![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Melanocytic nevi that is superficial & is in the Epidermis only
|
Lentigo nevi
|
|
|
Melanocytic nevi that occur at the junction of the epidermis & dermis
|
Junctional nevus
|
|
|
Nevi in which cells are present in both the epidermis & dermis
|
Compound nevi
|
|
|
Nevi in which benign melanocytes are only within the dermis
|
Dermal nevus
|
|
|
T or F: most melanocytic nevi mature over time
|
True
|
|
|
List the stages in which Melanocytic nevi mature
|
1. Lentigo = superficial, epidermis only
2. Junctional = jxn of epidermis & dermis 3. Compound = nevus cell present in both epidermis & dermis 4. Dermal = dermis only 5. Skin tag = Achrocordon |
|
|
What kind of neoplasm are Melanocytic Nevi?
|
Benign tumor of neural crest derived Nevus cells
|
|
|
Melanomas may appear de novo, but they may also occur via this way
|
In benign melanocytic nevi which acquire a malignant phenotype = Atypical Nevus with aberrant differentiation
|
|
|
Congenital Melanocytic Nevus
-usually present at birth -usually large |
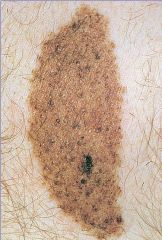
What is seen here?
|
|
|
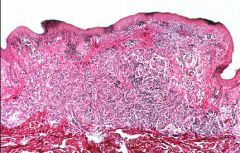
Intradermal Nevus
-on the right |
What is seen here?
|
|
|
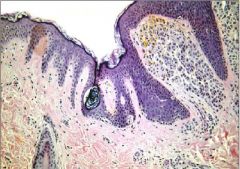
Compound nevus
-within Epidermis & Dermis -a couple of nests of cells at the base of the epidermis |
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs of Malignant Melanoma?
|
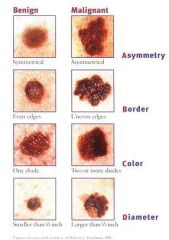
1. Asymmetry = shape of one half does not match the other
2. Border = edges are often ragged, notched, blurred, or irregular in outline; pigment may spread into surrounding skin 3. Color = uneven; shades of black, brown, & tan may be present; areas of white, grey, red, pink, or blue 4. Diameter = melanomas are usually larger than the eraser of a pencin (5 m or 1/4 inch) 5. Elevation = usually present but not always |
|
|
Malignant Melanoma
|
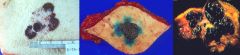
What are these pictures showing?
|
|
|
What are the 4 classifications of Malignant Melanoma?
|
1. Superficial spreading melanoma
2. Nodular melanoma 3. Acral Lentiginous Melanoma 4. Lentigo Maligna Melanoma |
|
|
This is the most common for of Malignant Melanoma
|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma = radial phase predominates with no invasion of dermis
-70% of cases |
|
|
Malignant melanoma form in which the vertical growth phase predominates
|
Nodular Melanoma
|
|
|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
|
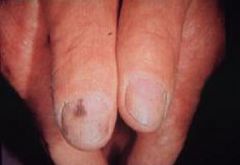
Malignant Melanoma form in which it is normally seen on the palms, soles, & sub-ungual regions
More common in dark-skinned individuals |
|
|
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
|
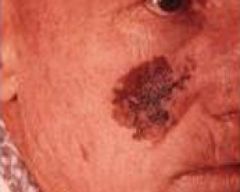
Large superficial spreading malignant melanoma occuring in the elderly (radial growth phase)
|
|
|
List the characteristics of Vertical Growth of Melanomas
|
1. cells tend to differ in appearance from those of the radial growth phase (e.g. no pigmentation)
2. the dominant site of tumor growth shifts from the epidermis to the dermis 3. tumors that extend into the lower half of the reticular dermis are, by definition, in the vertical growth phase 4. Cellular immune response may be absent |
|
|
List the prognostic features in Malignant Melanoma
|
1. Mitotic rate
2. Lymphocytic response 3. Tumor thickness (Breslow level 4. Location = extremeties have best prognosis 5. Sex = females have better prognosis 6. Regression = bad 7. Clark's level |
|
|
List the definitions of the 5 Clark's levels
|
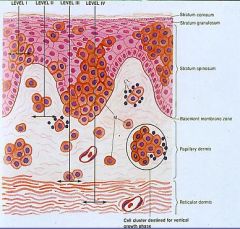
1. tumor cells are above the basement membrane
2. invasive cells are present only in the papillary dermis (radial growth phase) 3. tumor impinges on the reticular dermis, forming nodules that widen the papillary dermis 4. Tumor cells clearly invade the reticular dermis 5. tumor extends into the subcutaneous fat |
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
Malignant Melanoma
|
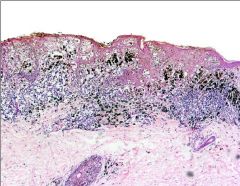
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Malignant Melanoma in the vertical growth phase = Nodular
|
What is this showing?
