![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
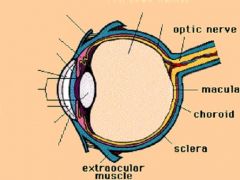
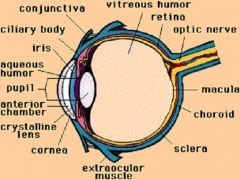
Where is most of the refractive power of the eye contained?
|
Cornea = 39-48 diopters
Lens = 15-24 diopters |
|
|
What determines if you are Myopic or Hyperopic?
|
the shape fo the eyeball
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
What part of the eye is immunologically privileged? Why?
|
Anterior Chamber b/c it doesn't receive blood flow
|
|
|
Basilar Skull Fracture
|
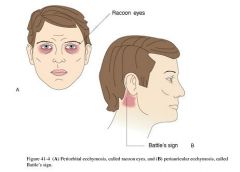
What is the cause of these symptoms?
|
|
|
Basilar Skull Fracture
|
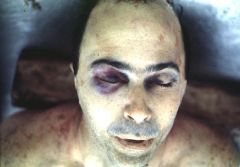
What is the cause of this?
|
|
|
Exophthalmos
Fatty tissue behind the globe may be infiltrated by myxedematous tissue -Grave's disease |
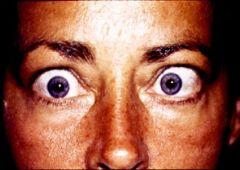
What is this called? What is the cause?
|
|
|
Blepharitis
|
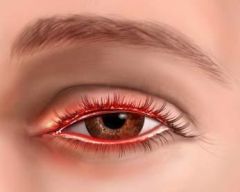
Acute inflammation of the eyelids, caused by allergen, mild trauma, etc
|
|
|
Hordeolum = Sty
|
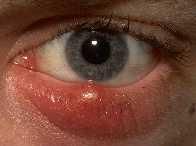
Acute Folliculitis of the Meibomain or Zeis glands (sebaceous glands)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Hordeolum (Sty)?
|
Hot compresses will ususally cause the Sty to "point" & drain.
Alternatively, it can be excised -Antibiotic are rarely necessary |
|
|
What is the most common carcinoma of the eyelid? 2nd most common?
|
Basal Cell CA = predilection for the lower eyelid & medial canthus
Sebaceous CA |
|
|
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage = usually due to minimal trauma
-coughing, sneezing, vomiting Does not require treatment, but warn patient that blood will change color like a bruise |
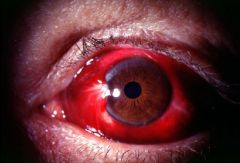
What is seen here? What is the treatment?
|
|
|
What type of Conjunctivitis is most common?
|
Allergic Conjunctivitis
|
|
|
What bacteria are the most common cause of Bacterial Conjunctivitis (pink eye)?
|
H. influenza
S. pneumoniae |
|
|
What is the cause of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis that is usually contracted from under-chlorinated public swimming pools?
|
Adenovirus
|
|
|
This is the leading cause of blindness worldwide
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
This is the cause of Ophthalmia Neonatorum
|
Gonoccal
|
|
|
Pink Eye due to H. influenza
-kids complain of waking up with their eye matted shut from pus |
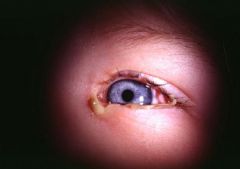
Dx?
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Conjunctivitis?
|
1. Vasoconstrictors
2. Antibiotics -topical Erythromycin is preferred -Contact lens-wearers should receive coverage for Pseudomonas = Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, or Tobramycin 3. Ophthalmia Neonatorum requires systemic therapy = Penicillin or Ceftriaxone |
|
|
What may dry eyes cause?
|
Drying & scarring of the Cornea
|
|
|
What group of people is Idiopathic Dry Eye common in? What is the treatment?
|
Older women = may be associated with Menopause
May also occur in younger, pregnant women Tx = Artificial tears |
|
|
With what syndrome do you have dry eyes?
