![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the three levels of expertise a leader needs for effective development of human skills. |
-Understand Behavior -Predict Behavior -Direct, change, and influence behavior |
|
|
Identify what happens to a motive when it is satisfied or blocked. |
When needs are satisfied - strength reduces When needs are blocked - strength may: -Decrease &/or commence trial and error problem solving -Cognitive dissonance -Frustration |
|
|
Identify the resultant behaviors a person may exhibit when frustrated by non-goal attainment. |
Aggression Rationalization Regression Fixation Resignation |
|
|
Explain the expectancy theory. |
A person perceives a positive relationship between effort and performance based on experience. |
|
|
Identify the correct definition of positional power and personal power. |
Position power - the extent to which those people to whom managers report are willing to delegate authority and responsibility down to them. Personal power - the extent to which followers respect, feel good about, and are committed to their leader and to which they see their own goals as being satisfied by the goals of their leader. |
|
|
Discuss the concept of power being a matter of perception. |
People must not only perceive you as having power, but also see you as able and willing to use it. |
|
|
Identify the seven power bases. |
Coercive Connection Reward Legitimate Referent Information Expert |
|
|
Discuss which power base might be used at each readiness level and why. |
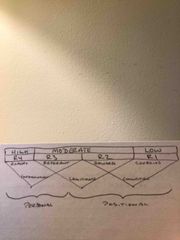
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Differentiate between punishment and constructive discipline. |
Punishment is a negative consequence. Constructive discipline is a learning process to provide positive growth. |
|
|
Identify the appropriate leadership style to use when an individual regresses. |
Use a leadership style appropriate to the present level of performance readiness instead of a higher level of performance readiness. |
|
|
Identify the guidelines for disciplinary intervention. |
Make the intervention timely Vary the emotional level Focus on performance Be specific; do your homework Keep it private |
|
|
Discuss problem ownership and situational leadership. |
R1 - Leader owns the problem R2 - Both leader and follower own the problem R3 - Follower owns the problem R4 - No owns the problem |
|
|
Identify the motives that fall under the core motive of drive. |
Ambition Achievement Initiative Energy Tenacity |
|
|
Describe the knowledge of effective leaders. |
Technological expertise Knowledge of the organization and industry |
|
|
Select the definition for “conflict”. |
The opposition of mutually exclusive impulses, desires, or tendencies. |
|
|
Select activities that are considered incompatible. |
One that prevents, blocks, interferes with, injures, or in some way makes the second activity less likely or less effective. |
|
|
Identify and define the three responses to conflict situations. |
Avoidance - avoid conflict Defusion - delaying action Confrontation - confront conflict with power (physical) or negotiation (mutual compromise) |
|
|
Demonstrate comprehension of the three categories of issues common to all groups. |
Personal identity Relationships among team members Identity with the organization |
|
|
Demonstrate comprehension of the stages of team growth. |
Forming - cautiously explore boundaries Storming - realize difficult/different; become testy, anxious, or overzealous Norming - accept the team Performing - begin diagnosing and solving problems; choose and implement changes. |
|
|
Demonstrate comprehension of the characteristics of task behaviors, maintenance behaviors and gate-keeping. |
Task Behaviors - concerned with effort to define and accomplish desired outcomes Maintenance Behaviors - effort to survive, regulate, grow, and strengthen group to achieve desired outcomes Gate-keeping - regulate flow of incoming participation; gate opening/gate closing |
|
|
Demonstrate comprehension of the five group maintenance behaviors. |
Encouraging Harmonizing Performance Checking Standard Setting Tension Relieving |
|
|
Discuss the rules for Brainstorming and how to use them in problem solving. |
1. All criticism and evaluation of members’ input is left out 2. Wild ideas are expected and accepted in the spontaneity that evolves 3. The quantity of ideas counts, not quality 4. Build on other’s ideas when possible 5. Focus on the issue 6. Make sure ALL members are heard 7. Record ALL ideas |
|
|
