![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What could cause a vasospasm in the lungs?
|
amphetamines (cocaine)
|
|
|
What are Pulmonary Infarcts most commonly the result of?
|
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
|
|
|
75% of pulmonary infarcts invlove which part of the lungs?
|
Lower lobes b/c perfusion is greater than ventilation in the lower lobes
|
|
|
What is the most common origin of Pulmonary Thromboembolisms?
|
Femoral Vein = deep veins in legs
|
|
|
Macroscopically, what is the classic appearance of Pulmonary Infarcts?
|

Hemorrhagic infarct, which extends to the periphery of the lung as a wedge
|
|
|
What can happen if the hemorrhagic infart extends to the pleural surface?
|
can be covered by Fibrinous exudate and cause Pleural friction rub
|
|
|
When an infarct is caused by a septic embolus, a septic infarct may occur and evolve into what?
|
Abscess
|
|
|
What is the classic triad associated with Pulmonary Embolism?
|
1. Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
2. Pleuritic chest pain 3. Hemoptysis **most patients are extremely dyspneic** |
|
|
List risk factors for pulmonary thromboembolism (6)
|
1. Cancer (Trousseau syndrome = pancreatic carcinoma cancer cells release thromboplastin)
2. Cardiac disease 3. Obesity 4. Prolonged bed rest 5. Acute paraplegia 6. oral contraceptive use |
|
|
What is Homan's sign?
|
Use to check for Deep vein thrombosis --> pain in the calf is produced by passive dorsiflexion of the foot
|
|
|
What is the underlying principle of order of scanning in the V/Q scan?
|
-1st scan using isotope with smallest dose or lowest energy to avoid down-scatter of higher energy isotope
-scan with highest energy isotope last |
|
|
When doing the V/Q scan, which imaging when done first can be cost effective?
|
Perfusion because if it is normal, a ventilation study is not needed to assess for pulmonary emboli
|
|
|
To determine the etiology of a perfusion defect, what 2 things are needed?
|
1. ventilation study
2. CXR |
|
|
A V/Q mismatch suggest (V/Q is infinite)?
|
Pulmonary embolism
|
|
|
A V/Q match suggests?
|
parenchymal disease
|
|
|
What is the risk of performing an angiogram in trying to detect the presence of Pulmonary Thromboembolism?
|
the radiographic contrast itself can cause thrombosis
|
|
|
What are Interstitial Pneumonias usually caused by? (2)
|
1. viral infections
2. Mycoplasma pneumonia |
|
|
Define Bronchopneumonia
|
-patchy consolidation centered around small bronchi
-PMN reaction |
|
|
What is the cause of Bronchopneumonia?
|
inhalation/aspiration, mostly bacteria, some fungi
|
|
|
Define Lobar Pneumonia
|
-homogenous
-identical involvement of alveoli, same time and same extent -intra-alveolar exudate resulting in consolidation |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Lobar Pneumonia?
|
Strep pneumo
*Klebsiella also |
|
|
List the 4 stages in Lobar Pneumonia
|
1. congestion
2. red hepatization 3. gray hepatization 4. resolution |
|
|
Describe the Congestion phase of Lobar Pneumonia
|
- heavy, boggy, red lung = active hyperemia
- histologically = vascular engorgement, intra-alveolar fluid with few NO and often the presence of numerous bacteria |
|
|
Describe the Red Hepatization phase of lobar pneumonia
|
- lobe is distinctly red, firm, and airless, with a liver-like consistency
- Histo = alveolar spaces are filled with RBC's, PMN's, and fibrin |
|
|
Describe the Gray Hepatization phase of Lobar pneumonia
|
-grayish,brown dry surface
- Histo = disintegration of RBC's and the persistence of fibrinopurulent (Fibrin + Neutrophils) exudate within air spaces |
|
|
Expected oropharyngeal flora in ~20% of adults
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
Normally sensitive to penicillin, but drug resistance is emerging
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
With this bacteria, African-Americans have a 3-5 fold higher incidence of bacteremia than whites and rates of invasive disease are also exceptionally high among Native Americans
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
What is the name of the vaccine available for adults against Strep pneumo?
What type of vaccine? |
Pneumovax
Polysaccharide vaccine that covers most of the bacteremic strains of pneumococcus |
|
|
Name of Strep pneumo vaccine given to children?
Vaccine properties? |
Prevenar
Heptavalent vaccine linked to Diphtheria toxin |
|
|
Classically "lancet-shaped" gram + diplococcus with a capsule
|
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
What are most Gram - pneumonias due to?
|
Endogenous aspiration of oropharyngeal flora
|
|
|
Eponymic name is Friedlander's pneumonia
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Encapsulated organism, 10% of all nosocomial pneumonias
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Gram -, fat rod surrounded by a mucoid capsule
