![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the __ classes of senses
|
2
General Special |
|
|
What are the __ General Senses
|
5
Temperature Pain touch stretch pressure |
|
|
What are the __ Special senses
|
5
Gustation(taste) olfaction vision equilibrium audition |
|
|
what are the different types of receptors
|
Chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, baroreceptors, nociceptors
|
|
|
what is a chemoreceptors
|
detects chemicals
|
|
|
what is a thremoreceptor
|
dectects temperature changes
|
|
|
what is a photoreceptor
|
detects light
|
|
|
mechanoreceptor
|
detects touch,mechanical movement
|
|
|
what is a barorecetor
|
detects pressure changes
|
|
|
what is nociceptor
|
pain receptor
|
|
|
gustation - what sensory cell, type of receptor, cranial nerve
|
gustatory cell
chemoreceptor 7 and 9 |
|
|
olfaction - what sensory cell, type of receptor, cranial nerve
|
olfactory neuron
chemoreceptor 1 |
|
|
vision - what sensory cell, type of receptor, cranial nerve
|
rods and cones
phoreceptors 2 |
|
|
audition - what sensory cell, type of receptor, cranial nerve
|
cochlear hair cells
mechanoreceptors 8 |
|
|
equilibrium - what sensory cell, type of receptor, cranial nerve
|
hair cells
mechanoreceptors 8 |
|
|
where are the tactile receptors for the general senses located
|
Dermis and hypodermis
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of the filiform papillae
|
anterior 2/3 tongue, no taste buds
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of the the fungiform papillae
|
tip and sides of tongue, few taste buds
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of the circumvallate papillae
|
back of tongue, largest
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of the foliate papillae
|
lateral tongue, taste buds during infancy
|
|
|
how often are gustatory cells replaced
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
what are the five flavors the tongue can snese
|
salty
sweet sour bitter umami (savory) |
|
|
the tongue is innervated by which two cranial nerves and which section is innervated by each
|
facial nerve 7 - anterior 2/3 of tongue
glossopharyngeal nerve 9 - posterior 2/3 of tongue |
|
|
what are the characteristics of the olfactory neurons
|
chemoreceptors, bipolar
|
|
|
how many different chemical stimuli can be recognized in olfaction's
|
thousands
|
|
|
olfaction slide
|
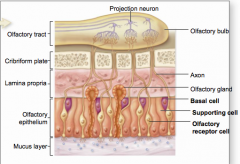
|
|
|
what are the accessory structures of the eye
|
conjuctiva
eybrows, eyelashes and palpebrae lacrimal system tarsal glands |
|
|
what is the function of the conjuctiva
|
Covers eye’s anterior surface and internal eyelid surface
|
|
|
what is the function of the eyebrows,eyelashes and palpebrae
|
Prevent foreign objects from contacting the eye
|
|
|
what are the steps of the lacrimal system
|
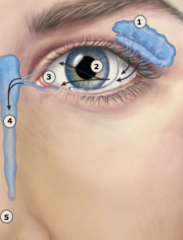
lacrimal glands
canaliculi, sac duct) |
|
|
what are the structures of the eye?
|
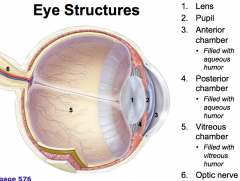
Lens
Pupil Anterior chamber Posterior chamber Vitreous chamber Optic nerve |
|
|
the anterior and posterior chamber of the eye are filled with.....
|
aqueous humor
|
|
|
the viteous chamber of the eye is filled with .....
|
vitreous humor
|
|
|
what are the causes of cataracts
|
Aging
Diabetes UV exposure Glaucoma Eye infections |
|
|
what is a cataract
|
lens becomes opaque
|
|
|
what is the treatment for a cataract
|
artificial lens
|
|
|
what are the different layers of the eye
|
Fibrous tunic
-Sclera -Cornea Vascular tunic -Choroid -Ciliary body -Suspensory ligaments -Iris Neural tunic -Retina -photoreceptors |
|
|
what is the anatomy of the posterior eye
|
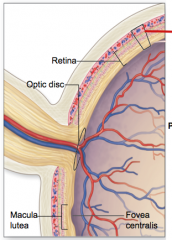
|
|
|
what is the function of rods in the eye
|
function in dim light, don’t provide sharp vision or color vision, more numerous than cones
|
|
|
what is the function of cones in the eye
|
operate best in bright light, provide high acuity color vision
|
|
|
close up of choroid and retina
|
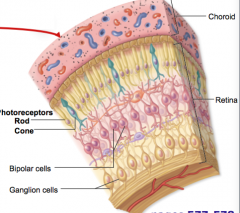
|
|
|
what are the ___ retinal regions
|
3
macula lutea fovea centralis optic disc |
|
|
does the macula lute contain mostly discs or cones
|
cones
|
|
|
does the fovea centralism contain discs or cons
|
only cones - maximal acuity
|
|
|
what is the function of the optic disc
|
contains no rods or cones, axons exit eye, blind spot
|
|
|
Picture of retinal regions
|
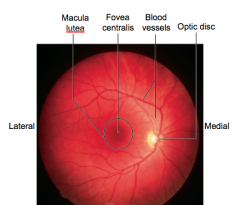
|
|
|
macular degeneration.....
|
retina starts to separated from choroid causing vision loss in center of vision
|
|
|
what has developed by week four in they eye by early week 4
|
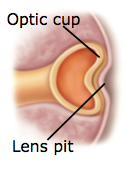
optic cup and lens pit
|
|
|
what has developed by week four in they eye by late week 4
|
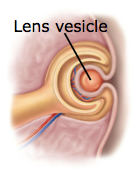
lens vesicle
|
|
|
by week __ the lens of the eye has developed
|
6
|
|
|
the optic cup is an outgrowth of the ......
|
diencephalon
|
|
|
the lens pit forms from .....
|
ectoderm
|
|
|
what are the structures of the external ear
|
auricle
external acoustic meatus ceruminous glands produce cerumen earwax impedes microorganism growth tympanic membrane |
|
|
what are the structures of the middle ear
|
auditory ossicles
malleus incus stapes stapedius muscle tensor tympani muscle round window auditory tube |
|
|
what is the technical term for a middle ear infection
|
otitis media
|
|
|
why are ear infections mor common in children than adults
|
auditory tubes are more horizontal making it easier for bacteria to migrate into the middle ear
|
|
|
what are the structures of the inner ear
|
vestibule
semicircular canals cochlea vestibular and cochlear nerves |
|
|
what is the function of the vestibule
|
Utricle and saccule
Detects acceleration and deceleration Helps sense equilibrium |
|
|
what is the function of the semicircular canals
|
Detect rotational movements
Help sense equilibrium |
|
|
what is the function of the cochlea
|
senses audition
|
|
|
how does sound makes it way through the cochlea
|
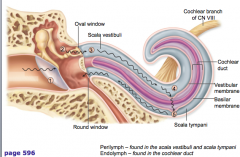
|
|
|
how does a cochlear implant work
|
Electrical impulses
from the transmitter are relayed through the lead and stimulate the cochlear nerve directly adjacent to the cochlea. |

