![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Intra-alveolar accumulation of fluid
|
Pulmonary edema
|
|
|
2 general causes of Pulmonary Edema
|
1. Hemodynamic derangements
-congestive heart failure -decreased plasma oncotic pressure 2. Increased capillary permeability due to direct microvascular injury |
|
|
Most common cause of Pulmonary Edema
|
Left-sided heart failure
|
|
|
How much can Lymphatic drainage increase before appreciable pulmonary edema occurs?
|
10-fold
|
|
|
Type of edema associated with alteration in Starling's pressure
-Congestive Heart Failure |
Transudate = low protein content
|
|
|
Type of edema associated with microvascular or alveolar damage?
|
Exudate
|
|
|
Edema with low protein content and low specific gravity
|
Transudate
|
|
|
What are 4 possible causes of increased Hydrostatic pressure resulting in Hemodynamic edema?
|
1. Left heart failure
2. Mitral Stenosis 3. Volume overload 4. Pulmonary Vein obstruction |
|
|
What are 3 diseases that would result in Hypoalbuminemia and therefore Pulmonary Edema
|
1. Nephrotic syndrome = losing protein in the urine
2. Liver disease/cirrhosis = not producing albumin 3. Protein-losing enteropathy = albumin is lost via the gut |
|
|
How could Lymphatics be involved in Pulmonary Edema?
|
Lymphatic obstruction such as Metastatic Cancer could prevent fluid from being drained off
|
|
|
Auscultation sound heard with Pulmonary Edema?
Treatment for Pulmonary Edema? |
Wet rales
Diuretic (Lasix = Furosemide) |
|
|
"Diffuse Alveolar Damage" is the same thing as...
|
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
|
|
Increase in Alveolar capillary permeability causing leakage of protein-rich fluid into alveoli
|
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
|
|
Drug that is used to treat testicular cancer that can cause ARDS
|
Bleomycin
|
|
|
Drug used to treat fungal infections that can cause ARDS
|
Amphotericin B
|
|
|
Drug used to treat Gout that can cause ARDS
|
Colchicine
|
|
|
What is the best way to treat ARDS?
|
remove the inciting cause
|
|
|
2 causes of Edema of Undetermined Origin
|
High Altitude Pulmonary Edema
Neurogenic edema -> severe brain trauma |
|
|
Most common cause of ARDS
|
sepsis
|
|
|
Pathognomonic feature of ARDS (5)
|
Hyaline Membranes
|
|
|
Clinical findings of ARDS
|
1. accelerated onset of respiratory insufficiency
2. progressive infiltrates on CXR -CXR is normal initially -progresses to diffuse bilateral infiltrates 3. Tachycardia 4. Cyanosis 5. Severe Arterial Hypoxemia which is refractory (unresponsive) to oxygen therapy |
|
|
Cells that line the alveoli
|
Type I pneumocytes
|
|
|
Cells that secrete Surfactant
|
Type II Pneumocytes
|
|
|
Loss of lung volume due to inadequate expansion of the airspaces = lung collapse
|
Atelectasis
|
|
|
When does Surfactant synthesis begin?
|
at or after 28th week of gestation
|
|
|
Major component of surfactant
|
Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin)
|
|
|
What is Surfactant stored in in Type II Pneumocytes
|
Lamellar bodies
|
|
|
Surfactant synthesis is increased by these 2 things
|
Cortisol (Glucocorticoids)
Thyroxine |
|
|
What causes decreased synthesis of Surfactant?
|
Insulin
|
|
|
What are 3 possible causes of decreased surfactant in fetal lungs?
|
1. Prematurity
2. Maternal diabetes = fetal hyperglycemia increases insulin release = insulin decreases surfactant synthesis 3. C-section = lack of stress-induced increase in Cortisol from a vaginal delivery = Cortisol increases Surfactant synthesis |
|
|
At what week is surfactant made most abundantly during gestation?
|
35th week
|
|
|
What are 4 complications of Hyaline Membrane Disease of the Newborn?
|
1. Pulmonary Interstitial Edema
2. Pneumothorax = accumulation of gas/air in pleural cavity 3. Retrolental Fibroplasia = abnormal replacement of the sensory retian by fibrous tissue and blood vessels, mostly due to high-O2 treatment 4. Ventricular Brain Hemorrhage |
|
|
Parts of the Respiratory passages that Obstructive Lung Diseases can affect
|
From the Trachea to the Respiratory Bronchioles
|
|
|
3 Pulmonary Functional Tests decreased in COPD
|
1. FEV1 = amount of air expelled from the lungs in 1 second after a maximal inspiration
2. FEV1/FVC = 4L / 5L in a normal person 3. Arterial pressure of O2 (PaO2) *FVC is usually normal or slightly increased in COPD **FVC = total amount of air expelled after a maximal inspiration (normal is 5L) |
|
|
What 2 Pulmonary Functional Tests are increased in Restrictive Lung Disease
|
1. FEV1/FVC
2. A-a gradient = increase in the difference in O2 in the Alveoli compared to the Arteries = hypoxemia of pulmonary origin |
|
|
Prognosis of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
30-50% fatality rate
|
|
|
Prognosis for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
60% fatality rate
|
|
