![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
tx of adolescents (legality)
|
most are able to make informed decisions by age 14. In some cases, state-specific laws clearly state that an adolescent has the right to make all treatment decisions in areas such as pregnancy, treatment of STDs and substance abuse (an emancipated minor). In these situations, your discussions are confidential, except if there is evidence that the patient will harm herself or someone else or has been abused (physically or sexually).
RUQ pain in association with pelvic inflammatory disease typically caused by N. gonorrhea or C. trachomatis. The infectious material may spill from the uterus and track along the paracolic gutter and cause inflammation of the hepatic capsule and diaphragm. This results in RUQ pain and referred scapular pain. |
|
|
abd pain
|
insidious onset of pain suggests either inflammation of the visceral peritoneum alone or a well-contained process (like an abscess).
Crampy or colicky pain suggests obstruction in a peristaltic organ (like bowel or ureter). Finally, progression of pain from a dull, diffuse pain to a sharp, well-defined pain suggests disease progression and possibly the need for surgery. Associated symptoms, such as dysuria, vaginal discharge, diarrhea and vomiting severe, has an abrupt onset, or is rapidly worsening merits a rapid surgical consultation |
|
|
S. aureus associated food poisoning
S. pyogenes |
usually occurs soon after eating contaminated food
pain from food-borne pathogens is diffuse and crampy typically doesn't cause diarrhea |
|
|
table of food born illnesses
|
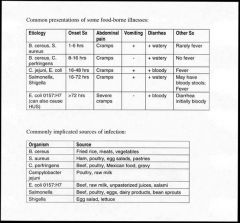
|
|
|
acute gastroenteritis
|
vomiting is a common presenting complaint in acute gastroenteritis, by three days into the illness, almost all patients have diarrhea as the most pronounced symptom. The lack of sick contacts, while not ruling out gastroenteritis, also makes it less likely
|
|
|
ovarian torsion
|
any age group but is more common in post-menarchal women.
Abdominal pain, stabbing lower abdomen or pelvic region. Nausea and vomiting in the majority |
|
|
pneumonia
|
uncommon but important case of abdominal pain in young children.
Irritation of the pleura by a lower lobe infection causes pain. Cough, difficulty breathing, rhinorrhea and chest pain are other complaints that would suggest a pulmonary process, |
|
|
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
|
presents with abdominal pain in almost all cases, lower abdomen.
Right upper quadrant pain can occur with perihepatitis that complicates PID in 5%. Vomiting is seen in some but not all sexually active patients highest rates in sexually active girls 15-19 years of age. fever and diffus abd pain + cervical motion tenderness! |
|
|
Pancreatitis
|
diffuse abdominal pain but other patterns (such as epigastric) are more common.
Band like pain radiating to the back is highly suggestive. constant and most often severe. Nausea and vomiting almost always low grade fevers diffuse abd as well as epigastric tenderness |
|
|
Hepatitis
|
fever, malaise, diffuse abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. NO diarrhea
jaundice and change in the color of urine. The onset of symptoms depends on the etiology of the hepatitis. (In Mandy's case, she could have Hepatitis A, B, C or less likely EtoH induced hepatitis). hepatomegaly in acute hep scleral icterus |
|
|
UTI
|
dysuria, frequency and urgency
Fever or back pain suggests pyelonephritis. Previous history of UTIs may suggest underlying structural abnormalities that would increase the risk of infection. |
|
|
ectopic preg
|
sexually active female w abdominal pain.
Fever and diffuse abdominal pain are uncommon in uncomplicated ectopic pregnancy. classically: lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding abnormal menstrual history. Diffuse abdominal tenderness, adnexal or cervical motion tenderness are all seen with ectopic pregnancy mild enlargement of the uterus might also be present. The physical examination may be completely normal in an early, unruptured ectopic pregnancy. |
|
|
Cholecystitis:
|
pain in right upper quadrant, is steady, and may radiate to the shoulder.
Eating fatty foods may worsen Decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting can accompany attacks. pain episodes may be intermittent (colicky). less common in children than in adults Increased pain when the patient takes a deep breath during palpation of the RUQ ( Murphy’s sign) |
|
|
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Synd
|
RUQ pain in PID b/c gonorrhea or chlamydia
sudden onset may refer to R shoulder RUQ pain in association with pelvic inflammatory disease typically caused by N. gonorrhea or C. trachomatis. The infectious material may spill from the uterus and track along the paracolic gutter and cause inflammation of the hepatic capsule and diaphragm. This results in RUQ pain and referred scapular pain. |
|
|
vomitting w no diarrhea
|
suggest extraintestinal process
appendicitis often there are no BM in last few hours all ones on DDx present w vomiting and no diarrhea |
|
|
McBurney's point
|
inch and a half and two inches from the anterior superior spinous process of the ilium on a straight line drawn from that process to the umbilicus.' "
The sensitivity of finding tenderness at McBurney's point for detecting appendicitis is 50-94%, and the specificity is 75-86%. Overall, it is probably the most predictive physical exam finding for appendicitis (whether present or absent |
|
|
chancre
|
usually found with syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection not usually associated with vaginal discharge unless a co-infection with another pathogen
|
|
|
pelvic examinations in girls?
|
With the availability of urine-based and vaginal swab STI testing, and new recommendations for following Pap tests, sexual activity in females under 21 years of age is not an indication for a pelvic examination. The first Pap test should be performed at 21 years of age
STI screening should occur every year in sexually active teens. STI screening may also include HIV and syphilis testing, which is done with blood tests. All teens who are sexually active should be counseled about their risk for these two diseases as well as Chlamydia, Gonorrhea and Trichomonas. |
|
|
appendicitis
|
Diffuse abdominal pain would suggest peritonitis due to a ruptured appendix.
