![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
This accounts for 80% of all Adult Primary brain tumors
|
Diffuse Fibrillary Astrocytomas
-includes Glioblastoma Multiforme |
|
|
When do most Diffuse Fibrillary Astrocytomas occur? What are the clinical manifestations?
|
40-60 years of age
Seizures, Headache, Focal signs |
|
|
What defines the prognosis of Astrocytomas?
|
Microscopic appearance varies as to Grade:
Atypia = II Mitoses = III Endothelial proliferation &/or Necrosis = IV |
|
|
Grade II Astrocytoma = low grade
-least frequent type |
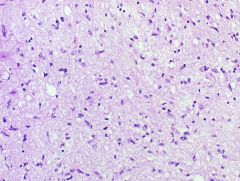
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Anaplastic Astrocytoma = Grade III = Mitoses
|
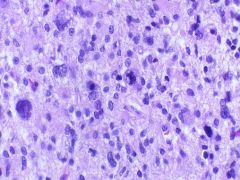
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Glioblastoma Multiforme
-Central areas of necrosis & hemorrhage surrounded by multiple tumor cells -arranged in Pseudopalisading fashion |
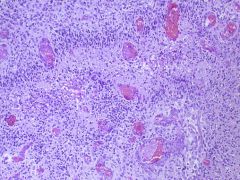
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Glioblastoma Multiforme
-varible, noncircumscribed lesion found in cerebral hemisphere |
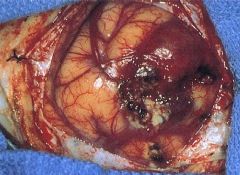
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Glioblastoma Multiforme
-ring with central area of necrosis |
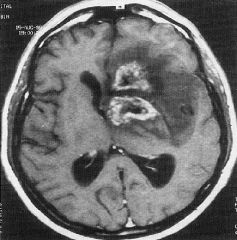
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the molecular genetic characteristics of Low Grade Astrocytomas?
|
1. inactivation of p53
2. overexpression of PDGF-A |
|
|
What are the molecular genetic characteristics of High Grade Astrocytomas?
|
1. RB gene
2. P16/CDKNZA gene 3. 19q |
|
|
What are Secondary Glioblastoma Multiforme's?
|
develop from Diffuse Astrocytomas
usually occur in younger patients associated with p53 mutation |
|
|
What are Primary Glioblastoma Multiforme's?
|
Begins as a highly malignant Glioblastoma Multiforme de novo
Usually occurs in older patients associated with EGFR amplification |
|
|
What is the therapy for Glioblastoma Multiforme? What is the prognosis?
|

Surgery + Radiation + Chemotherapy
8-10 month survival |
|
|
Brain tumor that microscopically has Central areas of necrosis & hemorrhage surrounded by multiple tumor cells, arranged in a Pseuddopalisading fashion
|
Glioblastoma Multiforme
|
|
|
This is a low-grade Astrocytoma that is benign, slow-growing & usually occurs in the Cerebellum in Children
|
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
|
|
|
What are the most common sites of Pilocytic Astrocytoma?
|
1. Cerebellum
2. near Optic nerve 3. Wall of 3rd ventricle |
|
|
Brain tumor that contains Rosenthal Fibers
|
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
|
|
|
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
-cyst with mural nodule Good prognosis |
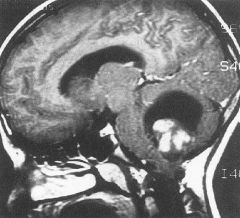
What brain tumor is seen here?
What is the prognosis? |
|
|
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
-Cerebellum = MC site -piloid cells -benign tumors of children |
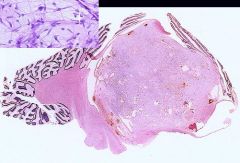
What is seen here?
|
|
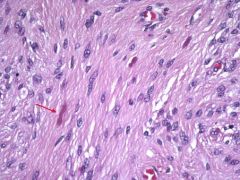
What is the red arrow pointing at? What brain tumor?
|
Rosenthal fibers
Pilocytic Astrocytoma |
|
|
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
|
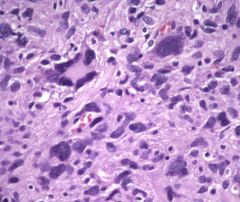
This brain tumor has large, bizarre cells with inflammation
|
|
|
What are the properties of Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma's?
