![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
|
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal dominant;
very few autosomal recessive kindreds; keratin 5 and 14 gene-on 12q and I 7q, respectively |
|
|
Prenatal
|
DNA Analysis
|
|
|
Incidence
|
Approximately 10 to 30 cases per million live births; M=F
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Weber Cockayne first to third decade
Generalized (Koebner) birth to early infancy Dowling Meara birth to first month of life |
|
|
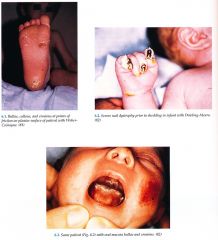
Clinical - Weber Cockayne
|
Skin
Palmoplantar bullae, callouses, hyperhidrosis; with/without pain, superinfection; worsening in summer months, warm temperatures |
|
|
Clinical - Generalize (Koebner)
|
Generalized (Koebner)
Skin Generalized bullae with/without superinfection; worsening in summer months, warm temperatures Mouth Mucosal erosions (mild) |
|
|
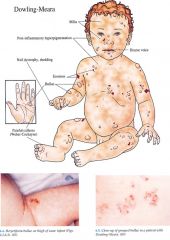
Clinical (Dowling-Meara)
|
Dowling Meara
Skin Widespread bu Ilae with "herpetiform" grouping of lesions may have marked severity with increased morbidity, mortality in infancy; nonscarring, postinflamma¬tory hyperpigmentation, milia; palmoplantar keratoderma with age Nails Dystrophy with shedding Mucous Membranes May have blistering, erosions in oral cavity (with/without secondary hoarseness) and esophagus |
|
|
DDx Weber-Cockayne
|
Weber Cockayne Pachyonychia congenital
Tinea pedis Dyshidrotic eczema Congenital syphilis |
|
|
DDx Generalized and Dowling Meara
|
Generalized (Koebner) and Dowling Meara
Neonatal (HSV) Bacterial sepsis Incontinentia pigmenti Congenital syphilis Bullous impetigo Linear IgA disease |
|
|
Lab
|
Skin biopsy for light microscopy Intraepidermal bullae), electron microscopy (clumped tonofilaments in Dowling Meara) and immunornapping with monoclonal antibodies (see junctional and Dystrophic EB, p. 204; 208)
Viral and bacterial cultures DNA analysis with blood, buccal swabs |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to dermatologist diagnosis, trauma avoidance, wound care with whirlpool, modified Dakin's solution, topical mupirocin, topical corticosteroids, cool environment with well ventilated leather shoes;
Dowling Meara patients may improve with increased temperature |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to podiatry silicone, plastizoate orthotics; thin, white cotton socks to decrease friction and sweat
Admit to neonatal intensive care unite (NICU) if severe blistering in neonate monitor fluids, electrolytes, sepsis |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Debilitating with normal life span; al( types tend to blister less with aging
Dowling Meara significant morbidity, mortality in first few months of life |

