![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Cardiac (Ebstein’s) anomaly |
Lithium
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Craniofacial defects, IUGR, stillbirth, CNS malformation |
Warfarin (Coumadin)
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Fingernail hypoplasia, craniofacial defects |
Carbamazepine (Tegretol, an anti-convulsant)
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
CNS, craniofacial, ear and cardiovascular defects |
Isotretinoin (Accutane, a synthetic analog of Vit A)
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Goiter, cretinism |
Iodide
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Cerebral infarcts, mental retardation |
Cocaine
|
|
|
Which teratogen is known to cause:
Clear cell vaginal cancer, adenosis, cervical incompetence |
Diethylstibestrol (DES)
|
|
|
Which type of spontaneous abortion (SAB)?:
IUP on sono + vag bleeding prior to 20wks + closed internal cervical os |
Threatened abortion
|
|
|
Which type of spontaneous abortion (SAB)?:
Nonviable IUP on sono + open cervical os + NO tissue passed |
Inevitable abortion
|
|
|
Which type of spontaneous abortion (SAB)?:
Nonviable IUP (fetal demise) that has not passed (lack of uterine activity) |
Missed abortion
|
|
|
Which type of spontaneous abortion (SAB)?:
Open cervical os + tissue at or beyond cervical os; some, but not all POC have passed |
Incomplete abortion
|
|
|
Which type of spontaneous abortion (SAB)?:
All POC have been passed |
Complete abortion
|
|
|
What are the indications for group B strep (GBS) prophylaxis?
|
If GBS (+) on vaginalrectal culture in last 4 weeks
GBS bacteruria during current pregnancy h/o early onset GBS in past pregnancy signs of infection |
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Initially asymptomatic but later develops a unilateral hearing loss |
CMV
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis |
Toxoplasmosis or CMV
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Rash + deafness + cataracts |
Rubella
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Hearing loss, chorioretinitis, intracranial calcifications |
CMV
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
PDA or Pulmonary Artery Stenosis |
Rubella
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Anemia, blood-tinged nasal secretions, hepatosplenomegaly |
Syphilis
|
|
|
Which congenital infection is a/w the following defect?
Temporal lobe encephalitis |
HSV
|
|
|
What is the 1st line treatment for hyperemesis gravidarum?
|
1st line: B6, Doxylamine (Unisom), Hydration
2nd line: Ondansetron (Zofran), Promethazine (Phenergan) |
|
|
What are the definitions of oligohydramnios & polyhydramnios?
|
Oligohydramnios → AFI <5 on ultrasound
Polyhydramnios → AFI >25 on ultrasound |
|
|
What tests are used to confirm rupture of membranes?
|
“pooling” of amniotic fluid in vaginal cault visible on sterile speculum exam
Nitrazine paper test: turns blue in the alkaline amniotic fluid (normally urine & vaginal secretions are acidic) Ferning test: electrolyte rich amniotic fluid dried on a glass microscope slide crystallizes in a fern-leaf pattern Oligohydramnios confirmed by ultrasound can also be useful |
|
|
What is the most frequent initial ultrasound finding for IUGR?
|
Abdominal circumference <10% for gestational age
|
|
|
In general, what are the AFI findings for oligohydramnios & polyhydramnios?
|
Oligohydramnios: < 5
Polyhydramnios: > 25 |
|
|
What might cause oligohydramnios in the 2nd trimester? 3rd tri?
|
2nd: fetal renal abnormalities, maternal problems, amniocentesis
3rd: PROM, preeclampsia, abruptio placenta, idiopathic |
|
|
Gastroesophageal atresia might cause what effect on amniotic fluid level and why?
|
Polyhydramnios (baby can’t swallow, leads to build up of amniotic fluid)
|
|
|
By what mechanism do NSAIDs decrease amniotic fluid vol?
|
NSAIDs ↓ blood flow
|
|
|
What is the difference btw PROM & P-PROM?
|
PROM: before labor
P-PROM: preterm, before labor |
|
|
What two tests on vaginal fluid can be used to detect a rupture of membranes?
|
Ferning Test
Nitrazine paper test |
|
|
How is preterm labor at less than 34 weeks gestational age managed?
|

|
|
|
How is preterm labor at 34-37 wks gestational age managed?
|
Active management if lung maturity proven, or beyond 34 wks
Steroids are of no benefit beyond 34 weeks Ampicillin 2g IV then 1g IV q 4hrs |
|
|
What drugs are used as tocolytics?
|
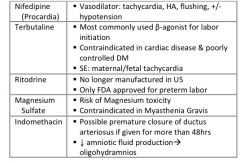
|
|
|
What are the first steps in the work-up of an infertile couple?