Select and define the 5-steps of the problem solving process. |
Define the problem Diagnose the problem Formulate alternative strategies Decide upon and implement a strategy Evaluate the solution and the group process |
|
|
Demonstrate comprehension of decision-making styles. |
Authoritative - make the decision and tell them what to do Consultative - make the decision after considering input from followers Facilitative - share the decision-making process with followers Delegative - give them the ball and let them run with it |
|
|
Identify remedies for Groupthink. |
Outside expert “Critical Evaluators” Avoid undue influence “Second Change” meeting (to prevent undue influence) |
|
|
Select, from a list, key meeting roles and the responsibilities of each role. |
Primary Facilitator Secondary Facilitators Time keeper Minute taker Scribe (optional) |
|
|
Identify the four primary segments and the sub-elements of conceptual framework, for effectively facilitating a group. |
Pre-planning - develop PDORA Start-up - review PDORA; discuss topic Move-out - draw meaningful conclusions Wrap-up - critique session for lessons learned |
|
|
Traits of an Undisciplined mind: |
Intellectual-arrogance Intellectual-cowardice Intellectual-self-centeredness Intellectual-hypocrisy Intellectual-laziness Intellectual-conformity Intellectual-distrust of reason Intellectual-disregard for justice Intellectual-unfairness |
|
|
Traits of a Disciplined mind: |
Intellectual-humility Intellectual-courage Intellectual-empathy Intellectual-integrity Intellectual-perseverance Intellectual-autonomy Intellectual-confidence in good reason Intellectual-sense of justice Intellectual-fairness |
|
|
Which power bases are most effective for personal power? |
Expert Information Referent |
|
|
Identify the Johari window and how giving and receiving feedback affects the four panes. |
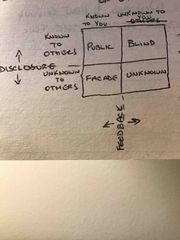
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are some negative ways to discipline? |
Focus on personal traits Focus on basis Generalities Apologize for having to discipline |
|
|
A leader needs to have what 3 traits? |
Knowledge Skills Ability |
|
|
What is the most important aspect of a leader? |
Develop the vision Get people to believe in the vision |
|
|
What are some proper ways to discipline? |
Sound alarm early Be honest Lead people to course correct |
|
|
Group dynamics, three types of behavior? |
Task Behaviors Maintenance Behaviors Gate-keeping |
|
|
Why should leaders give team members a “second chance” to think or express doubt? |
To prevent undue influence on team/group |
|
|
In 5-step problem solving, which step determines the size of the problem? |
Diagnosing the problem |
|
|
In brainstorming you want _____. |
quantity |
|
|
Traits of maintenance behaviors: |
Encouraging Harmonizing Performance Checking Standard Setting Tension Relieving |
|
|
What is a common issue affecting everyone in the group? |
Personal identity in the group |
|
|
What is paralanguage? |
Verbal Cues: Tone Pitch Volume Rate |
|
|
What are two types of discipline? |
Punitive Constructive |
|
|
What will every group face in problem solving? |
It is inevitable that every group will have conflict. |
|
|
If followers are unwilling to provide feedback to the leader: |
The blind pane of the Johari window will grow. |
|
|
When does conflict exist? |
Whenever incompatible activities occur. |
|
|
Anxiety about in-residence portion of SEA is what stage of team growth? |
Storming |
|
|
What is intellectual-courage? |
The need to face and fairly address ideas |
|
|
What is regressive intervention? |
Using an appropriate leadership style for a person at their current, regressive level not at their normal, higher performance readiness level. |
|
|
Delaying action in conflict resolution is _______ |
Defusion |
|
|
Most important social skills for an individual are: |
Ability to communicate with, Ability to work with, Ability to mediate/resolve conflict |
|
|
In terms of group effectiveness, when is the moment of truth? |
Conflict among group members |
|
|
In human behaviors, what does it mean to make excuses? |
Rationalizing |
|
|
What are the symptoms of frustration? |
Aggression Rationalization Fixation Regression Resignation |
|
|
Frustration can result in what? |
Blocking or thwarting of goal attainment |
|
|
What happens in the Johari window when disclosure happens? |
The public pane gets larger; facade pane shrinks |
|
|
As a leader you can use positional power to do what? |
Delegate from above because you have the authority to go with it |

