![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ppx for sickle cell under 5y/o
|
PCN
decreased splenic function leads to decreased resistance to infection with encapsulated organisms (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Neisseria meningitidis). Penicillin when given to infants with sickling disorders significantly decreases the risk of mortality from overwhelming sepsis. It is usually continued until the child is 5 or 6 years of age. After this age there is little data to support its use except in patients who have had documented sepsis and bacteremia, or who have had their spleens removed |
|
|
doctors for complications of sickle cell
|
neurologists (to help patients who have suffered a stroke), pediatric pulmonary physicians (to help patients that have had acute chest syndrome and may develop chronic lung disease), pediatric cardiologists (because of the potential for the development of high output strain on the heart), pediatric ophthalmologists (to evaluate for sickle retinopathy), pediatric orthopedists (to help evaluate aseptic necrosis of the femoral heads), and pediatric nephrologists (to help evaluate sickle cell nephropathy).
|
|
|
sickle cell pathophys
|
substitution of valine for glutamic acid at the sixth amino acid position of the hemoglobin molecule. This mutation leads to the formation of polymers of hemoglobin when the hemoglobin becomes deoxygenated. These polymers lead to deformation of the red blood cell into the characteristic sickle cells. These sickle cells have increased adherence and block blood flow in the microvasculature. This leads to local tissue hypoxia, pain and tissue damage. The abnormal hemoglobin induces hemolysis of the red blood cells leading to chronic anemia with an elevation of the reticulocyte count
autosomal recessive |
|
|
Hgb patterns assc w sickling
|
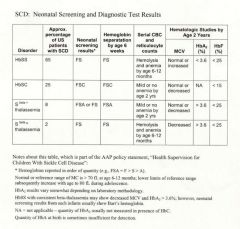
FS FSA FSC NOT FAS
At birth the predominant hemoglobin is hemoglobin F, so this always appears first; normal adult hemoglobin is hemoglobin A. Hemoglobin F is always listed first, then hemoglobins are listed in order of their concentration. FS would be the most common hemoglobin pattern when looking for sickle cell disease. However when one of the globin genes has a mutation for S and the other has a mutation for thalassemia (produces no or little normal hemoglobin) you might see patterns such as FSA (S-beta-thal plus) or FS (S-beta thal 0), both of which are sickling disorders, although they may behave in a milder fashion compared to SS (both genes with the sickling mutation). When one gene has the S mutation and one gene has the mutation for hemoglobin C, then the pattern may be FSC. |
|
|
most common surgeries for children w sickle cell
|
colecystectomy, tonsillectomy
Lymphoidal-tissue hypertrophy involving Waldeyer's ring is common in children with sickle cell disease. Excessive snoring may be observed as well as obstructive sleep apnea. Tonsillectomy with adenoidectomy will improve the obstructive apnea for most patients. Some physicians think tonsillar hypertrophy may relate to desaturation of hemoglobin and increase the risk of sickling. Bilirubin gallstones occur frequently in all patients with hemolytic anemia, including sickle cell disease, as a result of increased release of hemoglobin during the breakdown of the abnormal red blood cells. Although many children with sickle cell disease may have evidence of gallstones on screening ultrasounds, management is still conservative and cholecystectomies are reserved for patients who are symptomatic. If symptoms require it, cholecystectomy is preferably done as an elective procedure, with preoperative PRBC transfusions given to reduce the chances of acute chest syndrome or other complications following the surgery due to the time under anesthesia. Cholecystitis can be a serious infection to treat, so treatment is warranted if there are any symptoms from the cholelithiasis. Although rare in the first five years of life, an increasing number of children are found to have gallstones during adolescent ages. |
|
|
Dactylitis
|
look it up idiot
|
|
|
temp in sickle cell
|
Fever may be the only sign of sepsis in children with sickle cell disease and must be dealt with as a medical emergency, with rapid evaluation, blood cultures and institution of broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotics while waiting for culture results to guide the therapy. If cultures are negative and the patients is well, usually they are discharged in 48-72 hours
|
|
|
frequency of painful or other vaso-occlusive problems will give an indication of the need for other, more aggressive interventions such as the use of
|
hydroxyurea
|
|
|
With increased breakdown of the red blood cells, sickle cell disease leads to
anemia leads to weakness on one side of the body |
jaundice
pallor or decreased activity anemia that is seen in sickle cell disease can cause some fatigue, and can sometimes be more severe due to myelosuppression from infections such as Parvovirus or from hypersplenism when the spleen enlarges and traps blood cells. |
|
|
acute chest
|
fever, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and decreased oxygenation. X-ray findings include but are not limited to multilobar infiltrates (more commonly lower and middle lobes), effusions and atelectasis. Acute chest syndrome is one of the most common causes of death in patients with sickle cell disease
lungs are a site of occasional sickling problems. This can occur in the form of pneumonia because of the increased tendency to infections, as well as a result of vaso-occlusion in the lung parenchyma. This process, called acute chest syndrome, is a medical emergency requiring supplemental oxygen and transfusion therapy. infectious process, (pneumonia) or atelectasis from infarction or pulmonary fat embolus. Pain in the chest or abdomen can lead to difficulty with expansion of the lower lung leading to atelectasis. |
|
|
risk for stroke
|
Children with sickle cell are at risk of stroke --10% -- by the age of 15 years.
