![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What kind of adhesions occur at the Basement Membrane Zone?
|
Dermo-epidermal adhesion
|
|
|
What does the Basement Membrane Zone regulate?
|
- Cell differentiation
- Motility - Transmission of extracellular signasl |
|
|
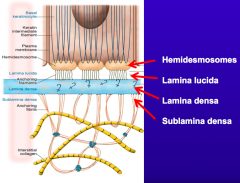
What are the components of the Basement Membrane Zone?
|
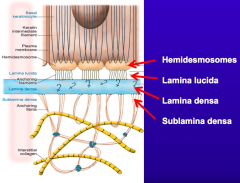
- Hemidesmosomes
- Lamina lucida - Lamina densa - Sublamina densa |
|
|
What is the function of hemidesmosomes? What are the components?
|
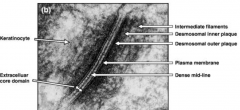
- Attach one cell to the ECM
- Made of BP-230 (Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1) and BP-180 (Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 2) |
|
|
What is BP-230 (Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen-1) part of?
|
Component of hemidesmosomes:
- Plakin family of proteins - Cytoplasmic localization - Important for organization of cytoskeletal architecture |
|
|
What is BP-180 (Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen-2) part of? Function?
|
Component of hemidesmosomes:
- Now known as Type XVII collagen - Transmembrane protein connecting basal keratinocytes through BP 230 to cytoskeleton and through laminin 332 to dermal collagen VII |
|
|
Patients with acquired, autoimmune blistering diseases have circulating auto-antibodies, what do they target?
|
Important structural proteins in epidermal basement membrane
|
|
|
What diseases are due to issues with the Basement Membrane?
|
- Bullous Pemphigoid (BP)
- Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (MMP) - Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita (EBA) - Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) |
|
|
What happens if there are auto-antibodies against BP-230 and BP-180? What is this targeting?
|
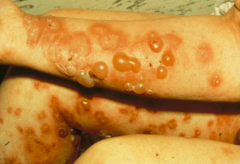
Bullous Pemphigoid (BP)
- Tense blisters w/ serous or rarely hemorrhagic content - Components of hemidesmosomes |
|
|
What kind of disease is Bullous Pemphigoid (BP)? Who does it primarily effect?
|
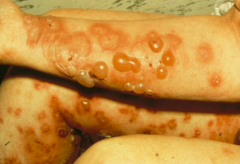
- Most common autoimmune bullous dermatosis
- Primarily in elderly (but young people too) - Causes subepidermal blisters |
|
|
What are the clinical characteristics of Bullous Pemphigoid (BP)?
|
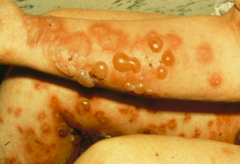
- Starts as highly pruritic (itching) urticaria (hives) without blistering
- Progresses to tense blisters w/ serous or rarely hemorrhagic content (appear in phases) - Blisters are extremely stable, as roof consists of entire epidermis |
|
What kind of diagnostic tests are done to confirm Bullous Pemphigoid?
|
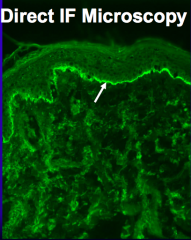
- Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) shows linear deposits of IgG and C3 along Basement Membrane
- Indirect Immunofluorescence (IIF) shows linear staining on epidermal side of salt-split skin - BP180 and BP230 ELISA show positive results correlating w/ disease activity |
|
|
How does Bullous Pemphigoid compare to Pemphigus Vulgaris?
|
BP has better prognosis than PV
|
|
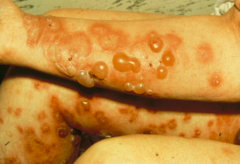
How do you treat Bullous Pemphigoid?
|
- Less severe cases can be treated w/ high potency steroids
- Oral steroids and other immunosuppressants are used for severe disease w/ caution d/t potential side effects in elderly |
|
|
What structure is immediately underlying the hemidesmosomes in the basement membrane?
|
Lamina Lucida (may be an artifact of tissue preparation and dehydration)
|
|
|
What is one of the major components of the Lamina Lucida?
|
BP-180
|
|
|
What structure is immediately underlying the Lamina Lucida in the basement membrane? What is it made of?
|
Lamina Densa - mostly type IV collagen and laminins (332)
|
|
|
What type of collagen is one of the most abundant in the Basement Membrane?
|
Type IV collagen (more than half of its mass)
|
|
|
What is the most important laminin in the Basement Membrane? What layer? Function?
|
Laminin 332 - found in Lamina Densa
- Binds to hemidesmosomal protein integrin α6β4 on basal keratinocytes - Also binds to type VII collagen in dermis providing adhesion between structures |
|
|
Who is most commonly affected by Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
|
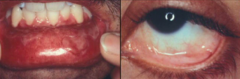
Older people
|
|
|
What are the clinical characteristics of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (MMP)?
|
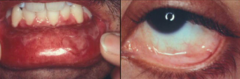
- Recurrent blistering of mucous membranes, but also skin
- Develop scars, strictures, synechiae, and blindness (20%) |
|
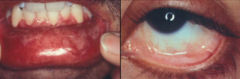
What is the cause of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (MMP)?
|
- Majority have antibodies against BP-180
- Some have antibodies against BP-230, Integrin β4, and laminin 332 |
|
|
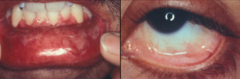
In which blistering disease should cancer screening examinations be performed? Why?
