![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Monogastric stomach regions listed in anatomical order from esophagus to small intestine |
1. Esophageal region 2. cardia 3. fundus 4. body 5. pyloric antrum 6. pylorus |
|
|
The esophageal region contains the what |
Cardia |
|
|
What does the cardia do? |
Contains mucous glands secrete mucus but not digestive enzymes |
|
|
Fundic region or fundus |
Book of the simple stomach contains most of the gastric glands digestive glands that produce gastric juice |
|
|
What is contained in gastric juice |
Hydrochloric acid or HCL, pepsin, and intrinsic factor |
|
|
Hydrochloric acid |
Breaks down organic and inorganic material |
|
|
Pepsin |
Well known digestive enzyme |
|
|
Intrinsic factor |
Required for vitamin B-12 absorption in the intestines |
|
|
The body of the stomach |
Distended malaria situated in the middle portion of the stomach |
|
|
Pyloric region |
Last region of the stomach sometimes called the pyloric antrum |
|
|
Pylorus |
Contains the pyloric sphincter |
|
|
Pyloric sphincter |
Helps regulate the passage of food from the stomach into the small intestines |
|
|
Chyme |
The resulting food that leaves the stomach and passes into the intestines |
|
|
What is the stomach's Main blood-supply |
Celiac artery comes from the abdominal aorta |
|
|
What vein leaves the stomach |
The vein that leaves the stomach joins the portal vein as it travels to liver |
|
|
Small intestines can be divided into three major divisions |
1. Duodenum 2. jejunum 3. ileum |
|
|
Mesentery |
The intestines are held in place by the folds of membranous tissue that arise from the peritoneum |
|
|
Prehension |
1st digestive process, grabbing food with lips and putting it in mouth |
|
|
Mastication |
Digestive process where food is broken down into smaller particles by the act of chewing |
|
|
What is chewed up food called |
Bolus |
|
|
Deglutition |
Swallowing |
|
|
Swallowing happens in three phases |
1. Voluntary response, to swallow 2. Involuntary pharyngeal response, reflex that's brought on by the pressure the food at the pharynx 3. Involuntary esophageal response, stimulation of the peristalsis |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
The process by which carbon bonds are broken |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins produced throughout the body |
|
|
How to enzymes aid in digestion |
Their key to the chemical digestion of food and are produced by glandular tissue in various parts of the digestive system |
|
|
Where would digestive enzymes be found |
Salivary glands, stomach, intestines, pancreas |
|
|
What are the three categories of enzymes in the digestive tract |
1. Protease 2. Lipase 3. Amylase |
|
|
Protease enzyme |
Breaks down proteins |
|
|
Lipase enzyme |
Breaks down fat molecules |
|
|
Amylase enzyme |
Breaks down carbohydrates |
|
|
What hormones are secreted from food entering the duodenum |
Secretin, cholecytokinin(CCK) |
|
|
Secretin and cck will stimulate secretions of what enzymes |
Pancreatic enzymes |
|
|
Cck |
Stimulates contraction of the gallbladder to release bile into the duodenum |
|
|
Lipase |
Pancreas produces this which breaks down fats into triglycerides fatty acids and glycerol |
|
|
, amylase |
Pancreas produces which breaks down starches into sugars |
|
|
Luminal digestion |
Where enzymatic digestion occurs in the lumen |
|
|
Bile |
Helps break down fat globules into smaller fat globules a process known as emulsification |
|
|
The large intestine has four main parts |
1. Cecum 2. Colon 3. Rectum 4. Anus |
|
|
Cecum |
Blind sac ejecting from the colon that is used for fermentation |
|
|
Large intestine versus small intestine |
Large intestine has absorptive functions but not digestive functions |
|
|
What are the four accessory digestive organs |
1. Pancreas 2. Liver 3. gallbladder 4. biliary ducts |
|
|
What is the pancreas do |
It secretes hormones such as insulin and glucagon which secrete digestive enzymes which help break down food |
|
|
What does the liver do? |
Detoxification of minerals in the blood filters the blood remove bacteria from the blood |
|
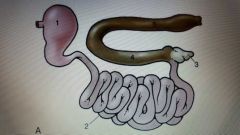
Dog |
1. Stomach 2. Small intestines 3. cecum 4. Ascending colon 5. Descending colon |
|
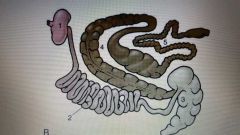
Horse |
1. Stomach2. Small intestines3. cecum4. Ascending colon 5. Descending colon |
|
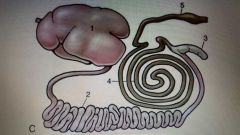
|
1. Stomach2. Small intestines3. cecum4. Ascending colon 5. Descending colon |
|
|
Teeth |
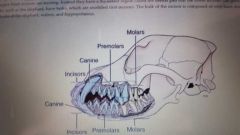
|
|
|
Comparative dental arcades |
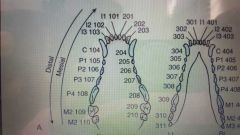
Canine |
|
|
Comparative dental arcades |
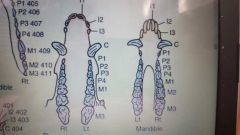
Porcine |
|
|
Comparative dental arcades |
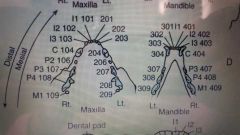
Feline |
|
|
Comparative dental arcades |
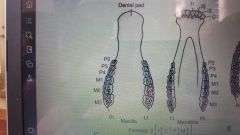
Bovine |
|
|
Comparative dental arcades |
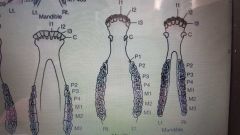
Equine |