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) studies are now recommended in children 2-15 years of age to determine risk for stroke. Stroke occurs in approximately 10% of children with sickle cell disease. TCD studies have been shown to predict the risk of patients for stroke and helps in evaluating which patients might benefit from prophylactic transfusion of red blood cells. |
|
|
blood transfusion hx
|
important to ask about blood transfusions as part of the history in all children with sickling disorders,
clues to the severity of some of the complications and about the potential for the development of alloimmunization to minor blood-group antigens. Blood-group minor antigens are known to be clustered along racial and ethnic lines. Exposure to blood that is cross-matched for the major A, B, and O and Rh antigens may still be mismatched for minor antigens (Kell, Duffy, Kidd, etc.). These minor antigens can induce the development of weak antibodies that can then react with future transfused blood. recommended that when a transfusion is first indicated, the patient should have a complete RBC antigen phenotype of his own red blood cells. That way the treating physicians will know which RBC antigens the patient has and does not have on his red blood cells, and can use blood that is "phenotypically matched" for the patient's specific antigens. If this is done (and it may not be possible in an emergency transfusion), the chances of the patient developing antibodies to minor antigens (alloimmunization) is decreased. |
|
|
immunizations for sickle cell
|
Hemophilus influenza type B conjugate vaccine and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (Prevnar 13) given at 2, 4 and 6 months have aided in protection against two bacteria that have been major leaders in morbidity and mortality in children with sickle cell disease. 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine given in the first year of life provides protection against the thirteen serotypes contained in the vaccine. Conjugating the antigens to a protein allows the infant's immune system to make antibodies. In a child under the age of two, the immune system has a suboptimal response to purely polysaccharide vaccine. To expand antibody coverage beyond the 13 initial serotypes, children with sickling disorders receive the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at two years of age. They will receive a repeat dose 3-5 years later.
Children with anatomic of functional asplenia should also receive the meningococcal conjugate vaccine at age 2 years. Unless they have a milder genotype than Gerardo’s Hgb SS, most children with sickle cell will have functional asplenia. They will receive a booster dose 3-5 years later. And of course, while all children should receive influenza vaccine annually, children with sickle cell disease are at higher risk and should be immuniz |
|
|
neonatal sickle cell testing
|
fetal blood obtained in utero.
DNA extraction from chorionic villi. |
|
|
weird tx methods
|
transplantation from haploidentical donors. Unfortunately, only about 20% of children with sickle cell disease have healthy, haploidentical siblings who can act as donors. An alternative treatment is based on the use of hematopoietic stem cells.