|
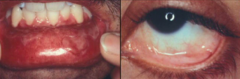
- Anti-laminin 332 version of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
- Associated w/ malignancies in 30% of cases |
|
What kind of diagnostic tests are done to confirm Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
|
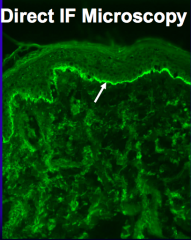
- Direct Immunofluorescence shows linear deposits of IgG and C3 along the Basement Membrane Zone (same as for Bullous Pemphigoid)
- Indirect Immunofluorescence shows linear staining of epidermal, dermal and epidermal, or just dermal (in case of anti-laminin 332 MMP) side of salt-split skin |
|
|
What structure is immediately underlying the Lamina Densa in the basement membrane? What is it made of?
|
Sublamina Densa
- Type VII Collagen - large protein composed of 3 identical α chains which form anchoring fibrils |
|
|
What is the function of Type VII collagen in the basement membrane?
|
- Necessary to maintain epidermal-dermal cohesion
- Binds to both type I and type IV collagens - Helps join lamina densa to papillary dermis |
|
|
What kind of disease is Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita (EBA)? Cause?
|
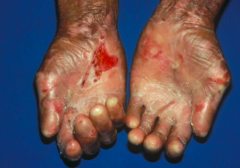
- Rare autoimmune bullous dermatosis
- Target antigen is type VII collagen - Slight trauma elicits blistering and erosions of skin |
|
|
What are the clinical characteristics of Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita?
|
- Slight trauma elicits blistering and erosions of skin
- Mechanically stressed areas such as hands, feet, elbows, and knees are more commonly affected - Healing of lesions leaves atrophy, milia, scars, and pigemntation disorders - Severe cases cause fibrosis of hands and feet - Nail dystrophy possible - Some hemorrhagic erosions of oral mucosa |
|
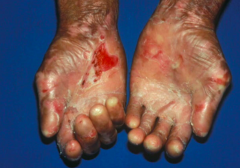
What kind of diagnostic tests are done to confirm Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita?
|
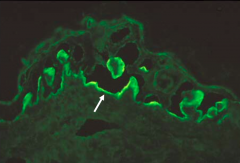
- Direct Immunofluorescence shows deposits of IgG and C3 along Basement Membrane
- Indirect Immunofluorescence shows staining of dermal side of salt-split skin - ELISA not available |
|
|
Mutations in the genes encoding Basement Membrane Zone proteins, results in what?
|
Group of inherited skin fragility disorders known as Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)
|
|
|
What are the types of Epidermolysis Bullosa (inherited)? What genes have mutations?
|
- EB Simplex (keratin 5, 14)
- Junctional EB (laminin, BP-180, integrins) - Dystrophic EB (type VII collagen) - Kindler Syndrome (kindlin 1) |
|
|
What are the clinical characteristics of Epidermolysis Bullosa (inherited)?
|
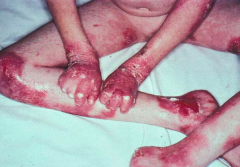
Erosions and blisters after minimal mechanical trauma (similar to acquired version)
|
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against Desmoglein 1 and/or 3?
|
* Autimmune (auto-Abs): PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
- Genetic (mutations): Striate Palmoplantar Keratoderma |
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against Keratins 5 and/or 14?
|
* Genetic (mutations): Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
|
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against BP-230?
|
* Autoimmune (auto-Abs): Bullous Pemphigoid
|
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against α6β4 integrins?
|
* Genetic (mutations): Epidermolysis Bullosa
* Autoimmune (auto-Abs): Bullous Pemphigoid |
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against BP-180 (collage type XVII)?
|
* Autoimmune (auto-Ab): Bullous Pemphigoid and Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
* Genetic (mutation): Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (NON-HERLITZ) |
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against Laminin 332?
|
* Autoimmune (auto-Ab): Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
* Genetic (mutation): Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (HERLITZ) |
|
|
What skin disorders are associated with mutations or antibodies against Type VII collagen?
|
* Autoimmune (auto-Ab): Epidermolysis Bullosa ACQUISITA
* Genetic (mutation): DYSTROPHIC Epidermolysis Bullosa |
|
|
What kind of tests are done for autoimmune bullous disorders?
|
- Biopsy for histological evaluation w/ H&E staining to determine blister level and inflammatory infiltrate
- Direct IF (DIF) detects Ig and Complement w/in biopsy specimen of PERILESIONAL skin - Indirect IF (IIF) detects Ab against BMZ in patient's SERUM - ELISA screens for detection of auto-antibodies |
|
|
What is accomplished in a routine biopsy of a blister?
|
Taken from edge of blister and processed w/ H&E staining to determine:
- Blister level - Inflammatory infiltrate |
|
|
What happens in a Direct Immunofluorescence test (DIF)?
|
- Detects molecules like Igs and Complement (C3) within biopsy specimens (perilesional skin)
- Fluorescein-conjugated Abs against human Igs or complement used to detect in-situ deposits of immunoreactants under fluorescence microscope |
|
|
What happens in a Indirect Immunofluorescence test (IIF)?
|
- Detects circulating Ab against BMZ in patient's SERUM
- Patient serum is applied to a foreign substrate such as normal human skin (sometimes with an artificial split at level of lamina lucida created by salt), monkey esophagus, or rodent bladder - Circulating Abs from sera bind to BMZ antigen in substrate - Ab antigen complex is then detected by fluorescein-conjugated Ab and visualized under fluorescence microscope |
|
|
What happens in ELISA?
|
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Used as an initial screen for detection of patient's circulating Auto-Abs - Based on principle of antibody-antibody interaction, test allows for easy visualization of results and can be completed in short period of time |

