![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Spinal Cord & Brain
Vertebral Column & muscles |
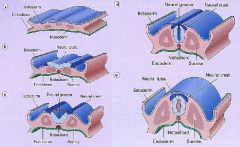
What structures does the Neural Tube give rise to?
What structures do Somites give rise to? |
|
|
List the 3 Neural Tube Defects
|
1. Anencephaly
2. Encephalocele 3. Spina Bifida -Occulta -Meningocele -Meningomyelocele |
|
|
Define Anencephaly
|
Failure of the ANTERIOR end of the Neural Tube to close
-absence of Forebrain -absence of Calvarium |
|
|
Anencephaly
-failure of anterior NT to close |

What NTD is this?
|
|
|
Define "Encephalocele
|
NTD in the cranium that allows for out-pouching of the brain thru the skull
- most commonly in the Posterior Fossa = area at the base of the skull attached to the spinal cord -diverticulum of the CNS |
|
|
Encephalocele
|
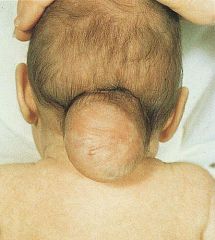
What NTD is this?
|
|
|
Encephalocele
-failure of Mesoderm to close -out-pouching of brain thru skull |
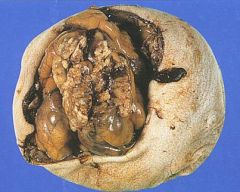
What NTD is this?
|
|
|
This is the most common NTD
|
Spina Bifida
|
|
|
What is Spina Bifida due to?
|
failure of the Posterior end of the NT to close
|
|
|
What is Spina Bifida Occulta?
|
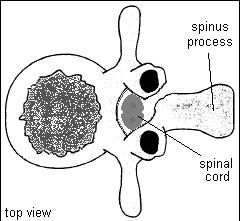
failure of the bony spinal canal to close, but no structural herniation
-commonly have a tuft of hair on lower back |
|
|
What is Meningocele?
|

Spina bifida in which the Meninges herniates thru the Spinal Canal defect
|
|
|
What is Meningomyelocele?
|

Spina Bifida in which the Meninges & Spinal Cord herniate thru spinal canal defect
-usually occurs in Lumbrosacral area |
|
|
List the 5 Forebrain Anomalies
|
1. Polymicrogyria
2. Lissencephaly 3. Neuronal Heterotopias 4. Holoprosencephaly 5. Agenesis of Corpus Callosum |
|
|
Developmental malformation of the human brain characterized by an excessive number of small folds (gyri) on the surface of the brain
|
Polymicrogyris
|
|
|
-4 or few layers of Cortex
-Entrapment of Meninges at points of fusion -Localized injury during neuronal migration What is the Forebrain Anomaly? |
Polymicrogyria
|
|
|
Polymicrogyria
|

What forebrain anomaly is this showing?
|
|
|
Pachygyria = congenital malformation of the cerebral hemisphere that results in unusually thick convolutions of the cerebral cortex
|

What forebrain anomaly is this showing?
|
|
|
Neurological disorder of early brain development that leads to the gross appearance of a smooth brain
|
Lissencephaly
|
|
|
What is Miller-Dieker Syndrome?
|
Characterized by:
1. Lissencephaly = agyria 2. 90% has a deletion on 17p 3. LIS1 gene absence 4. Seizures & Mental Retardation |
|
|
What are Neuronal Heterotopias?
|
Displacement of Gray Matter (perikaryon) into the cerebral White Matter (axons) or ventricles due to migrational defect
Almost always have seizures |
|
|
Neuronal Heterotopia
-Gray Matter is displaced in White Matter -due to migrational defect |

What is seen here?
|
|
|
What is Holoprosencephaly?
|
Incomplete separation of Cerebral Hemispheres
|
|
|
Holoprosencephaly
|

What congenital CNS anomaly is this?
|
|
|
What is Holoprosencephaly associated with?
|
Trisomy 13 (Patau Syndrome)
Children of Diabetic mothers |
|
|
What bodily malformation may accompany Holoprosencephaly?
|
Cyclopia = single median eye
Arrhinencephaly = part or all of the rhinencephalon is absent and the nose is malformed |
|
|
What mutation is Holoprosencephaly associated with?
|
Sonic Hedgehog mutation
|
|
|
What is the Forebrain anomaly in which radiologic studies show a "Bat-wing" deformity?
|
Agenesis of Corpus Callosum
|
|
|
Agenesis of Corpus Callosum
|

What forebrain anomaly is seen here?
|
|
|
What may accompany a partial Agenesis of Corpus Callosum?
|
Lipoma in the posterior part
|
|
|
List the 3 Posterior Fossa Abnormalities
|
1. Chiari I malformation
2. Arnold-Chiari Malformation 3. Dandy-Walker Malformation |
|
|
What is Arnold-Chiari Malformation?
|
Small Posterior Fossa, resulting in displacement of Cerebellum & Medulla thru the Foramen Magnum
|
|
|
What are the complications of Arnold-Chiari Malformation?
|
1. Non-communicating Hydrocephalus = obstructed flow of CSF from the Ventricles to the Subarachnoid space
2. Lumbar Meningomyelocele = spinal cord + meninges herniation |
|
|
Arnold-Chiari Malformation
-small Posterior Fossa -downward displacement of Cerebellar tonsils & Medulla |

What posterior fossa defect is this?
|
|
|
What is Dandy-Walker Malformation?
|
Enlarged Posterior Fossa with replacement of the Cerebellar Vermis with a large Cyst
-brainstem nuclei dysplasias |
|
|
Dandy-Walker Malformation
-hypoplasia of the Cerebellar Vermis -cystic dilation of the 4th ventricle |

What Posterior Fossa abnormality is this?
|
|
|
What is Syringomyelia?
|

formation of fluid-filled cavity often extending from the central canal of the Spinal Cord usually in the cervical region of the cord
Results in destruction of adjacent gray & white matter |
|
|
What is Syringomyelia associated with?
|
Chiari I, tumors, trauma
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Syringomyelia?
|
loss of pain & temperature in the upper extremities with preservation of touch & propioception
|
|
|
List 2 Perinatal Brain Injuries
|
1. Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage = Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage
2. White Matter Infarcts = Periventricular Leukomalacia |
|
|
Bleeding into the subependymal germinal matrix with or without subsequent rupture into the lateral ventricle. The microcirculation in this particular area is extremely sensitive to hypoxia and changes in perfusion pressure. It is most frequent before 35 weeks gestation and is typically seen in low birth-weight (<1500g) premature infants
|
Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage = Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage
|
|
|
What may result from Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage?
|
Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
What may Periventricular Leukomalacia lead to?
|
Cerebral Palsy
|
|
|
Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage = Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage
|

What is seen here?
|
|
|
White Matter Infarcts = Periventricular Leukomalacia
|

What is seen here?
|
|
|
What is Periventricular Leukomalacia (White Matter Infarct)?
|
Characterized by the death of the white matter of the brain due to softening of the brain tissue. It can affect fetuses or newborns; premature babies are at the greatest risk of the disorder. PVL is caused by a lack of oxygen or blood flow to the periventricular area of the brain, which results in the death or loss of brain tissue
|