|
|
|
growth delay in sickle cell
|
Impairment of growth is common in children with sickle cell disease. This is probably multifactorial -- due to chronic anemia, poor nutrition, painful crises, endocrine dysfunction or poor pulmonary function
|
|
|
splenic sequestration
|
massive enlargement or rapid change in size can indicate splenic sequestration crisis. This life-threatening complication occurs when blood pools in the spleen and leads to severe anemia and shock. Teaching the mother how to palpate the spleen can lead to earlier detection and treatment of this process
progressively fibrotic, and by the time the child is 4 to 6 years old, is no longer palpable. Children with hemoglobin SC or S beta thalassemia can have splenic enlargement into adolescence. |
|
|
baseline hemoglobins
|
between 6-9 g/dL
|
|
|
Priapism
|
sickling in the penile arteries can cause permanent damage.
|
|
|
Aplastic crisis
|
temporary inhibition of erythroid production frequently associated with viral illness, in particular Parvovirus B19.
bc baseline rapid destruction of red blood cells and baseline lower hematocrit, the brief inhibition of red blood cell production produced by the viral infection can have far greater consequences than in patients with normal red blood cell survival. |
|
|
Trans cranial doppler
|
Chronic transfusion therapy in children with elevated TCD blood flow has been shown to significantly decrease the risk of stroke. It is not known how long this transfusion therapy needs to continue. This question is currently under study. Chronic transfusion has the risk of iron overload, which may require the use of deferasirox or deferoxamine (iron chelators). Chronic transfusion increases the risk of alloimmunization and other transfusion reactions.
|
|
|
Pericarditis
|
uncommon cause of chest pain, but also presents with tachypnea and fever.
can present with effusion and infiltrate |
|
|
chf
|
sickle cell disease and chronic anemia.
lower lobe infiltrates and cardiomegaly are both consistent with the diagnosis. Tachypnea is one of the most common signs of CHF in children, but CHF usually does not cause chest pain on its own. |
|
|
Rib infarction
|
should always be suspected when child with sickle cell disease presents with chest pain.
fever with a vaso-occlusive crisis. tachypnea to avoid taking deep breaths, but there should not be any rhonchi Cardiomegaly and hypoxia would not usually be present (though patients with sickle cell disease may have baseline cardiomegaly). not be pulmonary infiltrates; a pleural effusion might happen as a sequela |
|
|
sepsis
|
non-focal; chest pain would not be present. Cardiomegaly would be present only if in cardiogenic shock, though a patient with sickle cell disease may have some at baseline. New infiltrates would not be a usual finding unless the sepsis leads to acquired/adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
|
|
|
pain scale not understood under the age of
|
4y/o
|
|
|
Patients with sickle cell disease frequently demonstrate an exaggerated ? in response to stress.
|
leukocytosis and thrombocytosis
|
|
|
tx for pain crisis
|
fluids and highly potent intravenous narcotics (morphine or derivatives of morphine) are frequently required to control the pain. Patient-controlled anesthesia (PCA)
basal pain control w PCA boloses monitored for respiratory depression using an oxygen saturation monitor. fluid 1.5 maintenance rate but watch for pulm edema from overload |
|
|
abx for acute chest?
|
third-generation cephalosporin and a macrolide antibiotic. However, the overall rate of positive cultures was < 10%
|
|
|
Exchange transfusion or erythrocytapheresis should be reserved for
|
especially severe disease and/or hypoxemia not corrected by oxygen therapy.
automated method of doing an exchange transfusion. It is the best way to rapidly lower the hemoglobin S level and to rapidly raise the hemoglobin. This method would be used with severe respiratory distress or failing pulmonary function. Other indications for this method include the acute onset of stroke. For acute chest syndrome, increasing the hemoglobin alone is usually effective to treat this life-threatening condition. |
|
|
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and another promising therapy...
|
only known curative therapy for sickle cell disease
high-risk procedure with a significant mortality rate (around 5%) in the early post-transplant period. myeloablative therapy is used prior to the transplant, causing a large percentage of the reported deaths appropriate in children with major complications Another promising therapy: hydroxyurea. a chemotherapeutic agent, decrease the severity and frequency of the sickling disorders when administered daily to patients with more severe disease inhibits ribonucleotide reductase, increases fetal hemoglobin (HgF), and improved nitric oxide metabolism, reduced RBC endothelial interaction, decreased erythrocyte density. considering wider use of this promising therapy. Careful monitoring is necessary to evaluate for side effects. |