fever most often in older children and is rare in children under 2 years of age. prevalence of appendicitis in children with acute abdominal pain ranges from 1% to 4%. 1/3 of pediatric patients have atypical presentations= both over-diagnosis of appendicitis (false-negative appendectomy rates of 5%-25%) and to a high incidence of perforation (23%-73%) order CBC with differential or CRP (C reactive protein |
|
|
different in a boy?
|
Mesenteric adenitis has many causes and often presents like appendicitis. A lack of sick contacts and no diarrhea argues against acute gastroenteritis. His age, sex and absence of CVA tenderness makes a UTI less likely.
hernia, testicular torsion |
|
|
incarcerated hernia
|
incarcerated when you no longer can reduce it to its usual position with manipulation.
most present before 1 year of age, thus in this case would be uncommon. Incarcerated hernias slightly more often in girls, and an ovary may be in the hernia instead of intestine. Incarcerated hernias are painful, so irritability is a common symptom. Vomiting and abdominal distention might occur if intestinal obstruction has occurred tender mass in the groin or labia majora if the hernia is in the inguinal region. |
|
|
testicular torsion
|
urologic emergency in which the goal is to save the affected testis (emergency urology consult
early adolescence acute onset of severe hemi-scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. enlarged tender testis, scrotal edema, and absence of the cremasteric muscle reflex. color Doppler ultrasound or nuclear testicular scan may be useful but should not delay treatment if the diagnosis is evident. Surgical exploration and detorsion must occur promptly, irreversible changes in the testis may occur within 4 hours. |
|
|
Kidney, Ureter, Bladder (KUB):
|
good screening examination.
Common findings with abdominal pathology include: ileus (sometimes with air), fluid levels, fecaliths (seen with appendicitis), free air (with perforated viscus), malrotation of the intestines, and gall stones. can be significant pathology with a normal KUB. |
|
|
CT abd
|
more sensitive and specific than KUB, but also more expensive and difficult to do in children. Increased attention is also focusing on the amount of radiation children receive from CT scans. They are an excellent way to look for abscesses and have been studied as a way to diagnose appendicitis. The sensitivity of CT scan for diagnosing appendicitis in children is 94-97%, the specificity of CT scan is 87-99%
|
|
|
ultrasound
|
ike the CT scan, is a useful adjunct to confirming a clinical diagnosis in a patient with abdominal pain. It has been evaluated as a method to diagnose appendicitis and is one of the critical tests to do when suspecting complicated pelvic inflammatory disease (tubo-ovarian abscess, or "TOA").
|
|
|
barium studies
|
important for the evaluation of more chronic abdominal pain (looking for inflammatory bowel disease), but they also have a role in diagnosing intussusception in younger patients with supportive history and physical findings.
|
|
|
PID more info
|
girls this young, there are fewer protective antibodies in the vagina (compared to those in older women).
cervical ectropion which represents the transitional zone between the columnar and the squamous epithelium- Cells in this zone are particularly susceptible to STDs. Therefore the cervix is easier to infect. Behavioral factors include intercourse during menses, infrequent or no condom use and multiple sexual partners. Microbiology: most common organisms to cause PID are Neisseria gonorrhea or Chlamydia trachomatis. More than 50% of women with PID have evidence of infection with these organisms. Lower-tract infection with these pathogens leads to an alteration of the normal vaginal flora and allows bacteria such as E. coli, Bacteroides species, other anaerobes, Mycoplasma hominis or Ureaplasma urealyticum access to the uterus and fallopian tubes. Diagnosis: Based on a combination of clinical findings (like cervical motion tenderness, abdominal pain, cervical discharge) and laboratory tests: Culture for bacteria (like N. gonorrhea) and molecular diagnostic test (e.g., nucleic acid amplification test) on urine or cervical discharge for Chlamydia and N. gonorrhea. Even though a gram stain was ordered for Mandy, most practitioners no longer obtain a gram stain. Complications: Tubo-ovarian abscess, sepsis or other intra-abdominal abscesses. The most worrisome long-term morbidity is increased rates of infertility. |
|
|
Hep B vaccine
|
Spacing of the doses to 0, 12 and 24 months is equally immunogenic in adolescent patients, making routine immunizations easier
adolescents w STI dx are more at risk and should get vaccinated Other at-risk adolescent populations include sexually active heterosexual persons with more than one partner in the preceding 6 months, men who have sex with men, inmates of juvenile detention or correctional facilities, residents of institutions for developmentally disabled persons, IV drug users and household contacts of HbsAg-positive people. Side effects of the vaccine are usually local tenderness (3-29% of recipients) or fever (> 37.7, seen in 1-6% of recipients). |
|
|
HPV vaccine
|
quadrivalent (HPV4, types 6, 11, 16 & 18, and the other is bivalent (HPV2, types 16 &18). Both vaccines are highly effective in preventing infection and disease associated with types included in the vaccines. Current recommendations are for routine vaccination of females ages 11-12 years, but the vaccines may be started as early as 9 years, and for catch-up vaccination of females 13-26 years of age. Women who receive an HPV vaccine should continue to have regular Pap smears, because the vaccine does not protect against all types of HPV. The vaccine also offers no protection against HPV infection acquired before vaccination. The quadrivalent vaccine is also licensed for males aged 9 through 26 years. Boys and young men may choose to get this vaccine to prevent genital warts.
|
|
|
reporting STIs
|
All states require reporting of sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and chancroid
CDC recommends expedited partner therapy (EPT) for partners of people with sexually transmitted infections. Patients are given sufficient medications to treat their partner(s) with EPT. While there is some experience using this method with adolescents, you aren't sure if the laws in your state permit this. As of 2011, over 25 states had implemented some form of partner therapy as a tool against the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, especially for gonorrhea and chlamydia. |

