![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the __ types of connective tissue
|
connective tissue proper
cartilage bone blood |
|
|
what are the __ types of cartilage
|
hyaline
fibrocartilage elastic |
|
|
what are the characteristics of hyalin cartilage
|
flexible but resilient
|
|
|
where is hyalin cartilage found
|
respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchi)
costal cartilage nose articular cartilage epyphyseal plate fetal skeleton |
|
|
what are teh characteristics of fibrocartilage
|
contains thick collagen fibers
shock absorber |
|
|
where is fibrocartilage found
|
interverterbral discs
menisci pubic symphisis |
|
|
what are teh characteristics of elastic cartilage
|
contains elastic fibers
provide flexibility |
|
|
where is elastic cartilage found
|
epiglottis
auricle of the ear |
|
|
where is cartilage
|
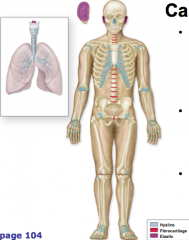
|
|
|
what is the structure of cartilage
|
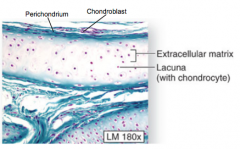
chondroblasts
chondrocytes extracellular matrix perichondrium |
|
|
what are chondroblasts
|
cells that produce cartilage matrix
|
|
|
what are chondrocytes
|
mature cartilage cells that reside in lacunae
|
|
|
what is the extracellular matrix
|
protein fibers embedded in agel like ground substance
|
|
|
what is perichondrium
|
dense irregular connective tissue
|
|
|
what are the charactiristcs of general cartilage
|
semirigid, weaker than bone
flexible and resilient due to elastic fibers and water content avascular receives nutrient supply through diffusion |
|
|
what are the functions of cartilage
|
support soft tissues
articulare surfaces fro joints provide a model for endochondral bone formation |
|
|
what are teh __ functions of bone
|
4
support and protect movement hemopoiesis(hematopoiesis) storage of minerals and energy reserves |
|
|
how does bone support and protect
|
creates framework of body
protects vital organs from injury |
|
|
how does bone allow movement
|
provide attachment sites for muscles
|
|
|
what is hematopoiesis
|
production of blood from red bone marrow
|
|
|
how does bone provide storage of minerals and energy reserves
|
calcium phosphate
yellow bone marrow |
|
|
what are teh __ classifications of bone structures
|
4
long short flat irregular |
|
|
what bones are classified as long bones
|
Humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, phalanges, femur, tibia, fibula, metatarsals
|
|
|
what bones are classified as short bones
|
Carpals, tarsals, sesamoid bones (patella
|
|
|
what bones are classified as flat bones
|
Skull, scapulae, sternum, ribs
|
|
|
what bones are classified as irregular bones
|
Vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, os coxa, ethmoid, sphenoid
|
|
|
what is the structure of long bones
|
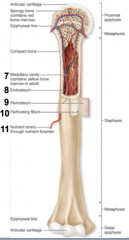
Compact bone
Spongy bone Epiphysis Diaphysis Metaphysis (epiphyseal plate or line) Articular cartilage medullary cavity endosteum periosteum perforating fibers nutrient foramen |
|
|
what is contained in the medullary cavity
|
contains yellow marrow in adults and red marrow in children
|
|
|
what is the endosteum
|
layer of ells lining the spongy bone and medullary cavity
|
|
|
what is the periosteum
|
dense irregular connective tissue outer covering of bone
|
|
|
what are teh __ types of bone cells
|
4
osteoprogenitor cells osteoblasts osteocytes osteoclasts |
|
|
what is an osteoprogenitor cells
|
bone stem cells
|
|
|
what is an oseoblasts
|
build bone by secreting osteoid
|
|
|
what is and osteocyte
|
mature bone cells tha maintain bone matrix
|
|
|
what are osteoclasts
|
cells that consume bone
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of compact bone
|
Also called cortical bone
Lined by the periosteum Contains osteon |
|
|
what are the characteristics of spongy bone
|
Also called cancellous or trabecular bone
Lined by endosteum Often contains red bone marrow |
|
|
what makes up the structure of compact bone
|
Osteon (Haversian system)
Central canal (Haversian canal) Lamellae Osteocytes Lacunae Canaliculi Perforating (Volkmann’s) canals |
|
|
memorize
|
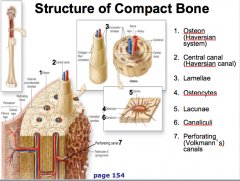
|
|
|
memorize
|
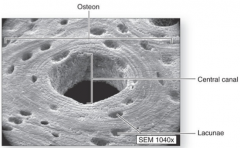
|
|
|
what is the structure of spongy bone
|
Trabeculae
Crisscrossing bars and plates Parallel lamellae Osteocytes within lacunae Canaliculi |
|
|
memorize
|
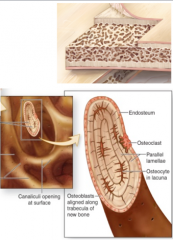
|
|
|
what is intramembranous ossification
|
bone growth within a membrane
|
|
|
what bones are formed by intramembranous ossification
|
flat bones of the skull
some facial bones, mandible clavicle |
|
|
memorize picture of intramembranous ossification
|
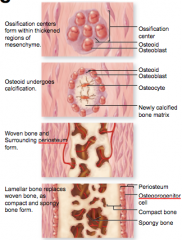
|
|
|
what is endochondral ossification
|
bone growth within cartilage
turns fetal framework of hyalin cartilage into bone |
|
|
what bones are formed by endochondral ossification
|
most bones
|
|
|
process of endochondral ossification
|
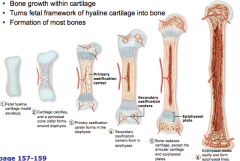
|
|
|
what are the __ types of bone growth
|
2
interstitial growhth (length) epiphyseal plates appositional growth (thickness) occurs at periosteum and endosteum |
|
|
bone growth
|
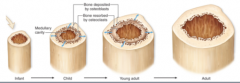
|
|
|
what are the __ types of bone fractures
|
4
simple open or compound stress pathologic |
|
|
what is a simple fracture
|
bone doesnet pierce the skin
|
|
|
what is an open or compund fracture
|
bone pierces the skin
|
|
|
what is a stress fracture
|
think break from repetitive loads
|
|
|
what is a pathologic fracture
|
disease weakens bones
|
|
|
what are the steps of fracture repair
|
fracture hematoma
fibrocartilage (soft) callus forms boney (hard) callus forms bone remodeled |
|
|
fracture repair photo
|
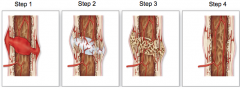
|
|
|
what are the characteristics and cause of osteomalacia
|
called rickets in children
soft bones bowed legs vitamin d deficieny calcium deficiency |
|
|
what are teh characteristics of osteoporosis
|
excessive bone resorption
among aged and post menopausal |
|
|
what are the characteristics of osteitis deformans
|
also called paget's disease
excessive oseteoclast and osteoblaxt function bone is unstable and immature most common in os coxa, skull, vertebrae, femur and tibia |

