![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Clinical Junctional EB
|
|
|
|
Inheritance - Herlitz Variant
|
Herlitz variant
autosomal recessive; LAMA3, LAMB3 (80% of mutations), and LAMC2 genes encoding laminin 5 polypepticle chains on 1 q32 |
|
|
Inheritance - Non Herlitz Variant
|
Non Herlitz variant
autosomal recessive; laminin 5 and COL 17A1 on 1 q32 and 1 Oq24, respectively (other mutations identified) |
|
|
JEB Pyloric Atresia
|
JEB pyloric atresia autosomal recessive; ITGA6 (integrin a6) and ITGB4 (integrin B4) genes on chromosome 2 and I 7q11, respectively
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Approximately 2 to 3 cases per million live births; M=F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
Prenatal |
Birth
DNA analysis if mutation in family known; preimplantation determination of genotype at eight cell stage |
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
Heterogeneous gene mutations encoding proteins at the dermal epidermal junction are responsible for phenotype; basal cell adhesion to the basement membrane is altered resulting in a split within the lamina lucida
|
|
|
Pathogenesis - Herlitz
|
Herlitz LAMA3, LAMB3, LAMC2 gene mutations coding for the polypepticle chains within laminin 5 responsible for anchoring filament development in the lamina lucida
|
|
|
Pathogenesis - non-Herlitz
|
Non Herlitz laminin 5 and COL 17A I (BPI 80 180 kDa bullous pemphigoid anti¬gen) gene mutations, the latter encoding type 17 collagen (hemidesmosome protein the lamina lucida)
|
|
|
Pathogenesis - JEB with Pyloric Atresia
|
JEB with pyloric atresia ITGB4 and ITGA6 mutations encoding a6, B4 integrin, a hemidesmosome transmembrane protein complex
|
|
|
Clinical Herlitz
|
Herlitz Variant
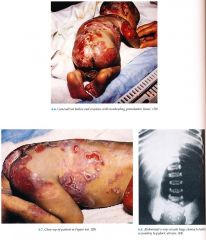
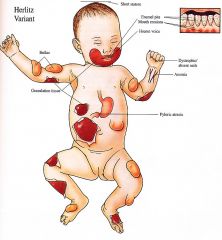
Skin Generalized bullae without scarring, milia mild atrophy with healing; nonhealing granulation tissue periorally, scalp, neck, upper trunk, nail folds, buttocks, pinnae of the ears Nails Absent (shed) Ear Nose Throat Dysplastic teeth with enamel defects, oral erosions, laryngeal involvement with hoarseness, croup, edema Hematologic Multifactorial anemia Musculoskeletal Growth retardation secondary to malnutrition |
|
|
Clinical Non-Herlitz
|
Non Herlitz Variant
Skin Bullae increased on extremities, heal with atrophic scarring; worse in warm envi¬ronment Nails Dystrophy Hair Scarring alopecia Otherwise similar to Herlitz without granulation tissue, anemia, growth retardation and poor prognosis (see Prognosis) |
|
|
Clinical JEB with pyloric Atresia
|
Junctional EBS Pyloric Atresia
Skin/mucosa Severe congenital blistering, mucosal erosions Gastrointestinal Pyloric atresia Genitourinary Hydronephrosis, renail failure secondary to stricture development |
|
|
DDx
|
other forms of EB (p. 204; 208)
Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (p.6) Neonatal HSV Bullous impetigo Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome Toxic epidermal necrolysis |
|
|
Lab
|
Bacterial, viral cultures
Skin biopsy for light, electron microscopy, immunofluoresence, cell culture DNA analysis with blood, buccal swabs |
|
|
Management
|
Herlitz Variant
See EBS (p. 206), tissue engineered skin grafts, nutritional support, iron supplementation, referral to ophthalmologist; protein and/or gene therapy in the future Non Herlitz Variant See EBS JEB Pyloric Atresia Referral to surgeon/urologist surgical release of GI/GU strictures, dilatation and gastrostomy |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Herlitz variant usually fatal by 3 to 4 years of age secondary to profound hypoproteinernia, anemia, and infection
Non Herlitz variant normal life span; bullae may improve with age JEB pyloric atresia usually fatal early on |