|
Sjogren Syndrome = Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
|
|
|
Vascularized conjunctival tissue, which may grow over the iris, obscuring vision
|
Pterygium
|
|
|
What people does Pterygium commonly occur in? What is the treatment?
|
Elderly
Surgical excision, often return so must be re-excised |
|
|
Pterygium
|
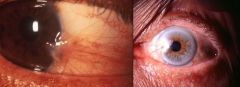
What is this?
|
|
|
This part of the Eye has more pain nerve fibers per millimeter squared than any other tissue in the body
|
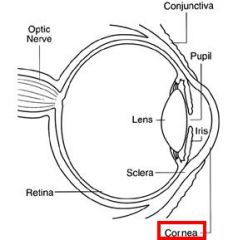
Cornea
|
|
|
T or F: Corneal epithelium heals faster than any other tissue in the body
|
True
|
|
|
When does the Corneal epithelium not regenerate?
|
When the Basement Membrane (Descemet's membrane) is injured
|
|
|
How are Corneal Abrasions usually treated?
|
1. Patch affected eye, usually heals within 24 hours
-Antibiotics are rarely necessary 2. Medicate for pain |
|
|
Eye problem in which the patient usually believes there is something in the eye, but physical exam reveals only conjunctivitis. Fluorescein may worsen the conjunctivitis
|
Corneal Abrasion
|
|
|
What do you not treat Herpex Simplex Corneal Ulcers with?
|
Corticosteroids
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Keratitis
-"chinese character" |
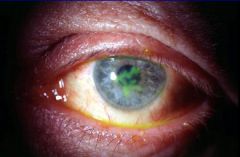
What is this?
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Keratitis
-"chinese character" |
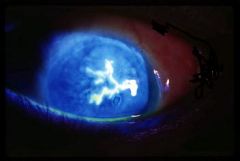
What is your diagnosis?
|
|
|
Acanthemeba = severe keratoconjunctivitis in pts who do not clean their contacts properly
|
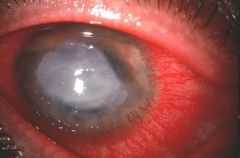
What is the cause of this?
|
|
|
This causes Keratoconjunctivitis in patients who do not clean their contancts lenses properly
|
Acanthamoeba
|
|
|
The patient was a 61 year old man who was mowing his lawn with a power mower. He was not wearing eye protection. He got something in his eye, but simply rubbed it and kept on mowing. By the next day the eye was swollen, red and pruritic. He consulted an ophthalmologist, who prescribed topical steroids. His vision worsened, and he consulted another ophthalmologist.
|
Fusarium
|
|
|
Fusarium
|

Dx?
|
|
|
Paecilomyces
|
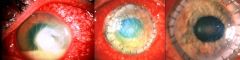
This is from a patient who had Elective Radial Keratotomy for myopia. Dx?
|
|
|
A collection of disorders featuring optic neuropathy, accompanied by a characteristic excavation of the optic nerve head and progressive loss of visual field sensitivity
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is Glaucoma?
|
Any of a group of eye diseases characterized by abnormally high intraocular fluid pressure, damaged optic disk, hardening of the eyeball, and partial to complete loss of vision
|
|
|
What is the most common type of Glaucoma?
|
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
|
|
|
Gradually increasing intraocular pressure, leading to visual impairment &, eventually, blindness
|
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
|
|
|
Glaucoma which is an ocular emergency, requiring intervention within 24-48 hours
|
Primary Closed-angle Glaucoma
|
|
|
Describe the normal flow of Aqueous Humor
|
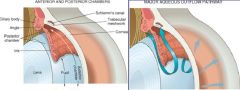
1. Fluid is produced in the Ciliary Body in the Posterior Chamber
2. Fluid then comes thru into the Cornea 3. Fluid exits thru Canal of Schlemm |
|
|
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
-transient apposition of the Iris at the Pupillary Margin to the Lens blocks passage of Aqueous Humor from the Posterior Chamber to the Anterior Chamber -pressure builds up in the Posterior Chamber, bowing the Iris forward & occluding the trabecular meshwork |
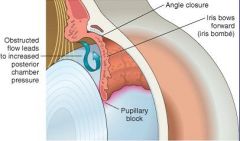
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Neovascular Membrane = Secondary Glaucoma
|
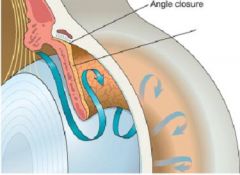
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
What are some causes of Cataracts?