|

|
|
|
What diagnostic study is used to identify an anatomic cause for infertility in females?
|
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
|
|
|
What are the diff anatomic causes of infertility in females?
|
Scarring of fallopian tubes most commonly from prior STD
Endometriosis Adhesions from prior surgery or pelvic inflammation (STD, appendicitis, IBD) Tumor, fibroids (leiomyomata) Traumatic disruption of normal anatomy Congenital anomalies such as septate uterus |
|
|
HYQ: What is the treatment for metastatic choriocarcinoma?
|
Hysterectomy to eradicate any drug-resistant local disease and shorten the course of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy Single agent for stage I and II → Methotrexate or dactinomycin Combination for Stage II-IV → (EMA/CO) Etoposide + Methotrexate + dactinomycin then cyclophosphamide + vincristine If future fertility is desired → chemotherapy alone then hysterectomy only if chemotherapy is ineffective |
|
|
Compare the treatment of preterm labor at 33 and 3/7 weeks to the treatment at 34 and 3/7 weeks gestational age:
|
33: expectant management, corticosteroids, prophylactic antibiotics, deliver after fetal lung maturity
34: induction of labor, antibiotic prophylaxis |
|
|
What drugs are used for tocolysis? What is the only FDA approved tocolytic?
|
Nifedipine (Procardia) – calcium channel blocker
Terbutaline (Brethine) – β-adrenergic agonist Ritodrine – β-adrenergic agonist – withdrawn from US market in 1993 Magnesium sulfate – works as calcium anatagonist to alter myometrial contractions Indomethacin (Indocin) – blocks prostaglandins from inducing contractions Only one FDA approved → Ritodrine, but no longer on market; IV Magnesium most commonly used |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of magnesium toxicity? What is the reversal agent?
|
s/s: lose DTRs, respiratory paralysis, cardiac arrest
tx: Calcium gluconate |
|
|
What is the management of a woman in labor who has a complete placenta previa?
|
Emergency C-section
|
|
|
Why does the donor (smaller) twin in cases of twin-twin transfusion syndrome have a better prognosis?
|
Corticosteroids mature the lungs
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of infertility in a couple?
|
Sperm problem (go for semen analysis)
|
|
|
Explain the how twins can share an amniotic sack or chorion depending on when the split takes place after fertilization:
|
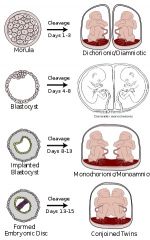
MonoCHORIONIC twins are monozygotic (identical) twins that share the same placenta
MonoAMNIOTIC twins are in the same amnionic sac (bubble) If the placenta divides, this takes place after the third day after fertilization 4 days: dichorionic, diamniotic (each twin has it's own placenta & own bubble/sac) 8 days: monochorionic, diamniotic ("Mono-di") - (these twins have to share a placenta but are swimming in their own bubble) 12 days: monochorionic, monoamniotic("Mo-mo") - (these twins are in the same bubble & share a placenta) . |
|
|
HYQ: What is the definition of PROM?
|
Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 weeks
|
|
|
HYQ: When should you suspect chorioamnionitis in a pt with PROM?
|
Fever + any of the following:
Maternal tachycardia Fetal tachycardia Maternal leukocytes Uterine tenderness Foul-smelling discharge |
|
|
HYQ: At what gestational age is labor managed actively instead of expectantly in preterm labor?
|
After 34 weeks
Or after proven lung maturity |
|
|
HYQ: what are the risks factors for placental abruption?
|
HTN, prior placental abruption, trauma, tobacco or cocaine use, PROM, multiple gestations, multiparity
|
|
|
What is typically included in an infertility work-up?
|
Semen analysis
Analysis of anovulatory cycles Hysterosalingogram (HSG) |
|
|
A 19yo G2P1 presents at 9 weeks gestation. She is vomiting all day every day, and has lost 7% of her body weight. On ultrasound, no gestational sac is found, but rather, there is a “snow storm” appearance to the uterine contents. What is the management of this patient?
|
Dx: Hyaditiform mole
Tx: D&C, monitor β-hCG, counsel on contraception (1 year) |
|
|
This same patient is lost to follow-up, only to present back to clinic 8 months later complaining of vaginal bleeding and hemoptysis. Her uterus is enlarged, but on ultrasound, there is no gestational sac. Rather, there is a uterine mass with a mix of hemorrhagic and necrotic areas with parametrial invasion. What is her prognosis?
|
Dx: choriocarcinoma
Prog: good with hysterectomy |