|
Enlargement of air spaces and decreased recoil resulting from destruction of alveolar walls
|
Emphysema
|
|
|
Increase in resistance to air flow out of the lungs, resulting in air trapped in the lungs
|
Obstructive Lung Disease
|
|
|
What is the major cause of Emphysema?
|
Smoking
*alpha1-antitrypsin is another cause |
|
|
Parts of the Respiratory passages that Obstructive Lung Diseases can affect
|
From the Trachea to the Respiratory Bronchioles
|
|
|
What is the most common type of Emphysema?
|
Centriacinar (Centrilobular)
|
|
|
What are 4 examples of Obstructive Lung Diseases
|
1. Asthma
2. Chronic Bronchitis 3. Emphysema 4. Bronchiectasis *BABE* |
|
|
Type of Emphysema caused by Smoking?
|
Centriacinar
|
|
|
Type of Emphysema caused by Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
|
Panacinar
|
|
|
What is Restrictive Lung Disease?
|
reduced expansion of the lung parenchyma and decreased total lung capacity
|
|
|
What is the most common type of Emphysema?
|
Centriacinar (Centrilobular)
|
|
|
Part of the acini that Centriacinar emphysema affects
|
central part, sparing the distal alveoli
Respiratory bronchioles are dilated |
|
|
Type of Emphysema with anthracotic pigment
|
Centriacinar
|
|
|
Type of Emphysema that primarily involves the apical segments of the upper lobe
|
Centriacinar
|
|
|
Gender that Centriacinar emphysema is most common in
|
Male
|
|
|
Type of Emphysema in which entire acinus is dilated
|
Panacinar
|
|
|
Emphysema associated with large subpleural bullae
|
Paraseptal
|
|
|
Emphysema associated with risk for spontaneous pneumothorax
|
Paraseptal
|
|
|
Emphysema that affects primarily the lower lobes
|
Panacinar
|
|
|
Emphysema with scarring (fibrosis) of the acinus within the walls of enlarged air spaces usually a complication of various inflammatory processes
|
Irregular emphysema
|
|
|
Enzyme that is at heightened activity in Emphysema
|
Neutrophil Elastase
|
|
|
Where is Alpha-1-antitrypsin synthesized?
What genotype interferes with AAT secretion? |
Liver
piZZ homozygous state *pi = proteinase inhibitor |
|
|
Decent of people who primarily have AAT deficiency emphysema
|
Northern European decent
|
|
|
Explain the age differences in AAT deficiency emphysema and Smoking emphysema
|
AAT = patients are classically around 25 yoa
Smoking = classically around 40 yoa |
|
|
Give 2 reasons why smoking causes emphysema
|
1. attracts neutrophils and macrophage = sources of Elastase
2. inactivates AAT = usually neutralize Elastase |
|
|
How is diagnosis of AAT deficiency made?
|
DNA-based cheek swab test
|
|
|
Restrictive Lung Disease:
- increase or decrease in compliance? - increase or decrease in elasticity? |
decrease = difficult to take air in
increase = easy to push air out |
|
|
chronic necrotizing infection of bronchi and bronchioles, resulting in abnormal dilation
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
|
4 diseases that Bronchiectasis is associated with
|
1. Bronchial obstruction
2. Cystic Fibrosis 3. Poor ciliary motility 4. Kartagener's syndrome |
|
|
Disease with sinusitis, bronchiectasis, and situs inversus, sometimes with hearing loss and male sterility
*ultimate cause is due to a defect in the motility of respiratory, auditory, and sperm cilia = absent DYNEIN arm in cilia |
Kartagener syndrome
|
|
|
Most common cause of Bronchiectasis in US?
Worldwide? |
Cystic Fibrosis (P. aeruginosa)
Tuberculosis |
|
|
Bronchiectasis most commonly occurs in which lobes of the lungs?
|
Lower lobes
|
|
|
3 clinical findings with Bronchiectasis
|
1. Purulent sputum
2. Recurrent infections 3. Hemoptysis |
|
|
At least 3 months of productive sputum for 2 or more consecutive years
|
Chronic Bronchitis
|
|
|
Hypertrophy of mucus-secreting glands in the bronchioles
|
Chronic Bronchitis
|
|
|
What is the Reid index?
|
= gland depth / total thickness of bronchial wall
-used in measuring Chronic Bronchitis |
|
|
What is the Reid index greater than in Chronic Bronchitis?
|
>50%
|
|
|
Type of metaplasia in Chronic Bronchitis
|
Squamous metaplasia
*loss of ciliated epithelia |
|
|
Describe Asthma
|
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness causes reversible bronchoconstriction resulting in trapping of air in the lungs
|
|
|
List 3 general causes of Asthma
|
1. Extrinsic = allergens = Type I HS = IgE mediated
2. Intrinsic = viral URI's 3. Aspirin sensitive = clinical triad = nonsteroidal drugs, asthma, nasal polyps |
|
|
Mucus plugs containing denuded epithelium found in asthma
|
Curschmann spirals
|
|
|
Collection of crystalloid composed of eosinophil membrane protein in asthma patients
|
Charcot-leyden crystals
|
|
|
Type of hyperplasia found in Asthma
|
Goblet cell hyperplasia
|
|
|
COPD with Eosinophils
|
Asthma
|
|
|
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Hyaline membranes - Bilateral infiltrates |