|
1. Advanced age = MC
2. Diabetes Mellitus = osmotic damage 3. Infection = Rubella, CMV 4. Toxins or Drugs 5. Autoimmune diseases = Scleroderma 6. Physical agents = UV light, radiation |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Cataracts in the US?
Treatment? |
Aging = Senile Cataracts = "senile degeneration" of lens fibers, thought to be related to UV exposure or aging
Lens replacement |
|
|
Early Cataract
|
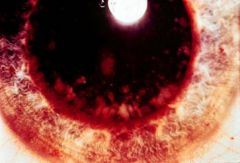
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Advanced Cataract
|
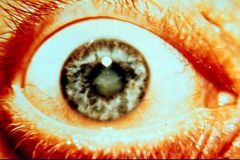
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Cataract
|
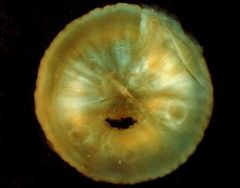
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Cataract of the Lens
|

What is seen here?
|
|
|
List the layers of the Retina
|
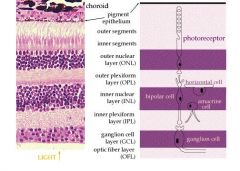
1. Pigmented epithelium (Outer layer)
2. Photoreceptors; bacillary layer (outer and inner segments of cone and rod photoreceptors) 3. External (outer) limiting membrane 4. Outer nuclear (cell bodies of cones and rods) 5. Outer plexiform (cone and rod axons, horizontal cell dendrites, bipolar dendrites) 6. Inner nuclear (nuclei of horizontal cells, bipolar cells, amacrine cells, and Müller cells) 7. Inner plexiform (axons of bipolar cells and amacrine cells, dendrites of ganglion cells) 8. Ganglion cells (nuclei of ganglion cells and displaced amacrine cells) 9. Axons (nerve fibers from ganglion cells traversing the retina to leave the eye at the optic disk) 10. Internal limiting membrane (separates the retina from the vitreous) |
|
|
What are the 4 layers beneath the outermost Pigmented epithelium of the Retina, from inside (closest to Retina) to outside?
|
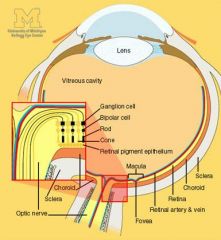
1. Bruch's Membrane = separates the Pigmented Epithelium of the retina from the Choroid
2. Choriocapillaries 3. Choroidal blood vessels 4. Sclera = white part of eye |
|
|
Temporal Arteritis = "Giant Cell" Arteritis
can affect the Ophthalmic Artery, causing retinal infarction |
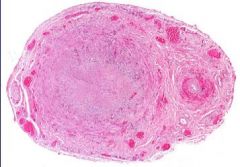
What is shown here? What is the significance?
|
|
|
Retina showing:
1. Arteriolar narrowing (AV nicking) 2. Hemorrhage 3. Microaneurysms 4. Exudates 5. Cotton Wool spots = infarcted nerve fiber layer |
Hypertensive Retinopathy
|
|
|
Hypertensive Retinopathy
-Arteriolar narrowing (AV nicking) -Hemorrhage -Microaneurysms -Exudates -Cotton Wool Spots (infarcted nerve fiber layer) |
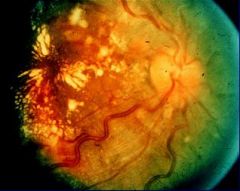
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Diabetic Retinopathy that has the following:
1. Hemorrhage 2. Microaneurysms 3. Exudates Does not impair vision |
Background (Non-proliferative) Retinopathy
|
|
|
Background (Non-proliferative) Retinopathy
|
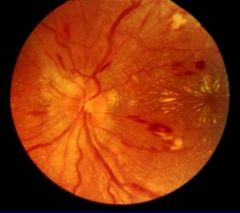
Dx?