|
|
|
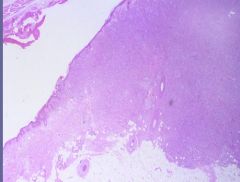
Malignant Melanoma with Lymphocytic reaction
|
What is this showing?
|
|
|
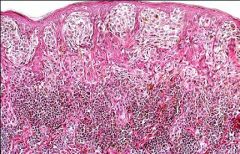
Malignant Melanoma
-anaplastic tumor cells with no evidence of pigmentation |
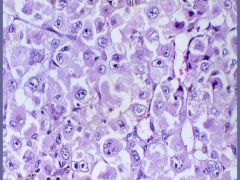
What is this?
|
|
|
Fine Needle Aspiration of Lymph Node from Metastatic Melanoma
|
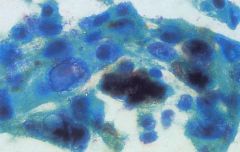
What is this?
|
|
|
What correlates an increased risk of metastasis of Melanoma?
|
Depth of tumor
|
|
|
Malignant Melanoma
|

This is a positive S-100 immunostain. What neoplasm?
|
|
|
Malignant Melanoma
-radial growth phase -edge of lesion, with nests of melanoma cells at the dermal-epidermal jxn |
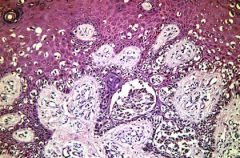
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Superficial Spreading Melanoma = radial phase predominates
-most common form of melanoma |
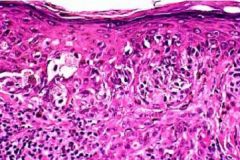
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Malignant Melanoma in the Vertical Growth Phase (Nodular)
-poorer prognosis -melanoma cells are now beginning to move down into the dermis |
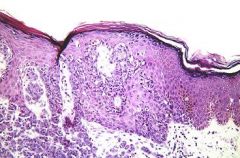
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
-common in dark-skinned people -affects palms, soles, subungual area |
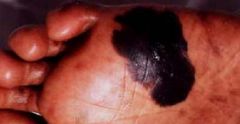
What is seen here?
|
|
|
_________ refers to any growth composed of a benign, localized proliferation of keratinocytes
|
Keratosis
|
|
|
Scaly, pigmented, elevated lesion or plaque in which the scales are easily rubbed off
Benign lesion Occurs most commonly in elderly Look like brown bubble gum that has been thrown at the skin & stuck there |
Seborrheic Keratosis
|
|
|
What parts of the body do Seborrheic Keratosis not occur?
|
Palms & Soles
-pretty much every where else though |
|
|
Seborrheic Keratosis = benign squamoproliferative neoplasm
-tan to brown coin-shaped plaques with a granular surface -"stuck on" appearance |
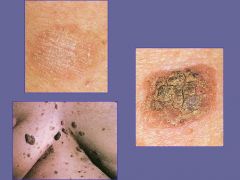
What are these lesions called?
|
|
|
Seborrheic Keratoses
|
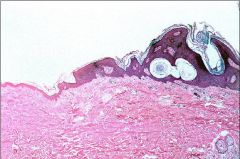
Horn Cysts...Dx???
|
|
|
Seborrheic Keratoses
|
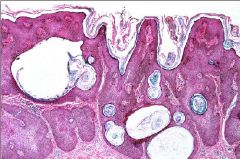
Horn Cysts...Dx???