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Most common gram - causing lobar pneumonia and typical pneumonia in elderly patients in nursing homes
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Common cause of Pneumonia in Alcoholics
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Pneumonia associated with blood-tinged, thick, mucoid sputum; lobar consolidation and abscess formation simulating TB
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Intracelluar organism that requires anti-microbial drugs with good cytoplasmic penetration, such as Macrolides
|
Legionella
|
|
|
Infection from inhalation of aerosol from contaminated stored water, most often in air-conditioning systems
|
Legionella
|
|
|
Detected by Immunofluorescence of sputum
|
Legionella
|
|
|
Inoculated on Charcoal Yeast extract plates
|
Legionella
|
|
|
Stained with Dieterle silver stain
|
Legionella
|
|
|
Gram - rod with green sputum (pyocyanin)
|
P. aeruginosa
|
|
|
Common colonizer of CF patients
|
P. aeruginosa
|
|
|
Pneumonia from this bacteria is often associated with infarction due to vessel invasion
|
P. aeruginosa
|
|
|
Mucoid colonies in chronically infected patients make eradication impossible
|
P. aeruginosa
|
|
|
Definition: a localized collection of pus in the lung resulting from liquefactive necrosis of lung tissue
|
Lung Abscess
|
|
|
List 4 bacteria that frequently cause abscesses
|
1. S. aureus ***
2. Pseudomonas 3. Klebsiella 4. Proteus |
|
|
List 4 mechanisms that can lead to Lung Abscesses
|
1. aspiration of infected material, especially Gram - and anaerobes in patients with dental caries
2. Antecedent primary bacterial infection 3. Septic embolism 4. obstruction secondary to neoplasm |
|
|
Definition: local aggregations of macrophages that become epithelioid cells
|
Granulomatous inflammation = granuloma
|
|
|
What are 3 causes of granulomatous inflammation in the lungs
|
1. Mycobateria
2. Dimorphic fungi -Histoplasma -Coccidioides -Blastomyces 3. Sarcoidosis |
|
|
What is the initial focus of Tuberculosis in primary infection?
|
Ghon Complex
|
|
|
What is a Ghon Complex?
|
1. Parenchymal subpleural lesion
2. enlarged hilar lymph nodes *both contain tuberculous granulomas |
|
|
Describe Miliary Tuberculosis
|
Secondary TB with the presence of multiple, small tuberculous granulomas in many organs, which result from the hematogenous spread of bacteria
|
|
|
Name 5 complications of TB
|
1. cavitation
2. hemorrhage 3. bronchopleural fistulas 4. Bronchopneumonia 5. Aspergillomas |
|
|
With Tuberculosis, swallowed sputum may lead to ________
|
GI TB
|
|
|
This complication of TB is particularly a problem in children and the immunosuppressed
|
TB meningitis
|
|
|
List 3 common causes of diffuse infiltrate in IC'ed hosts
|
CMV
PCP Drug reaction |
|
|
List 3 common causes of focal infiltrates in IC'ed hosts
|
Gram - rods
S. aureus Aspergillus |
|
|
Fruiting body and narrow-angled, branching septate hyphae
|
Aspergillus
|
|
|
Non-invasive "fungus ball", occupies a previously existing anatomical space, such as a sinus cavity or abscess cavity
|
Aspergilloma
|
|
|
Most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients
|
Pneumocystis carinii
|
|
|
Replicates in the human lung, with a complicated life cycle that includes formation of intra-alveolar CYSTS
|
Pneumocystis carinii
|
|
|
Most of the population is infected by age 5 with this organism
|
PCP
|
|
|
What is PCP probably acquired from?
|
Aerosolized mouse or rat urine
|
|
|
What drug is given prophylactically for PCP when CD4 counts drop below 200
|
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
|
|
|
What do CXR's look like with PCP?
|
Patchy, pneumonia, with a characteristic "ground-glass" appearance
|
|
|
Budding yeast with narrow-based buds
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
Systemic fungi surrounded by a thick capsule
|
Cryptococcus
|
|
|
Is ubiquitous in the environment, preferring alkaline bird droppings as its habitat
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
Usually causes meningitis in IC'ed, but primary lung disease may occur
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
What test is useful in detecting Cryptococcus in normal hosts?
|
Antigen testing of the CSF
|
|
|
What test is adequate for detecting Cryptococcus in IC'ed host?
|
India Ink prep
|
|
|
Dimorphic large yeast with Broad-based budding
|
Blastomyces dermitidis
|
|
|
Saddle embolus originating from the deep veins of the leg
-straddles right and left pulmonary artery = sudden death |
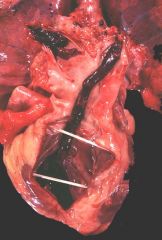
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Why are small Pulmonary Infarcts "Hemorrhagic" or "red" infarcts?
|
The lung has a dual blood supply
-Pulmonary Artery -Bronchial arteries |
|
|
Bronchopneumonia
-pathy areas where PMN's are within tiny bronchioles |

