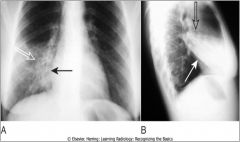
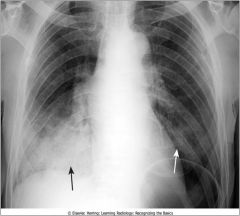
Silhouette sign, right middle lobe pneumonia
fluffy, indistinctly marginated airspace disease 1. is in contact with the right heart border 2. the dz is the same raidographic density as the heart |
|
|
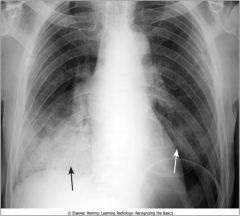
Aspiration; right and left lower lobes
|
|
|
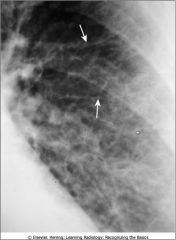
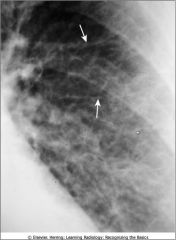
Kerley lines; appear when connective tissue near the bronchoarterial bundle distends with fluid
Produced in pts with CHF producing the prominence of the pulmonary intesttiial markings |
|
|
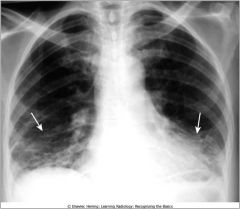
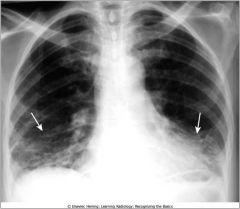
Rheumatoid lung; prominent markings at both lun gbases have a predominatly reticular appearance
|
|
|
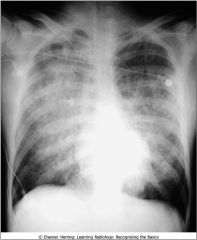
BAT-WING (ANGEL WING) PATTERN OF PULMONARY EDEMA.The radiographic findings of pulmonary alveolar edema include fluffy, indistinct, and patchy airspace densities frequently centrally located and sparing the outer third of the lung. This is called the bat-wing (bat's-wing) or butterfly pattern, and it is suggestive of pulmonary edema versus other airspace diseases such as pneumonia.
|
|
|
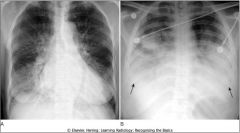
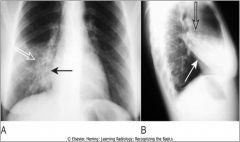
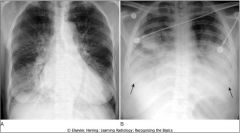
PULMONARY INTERSTITIAL EDEMA (A) VS. PULMONARY ALVEOLAR EDEMA (B). The key findings in pulmonary interstitial edema (A) include thickening of the interlobular septa (Kerley B lines), peribronchial cuffing, pleural effusion, and fluid in the fissure. The heart is also enlarged in this patient who had congestive heart failure. The key findings in pulmonary alveolar edema (B) are fluffy airspace densities, frequently perihilar in distribution and sparing the outer third of lungs. Pleural effusions are frequently present when the edema is cardiogenic in origin, as in this case with large, bilateral pleural effusions (closed black arrows)).
|
|
|
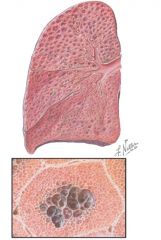
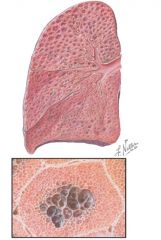
Emphysema; note the distended, intercommunicating sac like spaces in the central area of acini
|
|
|
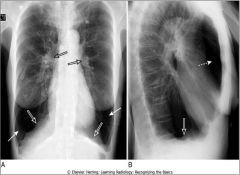
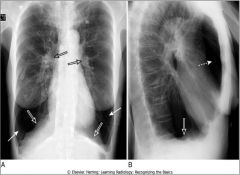
Emphysema; hyperinflation, flattening of diaphragm (esp on lateral exposure)
|
|
|
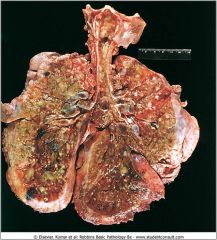
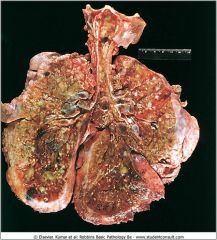
Lungs of a pt who died from CF; extensive mucous pluggin gand dilation of the tracheobronchial tree; green color is associated with Pseudomonas infections
|
|
|
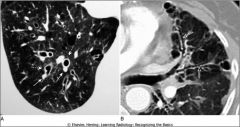
Signet ring sign of bronchiectasis
|
|
|
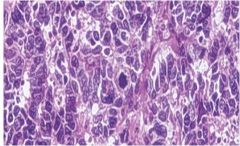
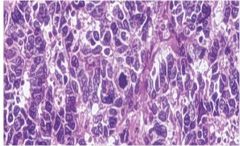
Small cell carcinomas of the lung; characterized by the presence of small, uniform, oval cells with little cytplasm; neuroendocrine neoplasm and can secrete ectopic hormones such as ACTH, ADH and calcitonin
|
|
|
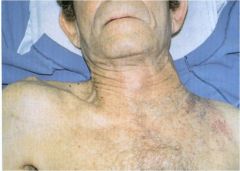
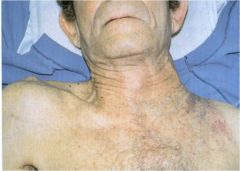
Apical lung mass (pancoast tumor) in apex of the left lung which has eroded into the chest wall
|

