![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
NAMSIT
|

|
|
|
|
IDEA
|

|
|
|
|
Components of Exercise Session
|

|
|
|
|
FITT
|
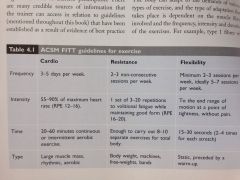
|
|
|
|
ABCS
- Resistance Exercise Order |

|
|
|
|
Periodisation
|

|
|
|
|
Mesocycles
|

|
|
|
|
Endurance Training Zones
|
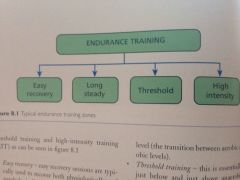
|
|
|
|
HIT Zones
|

|
|
|
|
HIT Zones
|

|
|
|
|
Endurance Training Adaptations
|

|
|
|
|
Short Term Anaerobic training
|

|
|
|
|
Long Term Anaerobic Endurance
|

|
|
|
|
Long Term Anaerobic Endurance
|

|
|
|
|
Resistance Training Methods
|

|
|
|
|
Increase in RM continuum
|

|
|
|
|
Increase in RM continuum
|

|
|
|
|
Strength Training Reommendations
|

|
Novice
Intermediate Advanced |
|
|
Power Training Recommendations
|

|
|
|
|
Plyometric Phases
|

|
|
|
|
Muscular Endurance Training Recommendations
|

|
|
|
|
Bone Structures
|
Compact (Cortical)
Cancellous (Trabecular) |
|
|
|
Bone Classifications
|
Long (humerus)
Short (carpals) Flat (parietal) Irregular (vertebra) Sesamoid (patella) |
|
|
|
Skeletal structure
|
Axial (skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum)
Appendicular (shoulder & pelvic girdles,upper & lower limbs) |
|
|
|
Vertebrae Structure
|
Cervical (7)
Thiracic (12) Lumbar (5) Sacrum Cocyx |
|
|
|
Postural Definitions
|
Kyphosis
Lordosis Scoliosis |
|
|
|
Types of Joint
|
Fibrous (skull, non-articulating)
Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
|
Types of Synovial Joint
|
Ball & Socket (shoulder,hip)
Hinge (elbow,knee,ankle) Gliding (carpals,tarsals) Pivot (radioulnar, cervical spine) Saddle (thumb) |
|
|
|
Structure of Synovial Joint
|
Hyaline cartilage
Capsular Synovial membrane Joint capsule Synovial fluid Propriceptors |
|
|
|
Types of muscle
|
Cardiac
Smooth Skeletal |
|
|
|
Types of muscle
|
Cardiac
Smooth Skeletal |
|
|
|
Types of Skeletal Muscle
|

Parallel (biceps)
Pennate Convergent (pectorals,deltoids) |
|
|
|
What carries Oygen in muscle?
|
Myoglobin
|
|
|
|
TypeII b fibers known as...
|
Fast Glycolytic
...only use glucose as fuel |
|
|
|
Types of Muscle Contraction
|
Isotonic
- concentric (upward movement in bicep curl, muscle gets shorter) - eccentric (lower movement in bicep curl) Isometric - no change in muscle length |
|
|
|
Roles of different muscle groups
|

|
|
|
|
Planes of Movement
|
Sagittal/median
Frontal/coronal Transverse/horizontal |
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
Neurotransmitters
|
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
Neurotransmitters
|
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
Hormones (secreted from glands)
|
|
|
|
CNS
|
Brain
Brain Stem Spinal Cord |
|
|
|
PNS
|
Autonomic (involuntary actions e.g. Heart)
Somatic (sympathetic, parasympathetic) |
|
|
|
Glands
|

|
|
|
|
Hormon Types
|
Lipid soluble
- cortisol, testosterone,oestrogen Water soluble - peptides (insulin, glucagon) |
|
|
|
Heart Valves
|
Atrioventricular
- tricupsid - bicupsid (mitral) Semi-lunar - pulmonary - aortic |
|
|
|
Cardiac Cycle
|
P (atrial contraction)
QRS (ventricular contraction) T |
|
|
|
Cardiac Output
|
HR (bpm) * stroke volume (mls)
|
|
|
|
Blood Composition
|
55% Plasma/45% Cells
Red = erthrocytes White = leukocytes Platelets |
|
|
|
Mechanisms of Core Stabilisation
|
Intra-abdominal pressure
Thoraco-lumbar fascia gain Hydraulic amplifier effect |
|