What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Strep pneumo
|
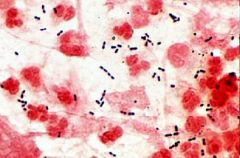
What are these microbes?
|
|
|
Lower Lobe consolidation
Pneumococcus |

What is this showing?
What is the most likely cause? |
|
|
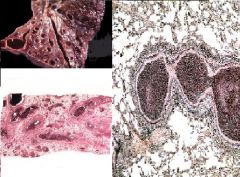
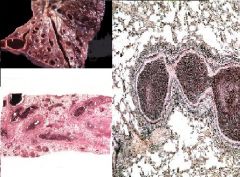
Lobar Pneumonia
-if the bronchi were filled with pus = Bronchopneumonia, but since they are spared it is Lobar |
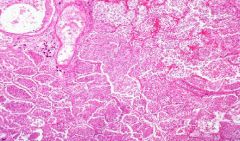
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Klebsiella
-consolidation + abscesses |

What is the likely cause of this? How do you know?
|
|
|
Legionella
|
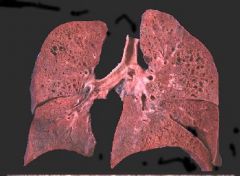
This person contracted 5-lobe consolidation by working in the produce section with water mist sprayers
|
|
|
Legionella
Immunofluorescence Dieterle Silver |
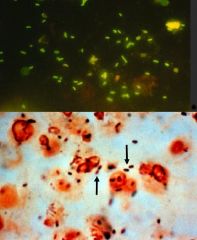
What microbe?
What are these 2 stains? |
|
|
Legionella
Immunofluorescence Dieterle Silver |
What microbe?
What are these 2 stains? |
|
|
1. P. aeruginosa
2. Cystic Fibrosis 3. Bronchiectasis |
What are the 3 associations here?
|
|
|
1. S. aureus
2. Klebsiella 3. Aerobic and anaerobic streptococci 4. Gram - organisms |

What organisms typically cause this?
|
|
|
What is a Simon focus?
|
Granuloma at the lung apex in Secondary Pulmonary TB
-occurs at apex due to high O2 tension |
|
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
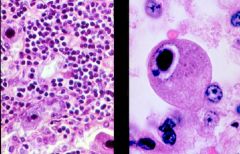
What is this microbe?
|
|
|
When does Invasive (disseminated) Aspregillosis usually only occur?
|
Immunocompromised
|
|
|
Aspergilloma
|
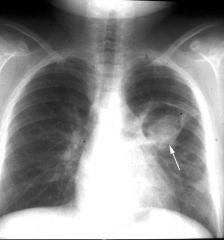
What is this?
|
|
|
Aspergilloma
|
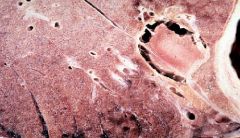
What is shown here?
|
|
|
Aspergillus
Acute (<45 degrees) branching Septate Hyphae |
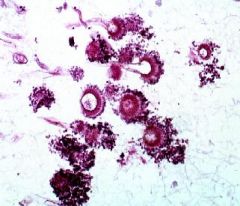
What is this?
In culture, what do the hyphae look like? |
|
|
Invasive Aspergillosis
|
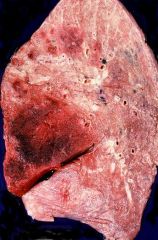
This was from an Immunocompromised patient.
What pathogen? |
|
|
Invasive Aspergillosis
Acutely branching septate hyphae |

What pathogen?
How do you know? |
|
|
-Cryptococcus neoformans = narrow-based budding
-Meningitis in IC'ed -Pigeon excreta |
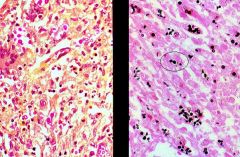
What pathogen?
What does it usually cause? How are you exposed to it? |
|
|
Pneumocystis carinii
IC'ed = AIDS |
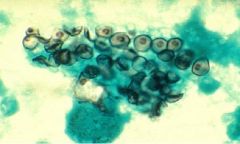
What pathogen is this?
Who does it usually affect? |
|
|
Bronchopneumonia
Patchy areas of pulmonary consolidation |

What is this showing?
How do you know? |