|
|
|
Seborrheic Keratosis
-"horn cysts" |
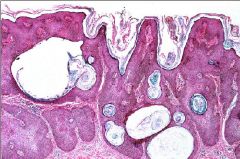
Dx???
|
|
|
Circumscribe plaque or patch, commonly in sun-exposed areas
may evolve into Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Actinic Keratosis
|
|
|
What are the most common sites for Actinic Keratosis?
|
Face, neck, back of hands
|
|
|
Actinic Keratosis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
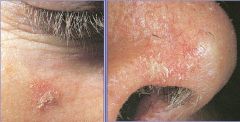
What are these lesions?
What do they have a chance of progressing to? |
|
|
Actinic Keratosis
-premalignant lesion |
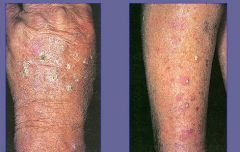
What are these?
|
|
|
Actinic Keratosis
|
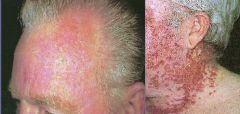
Dx?
|
|
|
Actinic Keratosis
-Hyperkeratosis = Hypertrophy of the cornea or the horny layer of the skin -Parakeratosis = Retention of nuclei in the cells of the stratum corneum of the epidermis |
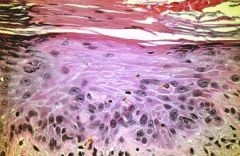
What is this?
|
|
|
Actinic Keratosis
|
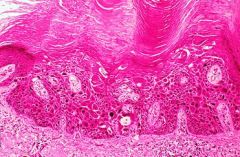
Dx?
|
|
|
What may certain subtypes of HPV evole into?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Verruca Vulgaris = HPV type I
|
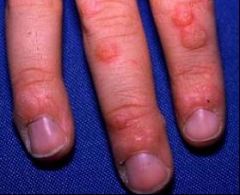
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Verruca Vulgaris = HPV type I
|
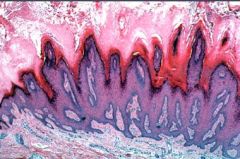
What is this?
|
|
|
Verruca Vulgaris = HPV type I
|
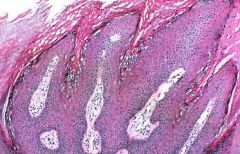
Dx?
|
|
|
Condyloma Accuminatum = Koilocytosis
|
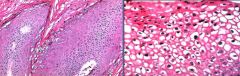
What is this biopsy from?
|
|
|
What are the classifications of Basal Cell Carcinoma?
|
1. Pearly papule
2. Rodent Ulcer 3. Superficial BCC 4. Morphea-like BCC 5. Pigmented BCC (may resemble melanoma) |
|
|
What are the most common sites of Basal Cell Carcinoma?
|
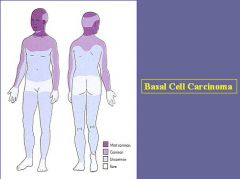
Sun-exposed areas of the body
|
|
|
MC malignant skin tumor
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma - Pearl type
MC sites are: 1. Inner Canthus of Eye 2. Upper Lip |
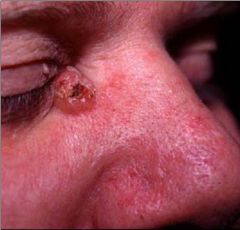
Dx?
|
|
|
Locally aggressive, infiltrating skin cancer that DOES NOT METASTASIZE
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
-invasive nests of basoloid cells with palisading growth pattern |
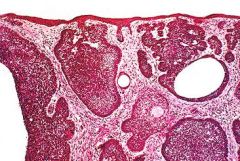
Dx?
|
|
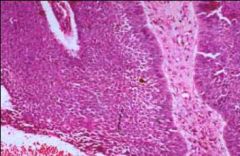
Dx?
