![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Case: 25-year old woman presents with a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. She has a greenish, frothy discharge and a "strawberry cervix" noted on exam.
What is the most likely organism causing this infection? |
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
Case: 25-year old woman presents with a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. She has a greenish, frothy discharge and a "strawberry cervix" noted on exam.
What is the expected microscopic finding? |
Motile, flagellated trichomonads, and many WBCs |
|
|
Case: 25-year old woman presents with a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. She has a greenish, frothy discharge and a "strawberry cervix" noted on exam.
What is the recommended treatment? |
Metronidazole 2g by mouth in a single dose for both the patient and her sexual partner.
Metronidazole 500mg BID for a week is an alternative regimen. |
|
|
What are the common causes of vaginitis? |
- Candida albicans - Trichomonas vaginalis - Gardnerella vaginalis |
|
|
A patient with vaginitis and recent antibiotic use is most likely to have what cause? |
Candida albicans (because antibiotic may alter normal vaginal flora and allow the overgrowth of a fungal organism) |
|
|
A patient with vaginitis and diabetes mellitus is most likely to have what cause? |
Candida albicans (predisposed to yeast infections) |
|
|
A patient with vaginitis and a history of multiple sexual partners is most likely to have what cause? |
A sexually transmitted infection, such as trichomonas |
|
|
What are the typical signs/symptoms of candidal vaginitis? |
- Thick discharge - Significant pruritus |
|
|
What are the typical signs/symptoms of bacterial vaginosis? |
- Thinner discharge - "Fishy" odor |
|
|
What are the typical signs/symptoms of trichomonas vaginitis? |
- Frothy discharge - Patient's cervix is frequently very erythematous |
|
|
How do you establish the cause of vaginal discharge? |
Microscopic exam of discharge - Sample is examined as a "wet mount" (mixed with small amount of saline) and as a "KOH prep" (mixed with small amount of 10% KOH) |
|
|
What do you look for on "wet mount"? |
- Evaluate normal epithelial cells - Look for WBCs, RBCs, clue cells, motile trichomonads |
|
|
What do you best visualize on "KOH prep"? |
Hyphae or pseudohyphae of Candida |
|
|
What is the definition of bacterial vaginosis (type of organism, pH)? |
Condition of excessive anaerobic bacteria in the vagina, leading to an alkaline discharge |
|
|
What is the definition of candida vulvovaginitis? |
Vaginal and/or vulvar infection caused by Candida species, usually with heterogenous discharge and inflammation |
|
|
What is the definition of Trichomonas vaginitis? |
Infection of the vagina caused by the protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis, usually associated with a frothy green discharge and intense inflammatory response |
|
|
How likely is a woman to have an episode of vulvovaginal candidiasis in her lifetime? |
>75% |
|
|
What are the presenting symptoms of vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
- Thick, whitish discharge - No odor - Significant pruritus of external and internal genitalia |
|
|
What is the appearance of patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
Vaginal area can be edematous with erythema present |
|
|
What is the typical pH associated with vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
4.0 - 5.0 (normal) |
|
|
How do you diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
Confirmed by wet mount or KOH prep showing budding yeast or pseudohyphae; fungal cultures are not needed to confirm the diagnosis (but they can be useful if the infection recurs or is unresponsive to treatment) |
|
|
How should you treat a patient with vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
- Uncomplicated can be treated effectively with short-term intravaginal preps (creams or vaginal suppositories) or single-dose oral therapies (fluconazole 150 mg) - Complicated or recurrent infections can be treated with higher doses for 10-14 days followed by 6 months of maintenance therapy to reduce chance of recurrence |
|
|
Do sexual partners need to be treated for vulvovaginal candidiasis? |
Not indicated unless symptomatic (e.g., man partners with balanitis = inflammation of glans) |
|
|
How long does trichomoniasis take to incubate prior to presentation? |
3-21 days post-exposure |
|
|
What factors can predispose to trichomoniasis? |
- Multiple sexual partners - Pregnancy - Menopause |
|
|
What is the presenting complaint for trichomoniasis? |
- Copious amounts of thin, frothy, green-yellow or gray discharge - Malodorous - May have vaginal soreness or dyspareunia - Symptoms may start or be exacerbated during the time of their menses |
|
|
What findings might there be on vaginal exam in a woman with trichomoniasis? |
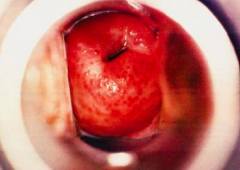
- Cervix may have a "strawberry" appearance (red and inflamed with punctations) - May also have redness of vagina and perineum |
|
|
How do you diagnose trichomoniasis? |
Wet mount prep can demonstrate motile trichomonads, although cultures may be necessary because of significant number of false negatives |
|
|
What is the recommended treatment for trichomoniasis? |
Oral metronidazole, given in a single 2g oral dose or a 1-week regimen of 500mg BID (for both patient and partner)
Should also screen for other STIs |
|
|
What causes bacterial vaginosis? |
Normal vaginal bacteria are replaced with overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria and G vaginalis |
|
|
What is bacterial vaginosis associated with? |
Multiple sexual partners |
|
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for bacterial vaginosis? |