A 60 year old man presented with Dyspnea, tachypnea, and cyanosis.
What is the diagnosis? |
|
|
What is the therapy for Hyaline Membrane Disease of the Newborn?
|
- remove the initial insult
- Ventilator -> Positive end-expiratory Pressure |
|
|
What are 4 examples of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease?
|
1. Asthma
2. Chronic bronchitis 3. Emphysema 4. Bronchiectasis |
|
|
Pink Puffer = slowing of forced expiration through pursed lips
What disease? |
Emphysema
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of obstruction in Emphysema?
|
Loss of elastic recoil of the acini = air gets trapped in the acini
|
|
|
What is the cause of Chronic Bronchitis in 90% of cases?
|
Smoking
|
|
|
Disease that affected are referred to as "Blue Bloaters"
|
Chronic Bronchitis
|
|
|
-Hypertrophy of Bronchial Smooth muscle
-Hyperplasia of bronchial submucosal glands -Mucous plugs |
Asthma
|
|
|
Asthma
-Bronchial cartilage at right -Mucus plug at left -Submucosa widened by Smooth Muscle Hypertrophy |

What lung pathology?
Explain what you see |
|
|
Hyperreactive airways, resulting in episodic bronchospasm when triggered by certain stimuli
|
Asthma
|
|
|
List some causes of Intrinsic Asthma
|
1. Respiratory infections
2. Stress 3. Exercise 4. Cold 5. Aspirin -> Asthma, Nasal Polyps, Chronic pain syndrome |
|
|
Asthma b/c there are Eosinophils present
|

What COPD would this be? Why?
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis = permanent dilation of bronchi and bronchioles
|

What COPD is this?
|
|
|
Asthma
|
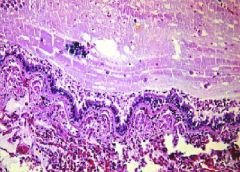
What is this picture showing?
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis
- dilated bronchi and bronchioles - P. aeruginosa with |

What do these indicate?
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis
- Dilated bronchioles with Signet-ring appearance - Due to Cystic Fibrosis |

What is this?
|
|
|
Panacinar Emphysema
AAT deficiency Lower lobes (but all part can be affected) |

What is this?
What causes it? What part of lung is primarily affects? |
|
|
Panacinar Emphysema
|

What are these showing?
|
|
|
Panacinar Emphysema
|

What is this?
|
|
|
Centriacinar Emphysema
-peripheral alveoli are normal |

What is this?
|
|
|
Diffuse Alveolar Damage
Hyaline Membranes |
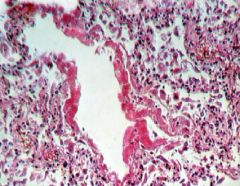
What is this?
|
|
|
Centriacinar Emphysema
-holes are located around the terminal bronchioles Rupture causing Pneumothorax |

What is this?
What is a potential complication? |

