![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the __ types of Fluid in the body and where can they be found? |
3
Plasma - Blood vessels Interstitial Fluid - in between cells Lymph - Lymph vessels |
|
|
what are the __ components of the Lymphatic System
|
3
Lymphatic vessels lymphatic organs Lymphatic cells |
|
|
What are the __ functions of the Lymphatic system
|
4 |
|
|
what is the flow of lymph
|
capillaries-vessels-nodes-trunks-ducts-circulation
|
|
|
t/f lymph capillaries are closed ended
|
t
|
|
|
t/f lymph fluid can move both directions in the capillaries
|
false
cells overlap to make one way flaps |
|
|
lymph capillaries occur everywhere blood capillaries occur except.....
|
red bone marrow, CNS, avascular tissues
|
|
|
what are lacteals
|
Special lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine
|
|
|
what is the function of lacteals
|
Pick up interstitial fluid, dietary lipids, and lipid-soluble vitamins |
|
|
lymph inside the Gi tract/lacteals is called
|
chyle
|
|
|
where do lymphatic vessels receive lymph from
|
lymphatic capillaries
|
|
|
how do lymphatic vessels prevent back flow in their low pressure system
|
valves
|
|
|
t/f lymphatic vessels are like veins in that they have three tunics
|
t
intima media externa |
|
|
t/f afferent vessels flow away from the lymph nodes
|
f
towards |
|
|
t/f efferent vessels flow away from the lymph nodes
|
t
|
|
|
what are the anatomical structures of a lymph node
|
afferent and efferetn vessels
cortex and medulla macophages, denderitic cells and lymphocytes |
|
|
what are the function of a lymph node
|
Screen lymph for foreign antigens
Initiate immune response |
|
|
what are the location of the lymph nodes
|
axillary
inguinal cervical scattered though out body |
|
|
what is the function of the lymphatic ducts
|
return lymph to cardiovascular system
|
|
|
where do the lymphatic ducts return lymph to the cardiovascular system
|
at the junction of the subclavian veins and the internal jugular veins on either side
|
|
|
what area of the body is drained by the lymphatic duct
|
upper right quadrant
|
|
|
what are of the body is drained by the thoracic duct
|
everything except upper right quadrant
|
|
|
what is lymphedema
|
Edema due to lymph node obstruction
|
|
|
what are some causes of lymphedema
|
worms lodge in lymph nodes
surgical removal of nodes malignant tumors of nodes |
|
|
what is elephantiasis
|
extreme case of lymphedema
|
|
|
where is lymphedema commonly found in the world
|
southeast asia and africa
|
|
|
is lymphedema curable or operable
|
no
|
|
|
what is the difference between the structures of lymphatic nodules and lymphatic organs
|
nodules are not surround by connective tissue
|
|
|
what is contained within lymphatic nodules
|
macrophages, dendritic cells and lymphovytes
|
|
|
what is the function of a lymphatic nodule
|
screen for and attack foreign antigens
|
|
|
where are the lymphatic nodules located
|
tonsils
-pharyngeal -palatine -lingual mucosa associated lymphoid tissue(MALT) -gastrointestinal, respiratory, genital and urinary tracts |
|
|
tonsils protect the ______ from infection
|
Pharynx
|
|
|
what are the symptoms of tonsillitis
|
fever
chills sore throat difficulty swallowing |
|
|
tonsillectomies are only advised if the person has had
|
6-7 infections in one year
or 2-3 infections per year for several years |
|
|
what are contained within the lymphatic organs
|
macrophages,
dendritic cells lymphocytes |
|
|
what is the only difference between lymphatic nodules and lymphatic organs
|
organs are surrounded by connective tissue
|
|
|
what are the lymphatic organs
|
lymph nodes
thymus spleen |
|
|
what is the function of the thymus
|
site for t-lymphocyte maturation
|
|
|
large in infants and young children, shrinks after.....
|
puberty
|
|
|
the cortex of the thymus contains_______ t-cells
|
immature
|
|
|
the medulla of the thymus contains ________ t-cells
|
mature
|
|
|
what is the largest lymphatic organ`
|
spleen
|
|
|
where is the spleen located
|
upper left quadrant of abdomen
|
|
|
what is contained within the white pulp of the spleen
|
lymphocytes and macrophages
|
|
|
what si the function of the white pulp of the spleen
|
monitors blood for feoren antigens initiates an immune response when antigens are found
|
|
|
what is the function of the red pulp of the spleen
|
blood reservoir
site for hemolysis removes debris from blood |
|
|
what are the different types of lymphatic cells
|
lymphocytes
macrophages and dendritic cells |
|
|
what are the characteristics of lymphocytes
|
Most abundant cell type
B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and Natural Killer cells Migrate through the lymphatic system searching for foreign antigens |
|
|
what are the characteristics of macrophages and dendrite cells
|
Phagocytosis of foreign substances
Antigen presentation to lymphocytes to initiate immune response |
|
|
what are the different types of lymphocytes
|
b-lymphocytes
t-lymphocytes natural killer celss |
|
|
what are the two main types of t-lymphocytes
|
helper t-cells CD4
cytotoxic t-cells CD8 |
|
|
how do helper t-cells work
|
Orchestrate an effective immune response by secreting cytokines (chemical signals that bind to and activate other immune system cells) |
|
|
how do cytotoxic t-cells work
|
Kill abnormal cells by secreting substances that break down the cell’s membrane
|
|
|
what are the "other" types of t- cells
|
memory t-cells
regulatory t-cells |
|
|
what is the function of memory t-cells
|
patro body after an attack
|
|
|
what is the function of regulatory t-cells
|
turn off immune response
|
|
|
once activated b-lymphocytes dived and becoem
|
plasma cells
memory b lymphocytes |
|
|
plasma cells produce
|
immunoglobulins (anibodies)
-antibodies bind to antigens, tagging them for destruction |
|
|
what is the function of memory b lymphocytes
|
patrol the body after an attack
easily activated if infected again |
|
|
T/f NK cells can only respond to one type of antigen
|
F
NK cells can kill a wide variety of infected cells and some cancerous cells |
|
|
t/f b and t cells can only respond to a singe antigen
|
t
|
|
|
where are NK cells and b cells developed
|
Red bone marrow
|
|
|
what cell are b, t and NK cells derived from
|
hemopoietic stem cells
|
|
|
hemopoietic stem cells migrate to the _________ to mature into t-cells
|
thymus
|
|
|
lymphocyte table
|
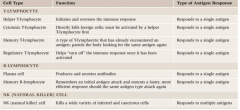
|
|
|
what is lymphoma
|
cancer of the lymphatic cells
|
|
|
lymphoma is often found as a
|
swollen lymph node
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of hodgkins lymphoma
|
Presence of Reed-Sternberg cell
If caught early prognosis is good |
|
|
is non-hodgkins lymphoma curable
|
Variable prognosis, depending on the type
|
|
|
why is HIV so troublesome
|
tagets helper t-cells
|
|
|
when does HIv become AIDS
|
when helper t-cells count below 200 cells/mm3 |
|
|
can AIDS be cured
|
No
Drug cocktail can stop progression but it must be taken for life |