|
|
|
Occurs later in Diabetes, often within 5 years of death from vascular causes
Characterized by neo-vascular proliferation of the retina, which obscures vision Retinal detachment & blindness are common |
Proliferative Retinopathy
|
|
|
Proliferative Retinopathy
|
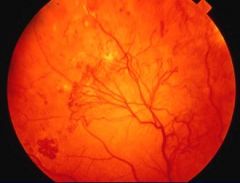
Dx?
|
|
|
What is an alternate name for Retinopathy of Prematurity?
|
Retrolental Fibroplasia
|
|
|
Describe Retinopathy of Prematurity (Retrolental Fibroplasia)
|
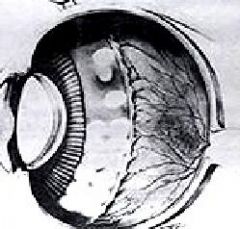
1. Caused by high oxygen tension in Premature infants due to therapeutic oxygen
2. Proliferative retinopathy occurs, similar to that in late stage Diabetes 3. May be accompanied by Retinal Detachment & a Fibrovascular mass behind the Lens |
|
|
Systemic mycoses that is endemic in the Mississippi & Ohio River valleys that is contracted from inhalation of air-borne spores from bird or bat droppings; can cause RETINITIS
|
Histoplasma captulatum
|
|
|
Protozoa that is usually congenital in origin & may reactivate in HIV disease or iatrogenic immunosuppression causing brain abscesses & Retinitis
|
Toxoplasmosis
|
|
|
Virus that can cause Retinitis
|
CMV
|
|
|
Nematode that is found in Cats & Dogs; can cause Visceral Larvae Migrans resulting in Retinitis leading to blindness; most common in pediatric age group
|
Toxocara
|
|
|
REtinitis caused by CMV
|
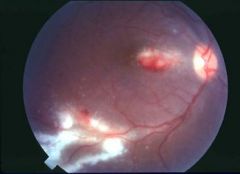
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Retinitis caused by Histoplasmosis
-inflammation has gone deep to the Pigmented Epithelium layer = see black appearance |
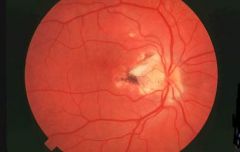
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Retinitis from Toxoplasmosis
-has gone into Pigmented Epithelium layer |
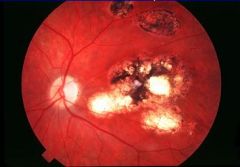
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Toxocara
-larvae is migrating across the eye in the Aqueous Humor right behind the lens |
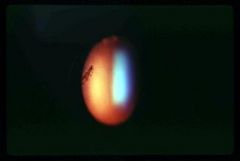
What is seen here?
|
|
|
List the 3 types of Retinal Detachment
|
1. Rhegmatogenous
2. Traction 3. Exudative |
|
|
Retinal Detachment that is associated with a retinal tear
|
Rhegmatogenous
|
|
|
Retinal Detachment in which adhesions are formed during diabetic retinopathy or infections & pull the retina away from the pigment layer
|
Traction
|
|
|
Retinal Detachment in which a collection of fluid between the retina & the pigment epithelium occurs during Choroiditis, Choroid Hemangioma, or Melanoma
|
Exudative
|
|
|
Most common cause of decreased visual acuity in the US
|
Macular Degeneration
|
|
|
What is the cause of Macular Degeneration?
|
Age-related, possiblly due to toxins (Chloroquine)
may also be related to smoking, hyperlipidemia, or genetic causes |
|
|
Papilledema
|
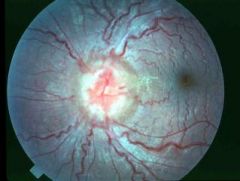
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What is Papilledema?
|
Optic Disc swelling that is caused by increased Intracranial pressure
|
|
|
What do you NOT want to do if a patient has Papilledema?
|
perform a Spinal Tap
Increased intracranial pressure will cause Cerebellar Tonsils to herniate down into the Foramen Magnum -> press on the Medulla where Respiratory Centers are -> death |
|
|
What is the most common malignancy of the eye?
|
Metastatic carcinoma
-usually involving the Uveal Tract (iris, choroid, & ciliary body) |
|
|
What does Uveal Tract Melanoma arise from?