|
1. Superficial
2. Temporal lobe 3. Seizure history 4. large, bizarre cells 5. inflammation 6. Good prognosis |
|
|
Brain tumor that has motononous fried-egg appearing cells that often contains calcifications
|
Oligodendrogliomas
|
|
|
What % of Gliomas do Oligodendrogliomas represent? What age do they most often appear in?
|
5-15%
4th-5th decades |
|
|
OLIGODENDROGLIOMAS:
1. Symptoms 2. Treatment 3. Prognosis |
1. Seizures, headaches, long history of neurological symptoms
2. Surgery + radiotherapy + CHEMOTHERAPY 3. 5-10 years after diagnosis |
|
|
Oligodendroma
-calcification |
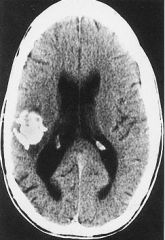
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Where do Oligodendrogliomas most often occur?
|
Frontal Lobe
|
|
|
Oligodendroglioma = Frontal Lobe
|
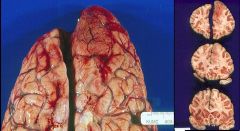
Based on location, what brain tumor is this?
|
|
|
Oligodendroglioma
-sheets of uniform cells with "fried egg" appearance -round nuclei with clear cytoplasm |
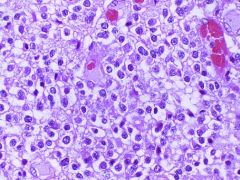
What brain tumor is this?
|
|
|
Oligodendroglioma
-loss of arms 1p & 19q Response to Chemotherapy |
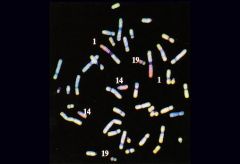
What brain tumor? What does this finding signify?
|
|
|
Tumor arising from the Ependyma of the Ventricular System
|
Ependymoma
|
|
|
What age do Ependymomas most commonly occur in? What part of the brain do they most commonly occur in?
|
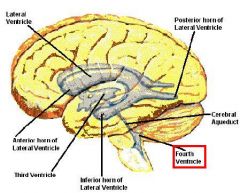
Children
4th Ventricle |
|
|
When Ependymomas occur in Adults, where do they often present?
|
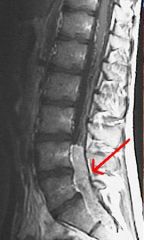
Spinal Cord
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Ependymomas?
|
Poor = 4 years after surgery
|
|
|
Brain tumor with Perivascular acellular regions with pseudorosettes; Rod-shaped blepharoplasts (basal ciliary bodies) found near the nucleus
|
Ependymoma
|
|
|
Ependymoma
-lesion has filled the 4th Ventricle -occurs in children |
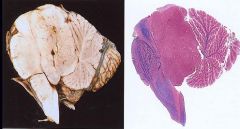
What brain tumor is this?
|
|
|
Ependymoma
-uniform cells with round nuclei set in a fibrillary stroma & arranged in a Perivascular Pseudorosette formation |
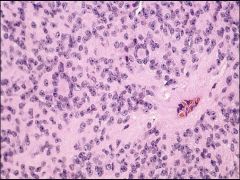
What brain tumor is this?
|
|
|
An 8-year-old girl presents to your clinic complaining of severe headaches & blurry vision. During physical exam, you note bilateral papilledema. CT demonstrates a mass extending from the floor of the 4th Ventricle & dilated Lateral & Third Ventricles. You suspect that a CT-guided biopsy would demonstrate cells with Blepharoplasts in a perivascular pseudorosette arrangement
|
Ependymoma
|
|
|
Neuronal tumor that most commonly occurs in the Temporal Lobe
Characterized by inflammation, EGB's & Rosenthal fibers Glial component may become anaplastic |
Ganglioglioma
|
|
|
Neuronal tumor that is Ventricle associated
|
Central Neurocytoma
|
|
|
Neuronal tumor that usually produces a long seizure history. Is Quasi-hamartomatous & has a good prognosis
|
DNT = Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor
|
|
|
Central Neurocytoma = associated with Ventricles
|
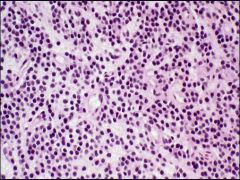
What neuronal tumor is this?
