![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is an agression? |

BEHAVIOUR WITH THE INTENTION TO HURT OTHERS |
|
|
3 CRUTIAL COMPONENTS OF AGRESSION |
aggresion is behavior -behavior is meant -behavior is with the intention to hurt someone else |
|
|
direct and indirect agression |
-direct- agression you show directly to smo. (hitting,making a mean remark.._ -indirect - has an indirect affect on person you want to hurt. (spreading mean gossips, demolishing smo's car..) |
|
|
emotional and instrumental agression |
emotional - to express anger and fury. purpose of the aggression is to damage or to control ones own emotions instrumental - aggressive behavior to achieve a goal. someone else is injured as a way to achieve some other goal. hurting someone to accomplish some goal. |
|
|
goals of aggressive behavior |
-coping with feeling of annoyance(irritation). ( to use aggression to reduce annoyance)- irritation -gaining material and social rewards - get what you want -gaining or maintaining social status - i am a boss -protecting ourselves and others -"when you hurt..., you hurt me" |
|
|
freud |
instincts: death and destruction: aggression behavior can be rewarding or can be costly. our behavior is intended to benefit us but it can backfire. we do have an aggression instinct and in general it helps us. see well in book |
|
|
aggression and adaptive goals |
see well in book |
|
|
displacement |
an indirect expression of aggression. like a bird preening its feathers in a conflict. |
|
|
catharsis theory |
aggressive energy needs to be expressed |
|
|
testosterone |
influences physical aggressive behavior. testosterone contributes to risk of antisocial behavior only in lower-class men. high testosterone is associated with substantially greater risk in lower-class men, who presumably have limited resources with which to achieve social dominance |
|
|
gender differences in agression |

|
|
|
frustration-aggression hypothesis |
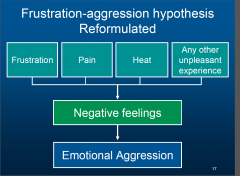
John Dolland. aggression is an automatic response to blockades of goal-orientated behavior. -if someone behaves aggressively it means that he was frustrated before - if a person is frustrated, an aggressive expression will follow. Berowitz reformulated this theory that frustration leads to only EMOTIONAL (anger-driven) aggression. and frustration only lead to aggressive behavior when the frustrations cause negative feelings. |
|
|
excitation-transfer theory |
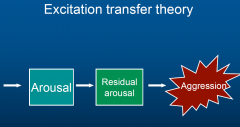
Zillman each form of excitement contributes to inner arousal inside a person.. example of woman watch in erotic movie. any arousing state could increase aggressiveness. |
|
|
type A peronality |
they are more easily irritated than others. therefore they show aggressive behavior more easily. easily frustrated |
|
|
unpleasant situations that provoke aggressive behavior |
pain sweltering(burning) heat poverty |
|
|
relative deprivation(loss) |
the feeling of having less than the people you compare yourself to. that's why when things go bad after a good period there is more aggression than when things go bad all the time. |
|
|
cognitive-neoassociation theory |
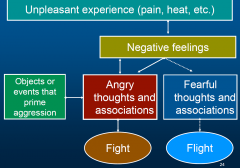
negative situation leads to negative feelings more negatively, and interpret things even more negatively. |
|
|
weapon effect |
seeing or holding a weapon induces negative and aggressive feelings |
|
|
social learning theory:rewarding violance |
people learn from the feedback they and people around them receive on their actions. example of parents throwing "bobo" toy aggressively |
|
|
who finds rewards in violence? |

|
|
|
psychopath |
someone who feels none or little empathy for others, who has a grandiose self-esteem, and who is insensitive to punishment. their aggression is instrumental. |
|
|
empathy |
causes you to feel bad when you see something bad happen to someone. |
|
|
violence in media |

|
|
|
differential parental investment |
women choose the person to have sex very carefully.. because they may become pregnant. they want the man to have good genes (sexual selection) |
|
|
culture of honor |
Culture of honor Set of societal norms with central idea that people (particularly men) should be ready to defend their honor with violent retaliation if necessary in some culture it is very important to be able to defend your own honor, with violence if this is needed it is expected to earn honor often by fighting when someone insults you, an appropriate answer is with aggression |
|
|
defensive attribution style |
A tendency to notice threats and interpret other people’s behavior as intended to do one harm. when we are very emotional and interpret other peoples behavior soon as threatening, we consider and use aggressive options faster. |
|
|
effect/danger ratio |
people look at the potential advantages and disadvantages of aggressive behavior in a situation . |
|
|
reducing violence |
-rewarding alternatives to aggression children need to be rewarded for non aggressive behavior. -focus on more acceptable behaviors -self-statements to manage anger see p 49 Zillmann’sapproach (table 10.4) (countingtoten) -Preparing for provocation -Confronting the provocation -Coping with arousal and agitation -Reflection on the provocation -legal punishments(penalties) to decrease aggressiveness in social level -deterrence -prevention by removing threats - preventing instead of punishing aggression works best. |
|
|
sex differences in aggression |

|