What part of the eye does NOT form Melanomas? |
Arises from Melanocytes or Nevi in the Uvea (vascular lining of the eye, including the Choroid)
Retinal Pigment Layer |
|
|
What race is more likely to get Uveal tract Melanoma?
|
Caucasians
|
|
|
What is the classical vignette for a Uveal tract Melanoma?
|
patient presents with an enlarged liver & a glass eye
*Uveal tract Melanoma commonly metastasizes Hematogenously to the Liver |
|
|
How is Uveal tract Melanoma treated & what is the prognosis?
|
Enucleation
Good prognosis if found early = 50% 15 year survival |
|
|
Anterior Segment Melanoma
-pupil tractions is seen |
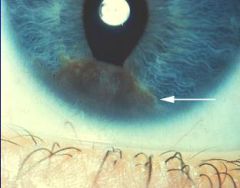
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Anterior Segment Melanoma
|
What is seen here?
|
|
|
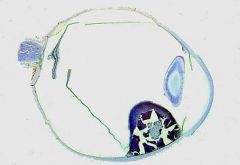
Posterior Segment Melanoma
|
What is seen here?
|
|
|
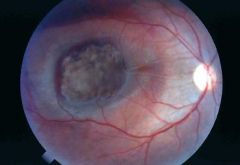
Posterior Segment Melanoma
|

WHat is seen here?
|
|
|
Melanoma
|
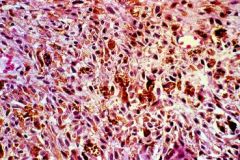
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Malignant neoplasm that arises from immature retinal neurons & is the most common intraocular neoplasm of childhood
-usually presents within the first 2 years of life |
Retinoblastoma
|
|
|
What percent of Retinoblastoma is bilateral?
|
up to 25%
|
|
|
What type of gene is the Rb gene? What chromosome is it located on?
|
Tumor Suppressor Gene
Chr. 13 |
|
|
How is Retinoblastoma treated?
Where may it spread to? |
Enucleation & chemotherapy
CNS along the optic nerve |
|
|
Explain the pathogenesis of Retinoblastoma
|
Knudson's "two-hit" hypothesis:
1. First deletion si inherited in germ line in familial cases or occurs as a somatic mutation in sporadic cases 2. Second deletion results from somatic mutation in both familial % sporadic cases |
|
|
What does Retinoblastoma increase the risk of having?
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
What percent of REtinoblastoma cases are inherited?
|
6-8%
the rest are spontaneous |
|
|
Retinoblastoma
-Red Reflex is something you look for at 2-3 ft away thru your ophthalmoscope -here you see a White reflex due to tumor |
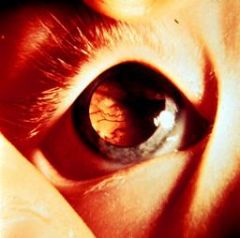
What is seen here?
|
|
|
REtinoblastoma
-fleshy tumor filling into the Vitreous Humor |
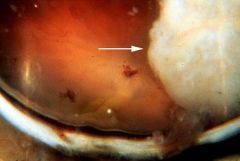
What is seen here?
|
|
|
REtinoblastoma = "little blue cells"
|
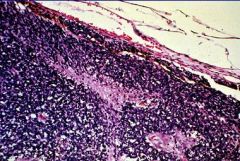
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Retinoblastoma with "rosettes"
|
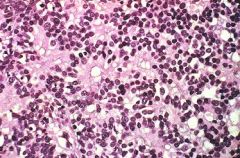
What is seen here?
|