|

Basal Cell Carcinoma
-tumor clumps surrounded by cells at the periphery with palisading arrangement of nuclei |
|
|
Skin Carcinoma that may evolve from Actinic Keratosis or from sun exposure
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Skin carcinoma that has the potential to metastasize
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the most common sites of Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
|
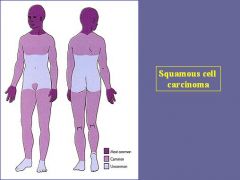
Face, neck, back of hands
*BRS = tends to involve Lower part of face = lower lip & down + ears + dorsum of hand |
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-small, ulcerating nodule |
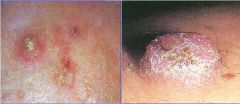
Dx?
|
|
|
Squamous Cell CA arising in Actinically damaged skin
|
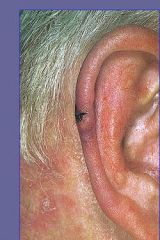
What is your Dx?
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-keratin pearls |
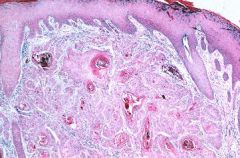
Dx?
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-infiltrating with Keratin Pearls |
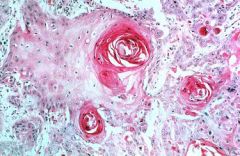
Dx?
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-dyskeratosis = premature keratinization in cells that are not in the keratinizing surface layer of the skin -Intercellular bridges |
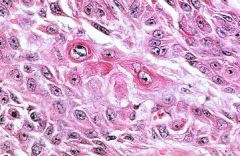
Dx?
|
|
|
Rapidly growing, benign crateriform tumor with a central keratin plug
-sun-exposed skin -spontaneous regression -variant of Squamous Cell CA |
Keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma
-rapidly growing skin epidermal tumor that mimics Squamous Cell Carcinoma -crateriform tumor with central keratin plug |
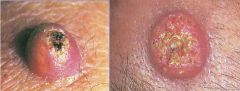
What are seen here?
|
|
|
Keratoacanthoma
-central, keratin filled crater surrounded by proliferating epidermal cells similar to those seen in squamous cell CA |
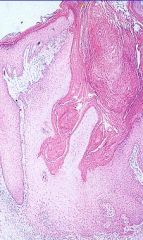
What is this?
|
|
|
Tumor of the Dermis that is a dome-shaped, firm, rubbery nodule 3-5 mm in diameter
|
Dermatofibroma
|
|
|
Where do most Dermatofibromas occur?
|
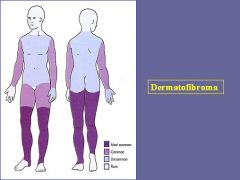
Arms & legs
|
|
|
Dermatofibroma = Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma
|
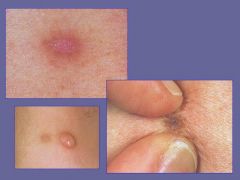
What are these benign tumors of the dermis?
|
|
|
Where does HIV-related Kaposi's Sarcoma usually occur?
|
Head & neck
|
|
|
Where does the classic form of Kaposi's Sarcoma usually occur?
|
Lower leg & Feet
|
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma = flat, pink lesion
|
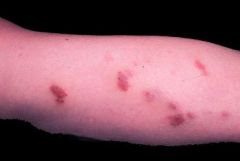
What is this?
|
|
|
Kaposi's Sarcoma
|
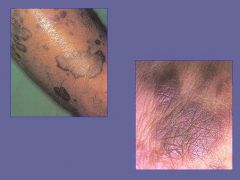
What are these showing?
|
|
|
Kaposi's Sarcoma
|
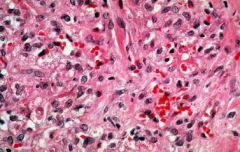
What is this?
|
|
|
Where do most Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma's occur?
|
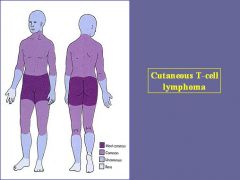
-
|
|
|
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
|
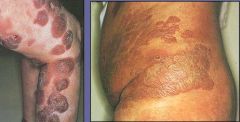
Dx?
|
|
|
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
|
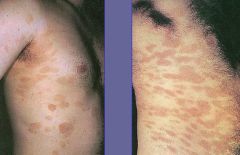
Dx?
|