|
|
|
Highly malignant Cerebellar tumor of Children associated with a deletion of short arm of chr. 17 (17p-)
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
Radiosensitive highly malignant brain tumor arising most commonly in children
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
Brain tumor that is a form of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET)
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
Where do Medulloblastoma's most commonly occur in children? Adults?
|
Children = Cerebellum midline
Adults = Cerebellar hemispheres |
|
|
What is the 5-year survival rate for Medulloblastoma?
|
75% with total excision & radiation
|
|
|
Medulloblastoma = midline Cerebellum
|
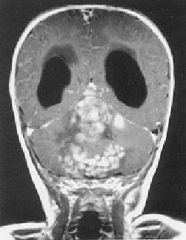
What brain tumor is this?
|
|
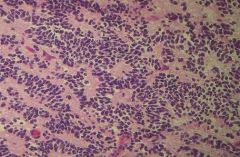
What brain tumor is this?
|

Medulloblastoma
-hypercellular sheets of anaplastic cells -cells arranged in a rosette or perivascular pseudorosette formation |
|
|
This is the #1 brain tumor in AIDS
|
Lymphoma
|
|
|
Brain tumor that has both Neuronal & Glial differentiation. Can cause hydrocephalus & seed the CSF
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
Medulloblastoma
|
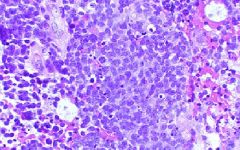
Brain tumor that may be referred to as "small blue cell tumor"
|
|
|
What type of cells are primarily found in AIDS Lymphoma's? What is associated with AIDS Lymphoma?
|
B-cells
EBV |
|
|
What do you want to avoid giving patients at all costs who you suspect of having AIDS Lymphoma?
|
Steroids - b/c can "melt" away the tumor & all you see are T cells = fucks up the diagnosis on biopsy
|
|
|
AIDS Lymphoma
|
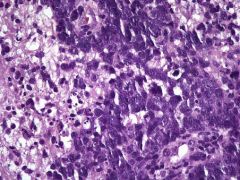
What is this?
|
|
|
List the properties of Germ Cell tumors of the brain
|
1. Usually Midline in the Pineal Gland (MC) or Suprasellar areas
2. most commonly in Young Men in Pineal Gland 3. Germinoma = Seminoma 4. Radiation & Chemosensitive |
|
|
Suprasellar Germinoma
|
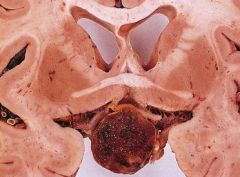
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Brain tumor that arises from Arachnoid cells external to the brain
|
Meningioma
|
|
|
The 2nd most common Primary intracranial neoplasm
|
Meningioma
|
|
|
What type of Meningioma carries a worse prognosis?
|
Papillary
|
|
|
What gender do Meningiomas most commonly occur in? Why?
|
Women after age 30
tumors have Progesterone receptors |
|
|
In what condition do people have Multiple Meningiomas?
|
Neurofibromatosis-2 = loss of NF2 gene on chr. 22
|
|
|
Meningioma
-Whorled pattern of tightly packed tumor cells -calcified Psamomma bodies |
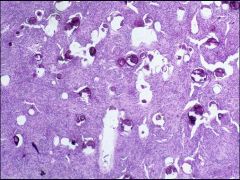
What benign, slow-growing tumor is this?
|
|
|
Whorled pattern of tightly packed tumor cells & calcified Psamomma bodies
|
Meningioma
|
|
|
From where do most Metastases come from in the brain?
|
1. Lung
2. Breast 3. Skin 4. Kidney 5. GI tract |
|
|
Meningioma
|
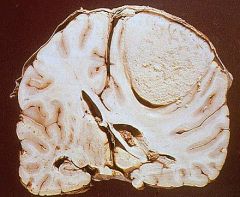
What brain tumor is this?
|
|
|
What is the most common brain malignancy?
|
Metastases
|
|
|
Melanoma
|
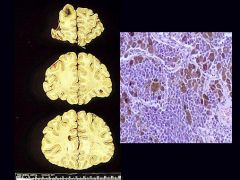
What metastatic tumor is this?
|
|
|
These brain tumors are sharply demarcated & occur at the Gray-White jxn
|
Metastases
|
|
|
What is Meningeal Carcinomatosis? What metastatic tumors tend to do this?
|
condition in which a solid tumor diffusely spreads to the leptomeninges
Small cell Adenocarcinomas of the breast Lung |