3 of 4 criteria: - Thin, homogenous vaginal discharge - Vaginal pH >4.5 - Positive KOH whiff test (fishy odor after adding 10% KOH to sample) - Presence of clue cells on wet mount |
|
|
How do you treat bacterial vaginosis? |
Oral or topical vaginal prep of metronidazole or clindamycin; no advantage to either regimen but women do report more satisfaction with vaginal prep
No need to test / treat sexual partners |
|
|
Should you check for bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women? Why or why not? |
Treatment of BV in asymptomatic pregnant women may reduce the incidence of preterm delivery |
|
|
What is mucopurulent cervicitis? |
Infection by Chlamydia or Gonorrhea that causes purulent or mucopurulent discharge from the endocervix, may be associated with vaginal discharge and/or cervical bleeding |
|
|
How often is chlamydial infection asymptomatic? |
70% in women |
|
|
How often is gonorrheal infection asymptomatic? |
50% in women |
|
|
What is the gold standard for diagnosing chlamydia / gonorrhea? |
Culture of the cervical discharge |
|
|
How should you treat suspected chlamydia / gonorrhea infections? |
Empiric treatment should be considered in areas of high prevalence of infection or if follow-up is unlikely |
|
|
What are the treatment recommendations for gonorrhea? |
Ceftriaxone 125 mg IM - Quinolone antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin) are NO longer recommended due to resistance |
|
|
What are the treatment recommendations for chlamydia? |
Doxycycline 100 mg orally BID for 7 days OR Azithromycin in single 1g oral dose when compliance is a concern
Recommended to treat sexual partners |
|
|
What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
Inflammation of the upper genital tract, including pelvic peritonitis, endometritis, salpingitis, and tuboovarian abscess caused by infection with gonorrhea, chlamydia, or vagina/bowel flora |
|
|
How do you diagnose pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
- Lower abdominal tenderness + - Adnexal tenderness + - Cervical motion tenderness Without other explanation of illness is enough to diagnose PID |
|
|
What other criteria enhance the specificity of the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
- Fever >101 degrees F - Abnormal cervical or vaginal discharge - Elevated sed rate - Elevated C-reactive protein - Cervical infection with gonorrhea or Chlamydia |
|
|
What is the way to definitively diagnose pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) which is not often used? |
- Laparoscopic findings consistent with PID - Endometrial biopsy showing endometritis - U/S exam findings showing thickened fluid-filled tubes with or without free pelvic fluid or tuboovarian complex |
|
|
How do you differentiate pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) from ectopic pregnancy? |
Pregnancy test - should be performed in all patients suspected of having PID |
|
|
How should you determine the treatment plan for a patient with pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
Consider pregnancy status, severity of illness, and compliance |
|
|
What factors require in-patient treatment with IV antibiotics for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
- Pregnancy - HIV - Severe disease |
|
|
What are the oral regimens for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
Regimen A: - Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM single dose OR Cefoxitin 2 g IM with Probenecid 1g PO given concurrently - PLUS Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for 14 days - With or without Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID for 14 days
Regimen B: - Cefotaxime 1g IM single dose OR Ceftizoxime 1g IM single dose - PLUS Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for 14 days - With or without Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID for 14 days |
|
|
What are the parenteral regimens for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? |
Regimen A: - Cefotetan 2 g IV q12h OR Cefoxitin 2 g IV q6h - PLUS Doxycycline 100 mg PO or IV q12h
Regimen B: - Clindamycin 900 mg IV q8h - PLUS Gentamicin 2 mg/kg loading dose followed by 1.5 mg/kg IV q2h
Regimen C: - Ampicillin / Sulbactam 3 g IV q6h - PLUS Doxycycline 100 mg PO or IV q8h |
|
|
What are the potential complications of PID? |
- Potential for recurrence - Development of tuboovarian abscess - Chronic abdominal pain - Infertility - Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy |
|
|
A 24-year old nulliparous woman is noted to have a bothersome vaginal discharge. On exam, she is found to have a homogenous discharge with a fishy odor.
Which is the most likely finding on examination of the discharge? a) motile protozoa on wet mount b) pH >4.5 c) strawberry cervix d) budding hyphae on KOH exam |
pH >4.5
Discharge of homogenous and fishy odor is most likely bacterial vaginosis associated with an alkaline pH. Partner treatment is not necessary for bacterial vaginosis. Oral metronidazole is one treatment. |
|
|
A 38-year old woman complains of vaginal discharge and irritation. She notes having had a UTI 10 days previously, with resolution of her symptoms.
What is the best therapy for her condition? |
Oral fluconazole
This patient most likely has candida vulvovaginitis, since her discharge appeared after her cystitis, likely treated with antibiotics. A treatment for this includes fluconazole or topical azalea agents such as miconazole |
|
|
A 24-year old woman is noted to have lower abdominal tenderness, cervical motion tenderness, and a vaginal discharge. She has a low grade fever of 100.5.
What is the best therapy for her condition? |
Ceftriaxone IM + Doxycycline orally |
|
|
What STIs should you check for in a patient with another STI? |
- HIV - Hepatitis B, C - Syphilis |

