![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dysphagia - have you learned what you're supposed to direct someone with dysphagia to do regarding eating? |
I believe someone with dysphagia should cough-swallow-cough. |
|
|
GERD. What is its full name and what is it? |
GERD is Gastric Esophageal Reflux Disease. Food enter stomach, mixes with digestive juices, lower esophageal sphincter closed insufficiently and the food is propelled back up in to throat. |
|
|
Small Bowel Obstruction. |
A bowel obstruction occurs when something partially or fully impedes passage through the bowel. The reasons can include tumor, scarring, cancer, and more. Surgery may be required. |
|
|
Neurogenic Bowel. |
Neurogenic bowel is generally limited to T-6 spinal injury folks. The are partially or completely unable to feel or control their bowel movements or sphincter. (Autonomic dysreflexia can result.) |
|
|
What is Kidney Disease? |
Kidney disease means that the kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood like they should. This damage can cause wastes to build up in the body. It can also cause other problems that can harm health. |
|
|
What is Neurogenic Bladder? |
Neurogenic bladder is the name given to a number of urinary conditions. It is the result of problems with nerves in the body that control how the bladder stores or empties urine. |
|
|
Name some conditions that fall under the umbrella name of Neurogenic Bladder. |
Some of the conditions under Neurogenic Bladder include: 1. overactive bladder (OAB). 2. incontinence, and. 3. obstructive bladder, in which the flow of urine is blocked. |
|
|
What is UTI? |
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and/or urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra. If the infection gets to the kidneys, there may be serious consequences. |
|
|
What are the stages of cancer? |
Stage 1. Tumor present, no perceived spread. (80 to 90% live to 5 years and beyond.) Stage 2. Localized spread of the tumor. (50% chance to live 5 years.) Stage 3. Extensive evidence of primary tumor spread to other organs. (20% live to 5 years.) Stage 4. Inoperable primary legion. (< 5% live 5 years and beyond.) |
|
|
What is rheumatism? |
Rheumatism is any disease marked byinflammation and pain in the joints, muscles, or fibrous tissue, especially rheumatoid arthritis. |
|
|
What is scleroderma? (First break down the word to figure its meaning.) |
Sclero- means hardened, like sclerosis or sclerotic arteries. -derma means skin.
Scleroderma is a chronic hardening and contraction of the skin and connective tissue, either locally or throughout the body. |
|
|
Yo bee-dog, describe the basic types of scleroderma. |
There are 2 basic types of scleroderma:
1. Limited. involves the skin 2. Systematic. involves systematic sclerosis of internal organs, which is life threatening. This can include raynaud's phenomenon, pulmonary artery problems, GI problems, Fibrosis of the lungs, or other. |
|
|
What is Raynaud's Phenomenon? |
Pronounced ray-nohz, also called ray-nohn syndrome or disease, causes some areas of your body, such as fingers and toes, to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In ray-NOHZ disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin narrow (called vasospasm), limiting blood circulation to affected areas. |
|
|
What does AIDS stand for and what is the AIDS virus? |
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. The AIDS virus is HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus. |
|
|
How does HIV work in the system? (this will help you know how someone with AIDS is affected.) |
HIV attacks the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system protects the body's immunity against opportunistic infections. The T-cells attack the cells of the body including cells of the central nervous system, GI tract, and uterine/cervix. |
|
|
Hey slappy, tell me about hepatitis. |
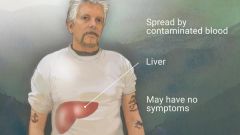
Hepatitis is liver inflammation. Hep A, B, & C can cause similar symptoms, but are each caused by different viruses and effect the liver in different ways. |
|
|
What does hepatitis mean? |
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Remember that hepato- means liver and -itis means inflammation. Hepatitis can result from many reasons, including the Hepatitis virus. |
|
|
Explain in general terms what the difference is between having Hep. A, B, and C. |
Hepatitis A: is only an acute or newly occurring infection and does not become chrah-nick. Patients usually improve without treatment. Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C can also begin as acute infections, but in some people, the virus remains in the body, resulting in chronic disease and long-term liver problems. |
|
|
What is MRSA (mursa) caused by? |
It is caused by a strain of staph bacteria that's become resistant to the antibiotics commonly used to treat ordinary staph infections. Most MRSA infections occur in people who've been in hospitals or other health care settings |
|
|
What are the symptoms of MRSA (mursa)? |
Most MRSA infections aren't serious, but some can be life-threatening. The symptoms of MRSA depend on where you're infected. Most often, it causes mild infections on the skin, like sores or boils. But it can also cause more serious skin infections or infect surgical wounds, the bloodstream, the lungs, or the urinary tract. |
|
|
What percentage of the population is diabetic? |
7% of the population is diabetic. |
|
|
What are the types of diabetes and what % is each? |
1. Type 1 diabetes is insulin-dependent. 5-10%. 2. Type 2 diabetes is non-insulin-dependent. 90-95%. 3. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. 2-5%. 4. Other types of diabetes. 1-2% |
|
|
Name some of the health risks associated with Obesity. |
Some health risks of obesity include: 1. hypertension. 2. type 2 diabetes. 3. cardiovascular disease. 4. stroke. 5. sleep apnea. 6. gall bladder disease, and 7. some cancers |
|
|
What are some of the sequelae of obesity? (stuff that results specifically from obesity) |
1. Decreased ability to perform areas of occupation, like A.D.L., I.A.D.L., mobility, and social participation. 2. Symptomatology related to larger body size, like musculoskeletal pain, limited mobility, and lower activity tolerance. |
|
|
What is Bell's Palsey? |
Bell's Palsey is paralysis of the facial nerve, causing muscular weakness in one side of the face |
|
|
What are the general affects that Lyme Disease has? |
Lyme Disease impairs the immune response and affects the neurological and orthopedic systems. |
|
|
Decubitus Ulcers -- where are we at greatest risk of getting them? |
We are at greatest risk of decubitus ulcers over bony prominences. |
|
|
Describe the stages of decubitus ulcers. |
There are 4 stages -- stages 1 & 2 are partial thickness ulcers, stage 3 is full thickness. 1. Stage 1 -- redness, edema, superficial epidermis and dermis involved. Stage 2 -- redness, edema, blistering and hardening of tissue, inflammation extends to fat. Stage 3 -- a full thickness skin lesion, it extends down to the muscle. Stage 4 -- ulcer extends down to the bone. it includes bone destruction. |
|
|
Decubitus Ulcers are also called what? |
Stupid lay persons also call Decubitis Ulcers pressure sores and bed sores. |
|
|
Images of the stages of decubitus ulcers are show on the back of this card. |
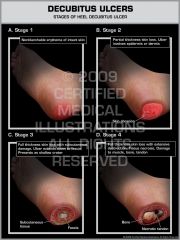
Image. |
|
|
What mofo's are at higher risk for overheating? |
At higher risk for overheating are the elderly, obese, and those taking drugs. |

